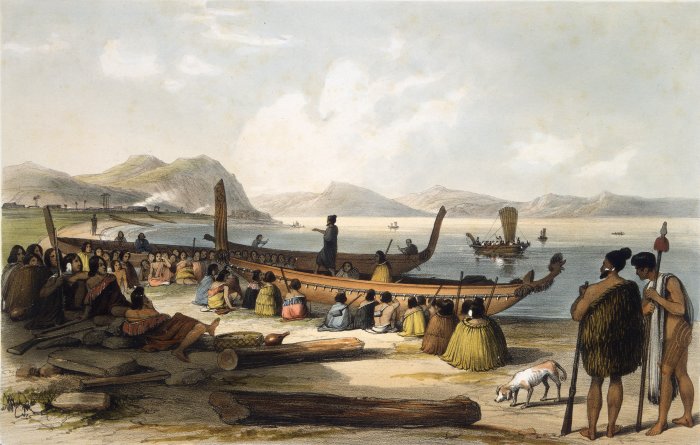|
2010s In New Zealand
This is a timeline of the history of New Zealand that includes only events deemed to be of principal importance – for less important events click the year heading or refer to List of years in New Zealand. Before humans (before c. 1300 CE) * 85 mya: Around this time New Zealand splits from the supercontinent Gondwana. * 5 mya: New Zealand's climate cools as Australia drifts north. Animals that have adapted to warm temperate and subtropical conditions become extinct. * 26,500 BP: The world's most recent supereruption occurs at the Taupō Volcano. The eruption covers much of the country with volcanic ash and causes the Waikato River to shift course from the Hauraki Plains to its current path to the Tasman Sea, while its caldera becomes modern Lake Taupō. * 18,000 BP: New Zealand's North and South islands are connected by a land bridge during the Otira Glacial Maximum of the last ice age. Glaciers spread from the Southern Alps carving valleys and making fiords in the Sout ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of New Zealand
The human history of New Zealand can be dated back to between 1320 and 1350 CE, when the main settlement period started, after it was discovered and settled by Polynesians, who developed a distinct Māori culture. Like other Pacific cultures, Māori society was centred on kinship links and connection with the land but, unlike them, it was adapted to a cool, temperate environment rather than a warm, tropical one. The first European explorer known to have visited New Zealand was the Dutch navigator Abel Tasman, on 13 December 1642. In 1643 he charted the west coast of the North Island, his expedition then sailed back to Batavia without setting foot on New Zealand soil. British explorer James Cook, who reached New Zealand in October 1769 on the first of his three voyages, was the first European to circumnavigate and map New Zealand. From the late 18th century, the country was regularly visited by explorers and other sailors, missionaries, traders and adventurers. The period from P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Juan Fernández (explorer)
Juan Fernández (c. 1536 – c. 1604) was a Spanish explorer and navigator in the Pacific regions of the Viceroyalty of Peru and Captaincy General of Chile west of colonial South America. He is best known for the discovery of a fast maritime route from Callao (Peru) to Valparaíso (Chile) as well as for the discovery of the Juan Fernández Islands off the coast of Chile. Discoveries and theories Juan Fernández Islands In 1574, he discovered an alternative maritime route from Callao to Valparaíso, much faster than the old route which bordered the coastline. By taking a detour west from the coast, he managed to avoid the northerly Humboldt Current which used to slow down ships sailing south along the coast. In doing so, he discovered the Juan Fernández Islands archipelago, located west of present-day Valparaíso in the southeastern Pacific Ocean, on 22 November 1574. He also discovered the Pacific islands of San Félix and San Ambrosio in 1574. The speed with which th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ngāi Tahu
Ngāi Tahu, or Kāi Tahu, is the principal Māori people, Māori (tribe) of the South Island. Its (tribal area) is the largest in New Zealand, and extends from the White Bluffs / Te Parinui o Whiti (southeast of Blenheim, New Zealand, Blenheim), Mount Māhanga and Kahurangi Point in the north to Stewart Island / Rakiura in the south. The comprises 18 (governance areas) corresponding to traditional settlements. According to the 2023 New Zealand census, 2023 census an estimated 84,000 people affiliated with the Kāi Tahu iwi. Ngāi Tahu originated in the Gisborne District of the North Island, along with Ngāti Porou and Ngāti Kahungunu, who all intermarried amongst the local Ngāti Ira. Over time, all but Ngāti Porou would migrate away from the district. Several were already occupying the South Island prior to Ngāi Tahu's arrival, with Kāti Māmoe only having arrived about a century earlier from the Hastings, New Zealand, Hastings District, and already having conquered W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Island
The North Island ( , 'the fish of Māui', historically New Ulster) is one of the two main islands of New Zealand, islands of New Zealand, separated from the larger but less populous South Island by Cook Strait. With an area of , it is the List of islands by area, world's 14th-largest island, constituting 43% of New Zealand's land area. It has a population of which is % of New Zealand's residents, making it the most populous island in Polynesia and the List of islands by population, 28th-most-populous island in the world. Twelve main urban areas (half of them officially cities) are in the North Island. From north to south, they are Whangārei, Auckland, Hamilton, New Zealand, Hamilton, Tauranga, Rotorua, Gisborne, New Zealand, Gisborne, New Plymouth, Napier, New Zealand, Napier, Hastings, New Zealand, Hastings, Whanganui, Palmerston North, and New Zealand's capital city Wellington, which is located at the south-west tip of the island. Naming and usage The island has been known ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waka (canoe)
Waka () are Māori people, Māori watercraft, usually canoes ranging in size from small, unornamented canoes (''waka tīwai'') used for fishing and river travel to large, decorated war canoes (''waka taua'') up to long. The earliest remains of a canoe in New Zealand were found near the Anaweka River, Anaweka estuary in a remote part of the Tasman District and Radiocarbon dating, radiocarbon-dated to about 1400. The canoe was constructed in New Zealand, but was a sophisticated canoe, compatible with the style of other Polynesian voyaging canoes at that time. Since the 1970s, about eight large double-hulled canoes of about 20 metres have been constructed for oceanic voyaging to other parts of the Pacific Ocean, Pacific. They are made of a blend of modern and traditional materials, incorporating features from ancient Melanesia, as well as Polynesia. Waka taua (war canoes) ''Waka taua'' (in Māori language, Māori, ''waka'' means "canoe" and ''taua'' means "army" or "war party") a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
