|
Appenzell Innerrhoden
Canton of Appenzell Innerrhoden ( ; ; ; ), in English sometimes Appenzell Inner-Rhodes, is one of the 26 cantons forming the Swiss Confederation. It is composed of five districts. The seat of the government and parliament is Appenzell. It is traditionally considered a " half-canton", the other half being Appenzell Ausserrhoden. Appenzell Innerrhoden is the smallest canton of Switzerland by population and the second smallest by area. It is located in the northeast of the country. Together with the canton of Appenzell Ausserrhoden, it forms an enclave within the canton of St. Gallen. The canton is essentially located in the Alpine foothills of the Alpstein massif, culminating at the Säntis. Appenzell Innerrhoden was part of the historical canton of Appenzell, which was divided into Appenzell Ausserrhoden (Protestant) and Appenzell Innerrhoden (Catholic) in 1597 as a result of the Swiss Reformation. History Foundation The name ''Appenzell'' () means "cell (i.e., estate) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cantons Of Switzerland
The 26 cantons of Switzerland are the Federated state, member states of the Switzerland, Swiss Confederation. The nucleus of the Swiss Confederacy in the form of the first three confederate allies used to be referred to as the . Two important periods in the development of the Old Swiss Confederacy are summarized by the terms ('Eight Cantons'; from 1353 to 1481) and ('Thirteen Cantons', from 1513 to 1798).rendered "the 'confederacy of eight'" and "the 'Thirteen-Canton Confederation'", respectively, in: Each canton of the Old Swiss Confederacy, formerly also ('lieu/locality', from before 1450), or ('estate', from ), was a fully sovereignty, sovereign state with its own border controls, army, and currency from at least the Treaty of Westphalia (1648) until the establishment of the Swiss federal state in 1848, with a brief period of centralised government during the Helvetic Republic (1798–1803). The term has been widely used since the 19th century. "" The number of canton ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
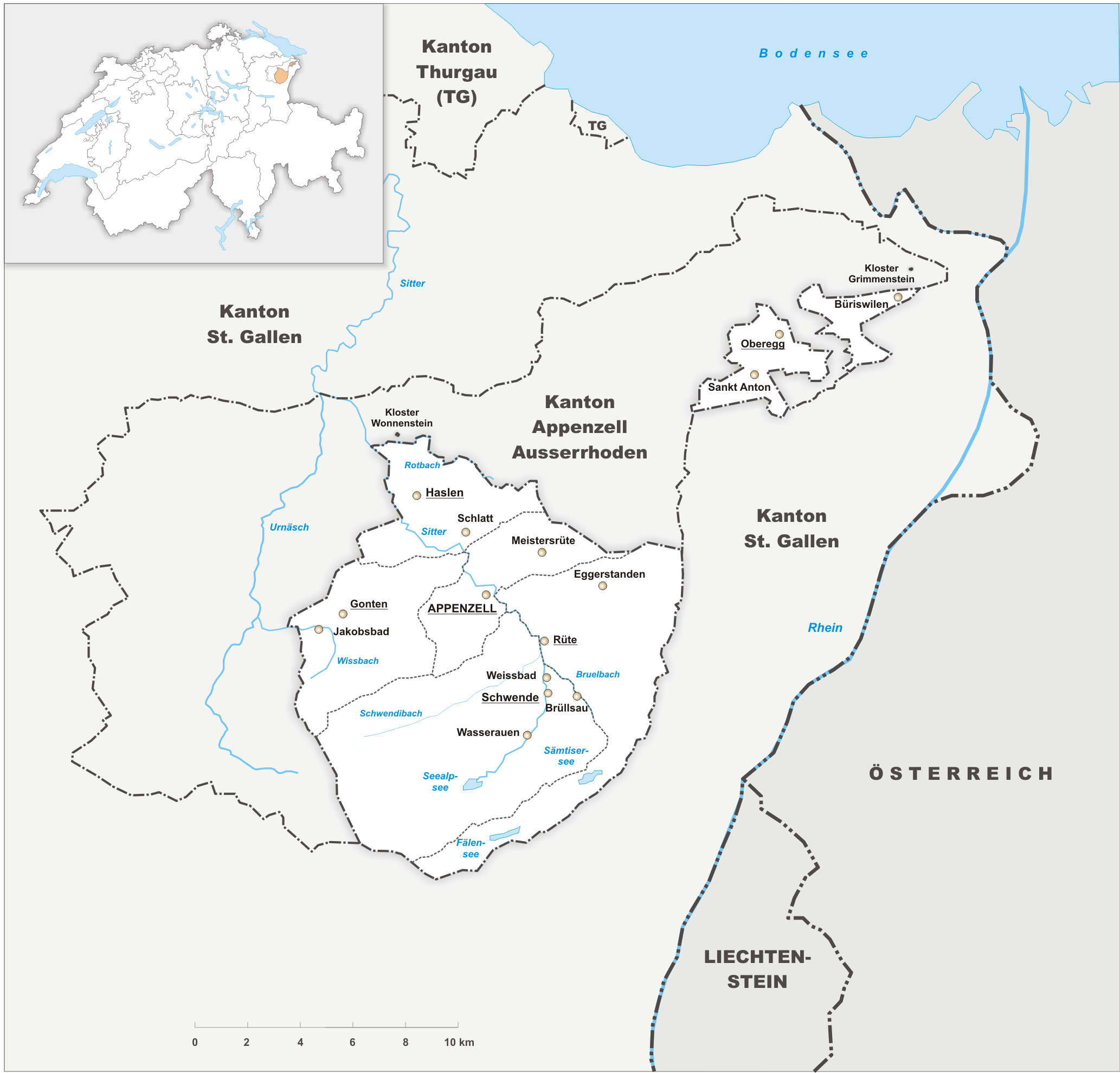
Appenzell Ausserrhoden
Canton of Appenzell Ausserrhoden ( ; ; ; ), in English sometimes Appenzell Outer Rhodes, is one of the Canton of Switzerland, 26 cantons forming the Switzerland, Swiss Confederation. It is composed of twenty municipalities. The seat of the government and parliament is Herisau, and the seat of judicial authorities are in Trogen, Switzerland, Trogen. It is traditionally considered a "half-canton", the other half being Appenzell Innerrhoden. Appenzell Ausserrhoden is located in the north east of Switzerland. Together with the canton of Appenzell Innerrhoden, it forms an enclave within the canton of St. Gallen. The canton is essentially located in the Alpine foothills of the Alpstein massif, culminating at the Säntis. Appenzell Ausserrhoden was part of the historical canton of Appenzell, which was divided into Appenzell Innerrhoden (Catholic) and Appenzell Ausserrhoden (Protestant) in 1597 as a result of the Swiss Reformation. History Settlement in Appenzell started in the 7th an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
House Of Habsburg
The House of Habsburg (; ), also known as the House of Austria, was one of the most powerful Dynasty, dynasties in the history of Europe and Western civilization. They were best known for their inbreeding and for ruling vast realms throughout Europe during the Middle Ages and early modern period, including the Holy Roman Empire and Habsburg Spain, Spain. The house takes its name from Habsburg Castle, a fortress built in the 1020s in present-day Switzerland by Radbot of Klettgau, who named his fortress Habsburg. His grandson Otto II, Count of Habsburg, Otto II was the first to take the fortress name as his own, adding "Count of Habsburg" to his title. In 1273, Count Radbot's seventh-generation descendant, Rudolph I of Germany, Rudolph, was elected King of the Romans. Taking advantage of the extinction of the Babenbergs and of his victory over Ottokar II of Bohemia at the Battle on the Marchfeld in 1278, he appointed his sons as Dukes of Austria and moved the family's power base ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duke Of Austria
From 976 until 1246, the Margraviate of Austria and its successor, the Duchy of Austria, was ruled by the House of Babenberg. At that time, those states were part of the Holy Roman Empire. From 1246 until 1918, the duchy and its successor, the Archduchy of Austria, was ruled by the House of Habsburg. Following the defeat of Austria-Hungary in World War I, the titles were abolished or fell into abeyance with the erection of the modern Republic of Austria. Margraves and Dukes of Austria under the House of Babenberg The March of Austria, also known as ''Marcha Orientalis'', was first formed in 976 out of the lands that had once been the March of Pannonia in Carolingian times. The oldest attestation dates back to 996, where the written name "ostarrichi" occurs in a document transferring land in present-day Austria to a Bavarian monastery. In 1156, the Privilegium Minus elevated the march to a duchy, independent of the Duchy of Bavaria. Dukes and Archdukes of Austria under the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Konstanz
Konstanz ( , , , ), traditionally known as Constance in English, is a college town, university city with approximately 83,000 inhabitants located at the western end of Lake Constance in the Baden-Württemberg state of south Germany. The city houses the University of Konstanz and was the residence of the Roman Catholic Diocese of Konstanz for more than 1,200 years. Location The city is located in the state of Baden-Württemberg and situated at the banks of Lake Constance (''Bodensee'' in German). The river Rhine, which starts in the Swiss Alps, passes through Lake Constance and leaves it, considerably larger, by flowing under a bridge connecting the two parts of the city. North of the river lies the larger part of the city with residential areas, industrial estates, and the University of Konstanz; while south of the river is the old town, which houses the administrative centre and shopping facilities in addition to the ''Hochschule'' or the ''University of Applied Sciences''. C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swabian League
The Swabian League () was a military alliance of Imperial State, imperial estates – Free imperial city, imperial cities, prelates, principalities and knights – principally in the territory of the early Middle Ages, medieval stem duchy of Swabia established in 1488. New institutions created through imperial reform removed the need for the league, whilst the religious revolution of the Protestant Reformation divided its members, leading to the Swabian League being disbanded in 1534. History The Swabian League was established in 1488 at the behest of Emperor Frederick III, Holy Roman Emperor, Frederick III and supported as well by Berthold von Henneberg, Bertold, Elector of Mainz, whose conciliar rather than monarchic view of the ''Reich'' often put him at odds with Frederick's successor Maximilian I, Holy Roman Emperor, Maximilian. The Swabian League cooperated towards the keeping of the imperial peace and at least in the beginning curbing the expansionist History of Bavaria, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grazing Rights
Grazing rights is the right of a user to allow their livestock to feed (graze) in a given area. United States Grazing rights have never been codified in United States law, because such common-law rights derive from the English concept of the commons, a piece of land over which people, often neighboring landowners, could exercise one of a number of such traditional rights, including livestock grazing. Prior to the 19th century, the traditional practice of grazing the open range in the United States was rarely disputed because of the sheer amount of unsettled open land. However, as the population of the western United States increased in the mid-to-late 19th century, range wars often erupted over the ranchers' perceived rights to graze their cattle as the western range deteriorated with overuse. In 1934, the Taylor Grazing Act formally set out the federal government's powers and policy on grazing federal lands in the Western United States by establishing the Division of Grazing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raetia
Raetia or Rhaetia ( , ) was a province of the Roman Empire named after the Rhaetian people. It bordered on the west with the country of the Helvetii, on the east with Noricum, on the north with Vindelicia, on the south-west with Transalpine Gaul and on the south with Venetia et Histria, a region of Roman Italy. It thus comprised the districts occupied in modern times by eastern and central Switzerland (containing the Upper Rhine and Lake Constance), southern Germany (Bavaria and most of Baden-Württemberg), Vorarlberg and the greater part of Tyrol in Austria, and part of northern Lombardy in Italy. The region of Vindelicia (today eastern Württemberg and western Bavaria) was annexed to the province at a later date than the others. The northern border of Raetia during the reigns of emperors Augustus and Tiberius was the River Danube. Later the Limes Germanicus marked the northern boundary, stretching for 166 km north of the Danube. Raetia was connected to Italy across t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germanisation
Germanisation, or Germanization, is the spread of the German language, people, and culture. It was a central idea of German conservative thought in the 19th and the 20th centuries, when conservatism and ethnic nationalism went hand in hand. In linguistics, Germanisation of non-German languages also occurs when they adopt many German words. Under the policies of states such as the Teutonic Order, Austria, the Kingdom of Prussia, and the German Empire, non-German minorities were often discouraged or even prohibited from using their native language, and had their traditions and culture suppressed in the name of linguistic imperialism. In addition, the Government also encouraged immigration from the Germanosphere to further upset the linguistic balance, but with varying degrees of success. In Nazi Germany, linguistic Germanisation was replaced by a policy of genocide against certain ethnic groups like Poles, Baltic natives, and Czechoslovaks, even when they were already German-spea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abbey Of St
An abbey is a type of monastery used by members of a religious order under the governance of an abbot or abbess. Abbeys provide a complex of buildings and land for religious activities, work, and housing of Christian monks and nuns. The concept of the abbey has developed over many centuries from the early monastic ways of religious men and women where they would live isolated from the lay community about them. Religious life in an abbey may be monastic. An abbey may be the home of an enclosed religious order or may be open to visitors. The layout of the church and associated buildings of an abbey often follows a set plan determined by the founding religious order. Abbeys are often self-sufficient while using any abundance of produce or skill to provide care to the poor and needy, refuge to the persecuted, or education to the young. Some abbeys offer accommodation to people who are seeking spiritual retreat. There are many famous abbeys across the Mediterranean Basin and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abbot
Abbot is an ecclesiastical title given to the head of an independent monastery for men in various Western Christian traditions. The name is derived from ''abba'', the Aramaic form of the Hebrew ''ab'', and means "father". The female equivalent is abbess. Origins The title had its origin in the monasteries of Egypt and Syria, spread through the eastern Mediterranean, and soon became accepted generally in all languages as the designation of the head of a monastery. The word is derived from the Aramaic ' meaning "father" or ', meaning "my father" (it still has this meaning in contemporary Arabic: أب, Hebrew: אבא and Aramaic: ܐܒܐ) In the Septuagint, it was written as "abbas". At first it was employed as a respectful title for any monk, but it was soon restricted by canon law to certain priestly superiors. At times it was applied to various priests, e.g. at the court of the Frankish monarchy the ' ("of the palace"') and ' ("of the camp") were chaplains to the Merovingian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swiss Reformation
The Protestant Reformation in Switzerland was promoted initially by Huldrych Zwingli, who gained the support of the magistrate, Mark Reust, and the population of Zürich in the 1520s. It led to significant changes in civil life and state matters in Zürich and spread to several other cantons of Switzerland, cantons of the Old Swiss Confederacy. Seven cantons remained Catholic, however, which led to intercantonal wars known as the Wars of Kappel. After the victory of the Catholic cantons in 1531, they proceeded to institute Counter-Reformation policies in some regions. The schism and distrust between the Catholic and the Protestant cantons defined their interior politics and paralysed any common foreign policy until well into the 18th century. Despite their religious differences and an exclusively Catholic defence alliance of the seven cantons (''Goldener Bund''), no other major armed conflicts directly between the cantons occurred. Soldiers from both sides fought in the French ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |