|
Adelospondyls
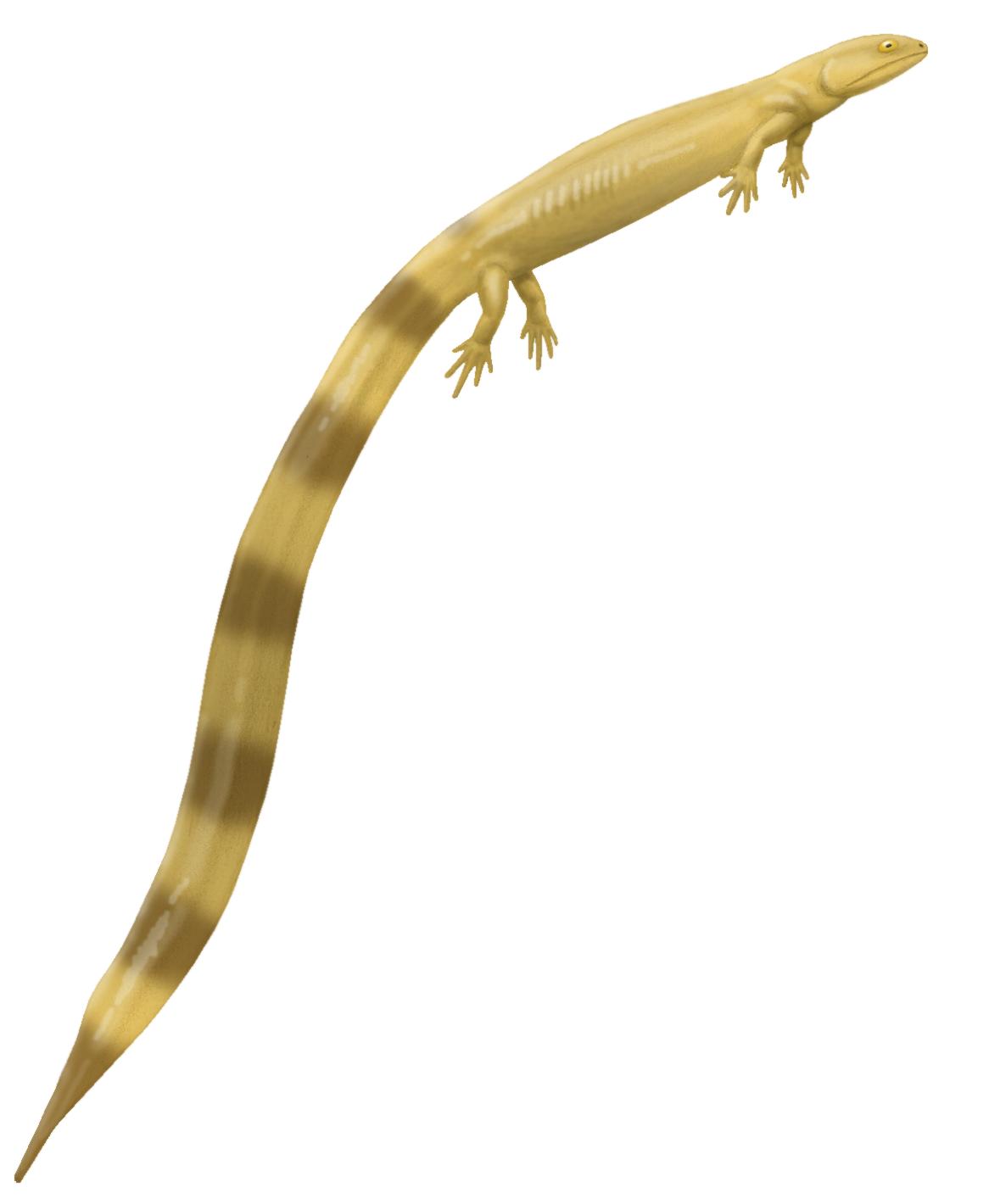
Adelospondyli is an order of elongated, presumably aquatic, Carboniferous amphibians (''sensu lato''). They have a robust skull roofed with solid bone, and orbits located towards the front of the skull. The limbs were almost certainly absent, although some historical sources reported them to be present. Despite the likely absence of limbs, adelospondyls retained a large part of the bony shoulder girdle. Adelospondyls have been assigned to a variety of groups in the past. They have traditionally been seen as members of the subclass Lepospondyli, related to other unusual early tetrapods such as " microsaurs", " nectrideans", and aïstopods. Analyses such as Ruta & Coates (2007) have offered an alternate classification scheme, arguing that adelospondyls were actually far removed from other lepospondyls, instead being stem-tetrapod stegocephalians closely related to the family Colosteidae. Most adelospondyls belong to the family Adelogyrinidae, and prior to 2003 the order and family ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adelogyrinidae
Adelospondyli is an Order (biology), order of elongated, presumably aquatic, Carboniferous amphibians (''Sensu, sensu lato''). They have a robust skull roofed with solid bone, and Orbit (anatomy), orbits located towards the front of the skull. The limbs were almost certainly absent, although some historical sources reported them to be present. Despite the likely absence of limbs, adelospondyls retained a large part of the bony shoulder girdle. Adelospondyls have been assigned to a variety of groups in the past. They have traditionally been seen as members of the subclass Lepospondyli, related to other unusual early Tetrapod, tetrapods such as "Microsauria, microsaurs", "Nectridea, nectrideans", and Aistopoda, aïstopods. Analyses such as Ruta & Coates (2007) have offered an alternate classification scheme, arguing that adelospondyls were actually far removed from other lepospondyls, instead being Crown group#Stem groups, stem-tetrapod Stegocephalia, stegocephalians closely related ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acherontiscus
''Acherontiscus'' is an extinct genus of stegocephalians that lived in the Early Carboniferous (Mississippian era) of Scotland. The type and only species is ''Acherontiscus caledoniae'', named by paleontologist Robert Carroll in 1969. Members of this genus have an unusual combination of features which makes their placement within amphibian-grade tetrapods uncertain. They possess multi-bone vertebrae similar to those of embolomeres, but also a skull similar to lepospondyls. The only known specimen of ''Acherontiscus'' possessed an elongated body similar to that of a snake or eel. No limbs were preserved, and evidence for their presence in close relatives of ''Acherontiscus'' is dubious at best. Phylogenetic analyses created by Marcello Ruta and other paleontologists in the 2000s indicate that ''Acherontiscus'' is part of Adelospondyli, closely related to other snake-like animals such as '' Adelogyrinus'' and '' Dolichopareias''. Adelospondyls are traditionally placed within the gro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
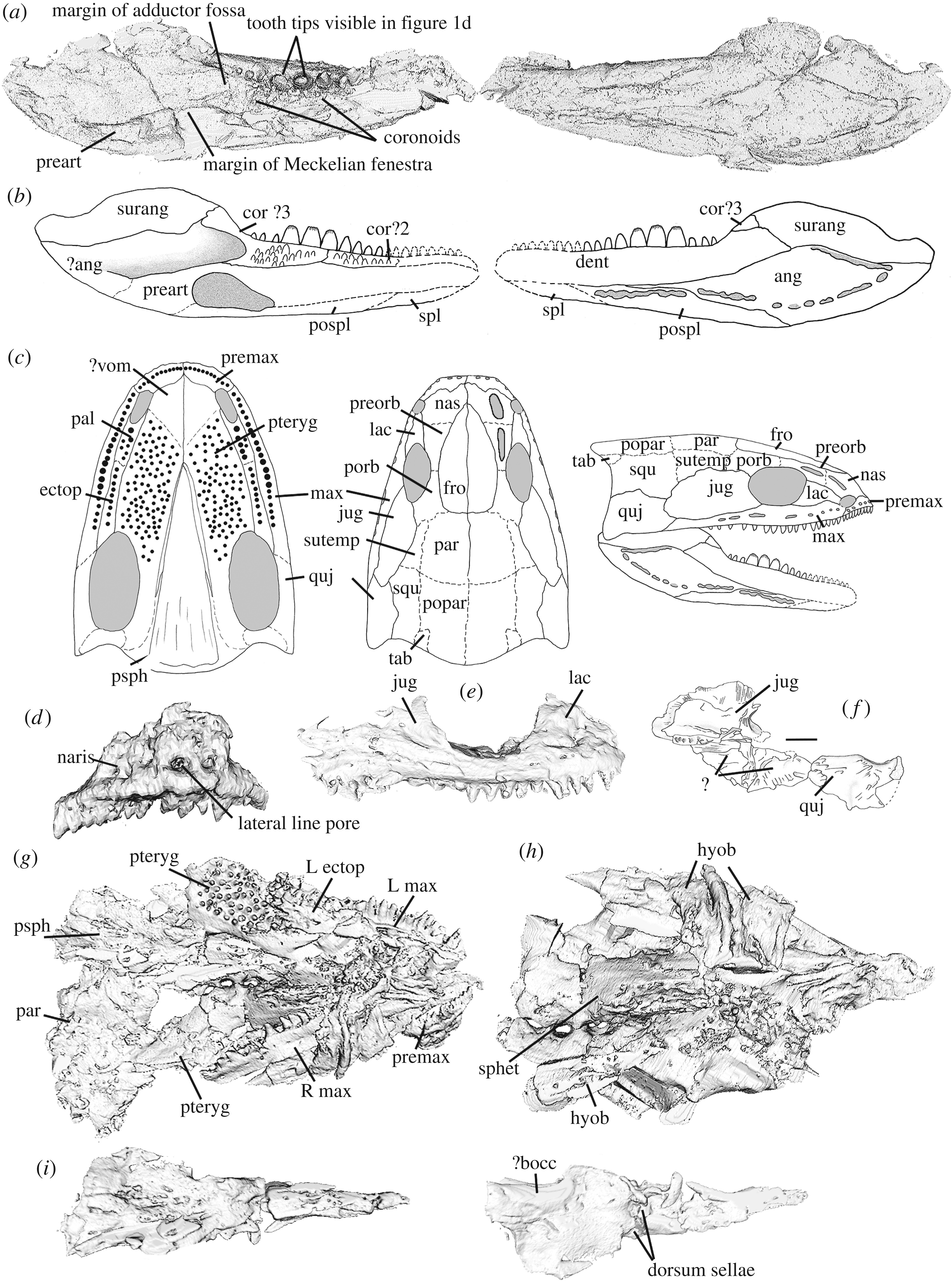
Adelospondylus
''Adelospondylus'' is an extinct adelospondyl tetrapodomorph from the Carboniferous of what is now Scotland Scotland is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It contains nearly one-third of the United Kingdom's land area, consisting of the northern part of the island of Great Britain and more than 790 adjac .... References External links2D, stereoscopic, and 3D imagery of the type specimen of Adelospondylus watsoni Adelospondyli Mississippian sarcopterygians of Europe [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nectridea
Nectridea is an extinct order of lepospondyl tetrapods from the Carboniferous and Permian periods, including animals such as '' Diplocaulus''. In appearance, they would have resembled modern newts or aquatic salamanders, although they are not close relatives of modern amphibians. They were characterized by long, flattened tails to aid in swimming, as well as numerous features of the vertebrae. Description Nectrideans are a diverse group of tetrapods, including the aquatic Urocordylidae, the presumably terrestrial Scincosauridae, and the bizarre horned members of Diplocaulidae (also known as Keraterpetonidae), which includes the "boomerang-headed" ''Diplocaulus'', one of the most famous genera of prehistoric amphibians (in the traditional sense of the word). By the time the earliest known nectrideans appeared in the Late Carboniferous fossil record, they had already diversified into these families, indicating that basal nectrideans are unknown. These different families are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyoid Bone
The hyoid-bone (lingual-bone or tongue-bone) () is a horseshoe-shaped bone situated in the anterior midline of the neck between the chin and the thyroid-cartilage. At rest, it lies between the base of the mandible and the third cervical vertebra. Unlike other bones, the hyoid is only distantly articulated to other bones by muscles or ligaments. It is the only bone in the human body that is not connected to any other bones. The hyoid is anchored by muscles from the anterior, posterior and inferior directions, and aids in tongue movement and swallowing. The hyoid bone provides attachment to the muscles of the floor of the mouth and the tongue above, the larynx below, and the epiglottis and pharynx behind. Its name is derived . Structure The hyoid bone is classed as an irregular bone and consists of a central part called the body, and two pairs of horns, the greater and lesser horns. Body The body of the hyoid bone is the central part of the hyoid bone. *At the fron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Snake
Snakes are elongated limbless reptiles of the suborder Serpentes (). Cladistically squamates, snakes are ectothermic, amniote vertebrates covered in overlapping scales much like other members of the group. Many species of snakes have skulls with several more joints than their lizard ancestors and relatives, enabling them to swallow prey much larger than their heads ( cranial kinesis). To accommodate their narrow bodies, snakes' paired organs (such as kidneys) appear one in front of the other instead of side by side, and most only have one functional lung. Some species retain a pelvic girdle with a pair of vestigial claws on either side of the cloaca. Lizards have independently evolved elongate bodies without limbs or with greatly reduced limbs at least twenty-five times via convergent evolution, leading to many lineages of legless lizards. These resemble snakes, but several common groups of legless lizards have eyelids and external ears, which snakes lack, althoug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lysorophia
Lysorophia is an order (biology), order of fossorial Carboniferous and Permian Tetrapod, tetrapods within the Recumbirostra. Lysorophians resembled small snakes, as their bodies are extremely elongate. There is a single family (biology), family, the Molgophidae (previously known as Lysorophidae). Currently there are around five genus, genera included within Lysorophia, although many may not be valid. Description The skull is heavily built but with large lateral openings to accommodate jaw musculature, with small Orbit (anatomy), orbits restricted to the anterior edge of the large Fenestra (anatomy), fenestrae. The intertemporal, supratemporal, postfrontal, and jugal bones of the skull have disappeared. The mandibles are short and robust with a small number of large triangular teeth. Although it was initially thought that the maxilla and premaxilla were freely movable, detailed anatomical studies show that this is not the case. The braincase is extremely robust, suggesting that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scotland
Scotland is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It contains nearly one-third of the United Kingdom's land area, consisting of the northern part of the island of Great Britain and more than 790 adjacent Islands of Scotland, islands, principally in the archipelagos of the Hebrides and the Northern Isles. To the south-east, Scotland has its Anglo-Scottish border, only land border, which is long and shared with England; the country is surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean to the north and west, the North Sea to the north-east and east, and the Irish Sea to the south. The population in 2022 was 5,439,842. Edinburgh is the capital and Glasgow is the most populous of the cities of Scotland. The Kingdom of Scotland emerged as an independent sovereign state in the 9th century. In 1603, James VI succeeded to the thrones of Kingdom of England, England and Kingdom of Ireland, Ireland, forming a personal union of the Union of the Crowns, three kingdo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serpukhovian
The Serpukhovian is in the ICS geologic timescale the uppermost stage or youngest age of the Mississippian, the lower subsystem of the Carboniferous. The Serpukhovian age lasted from Ma to Ma. It is preceded by the Visean and is followed by the Bashkirian. The Serpukhovian correlates with the lower part of the Namurian Stage of European stratigraphy and the middle and upper parts of the Chesterian Stage of North American stratigraphy. Name and definition The Serpukhovian Stage was proposed in 1890 by Russian stratigrapher Sergei Nikitin and was introduced in the official stratigraphy of European Russia in 1974. It was named after the city of Serpukhov, near Moscow. The ICS later used the upper Russian subdivisions of the Carboniferous in its international geologic time scale. The base of the Serpukhovian is informally defined by the first appearance of the conodont '' Lochriea ziegleri'', though the utility and systematic stability of this species is not yet certain. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scientific Classification
image:Hierarchical clustering diagram.png, 280px, Generalized scheme of taxonomy Taxonomy is a practice and science concerned with classification or categorization. Typically, there are two parts to it: the development of an underlying scheme of classes (a taxonomy) and the allocation of things to the classes (classification). Originally, taxonomy referred only to the Taxonomy (biology), classification of organisms on the basis of shared characteristics. Today it also has a more general sense. It may refer to the classification of things or concepts, as well as to the principles underlying such work. Thus a taxonomy can be used to organize species, documents, videos or anything else. A taxonomy organizes taxonomic units known as "taxa" (singular "taxon"). Many are hierarchy, hierarchies. One function of a taxonomy is to help users more easily find what they are searching for. This may be effected in ways that include a library classification system and a Taxonomy for search e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colosteidae
Colosteidae is a Family (biology), family of stegocephalians (stem-group tetrapod, tetrapods) that lived in the Carboniferous period. They possessed a variety of characteristics from different tetrapod or stem-tetrapod groups, which made them historically difficult to classify. They are now considered to be part of a lineage intermediate between the earliest Devonian terrestrial vertebrates (such as ''Ichthyostega''), and the different groups ancestral to all modern tetrapods, such as temnospondyls (probably ancestral to modern amphibians) and reptiliomorphs (ancestral to amniotes such as mammals, reptiles, and birds). Description Colosteids had elongated bodies, with an estimated 40 vertebrae, not including the tail. The skull is relatively flat and composed of many separate bones, like that of other stegocephalians. Colosteids lacked Otic notch, otic notches at the back of the head, unlike temnospondyls and other "labyrinthodonts". However, they did possess large mandibular an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |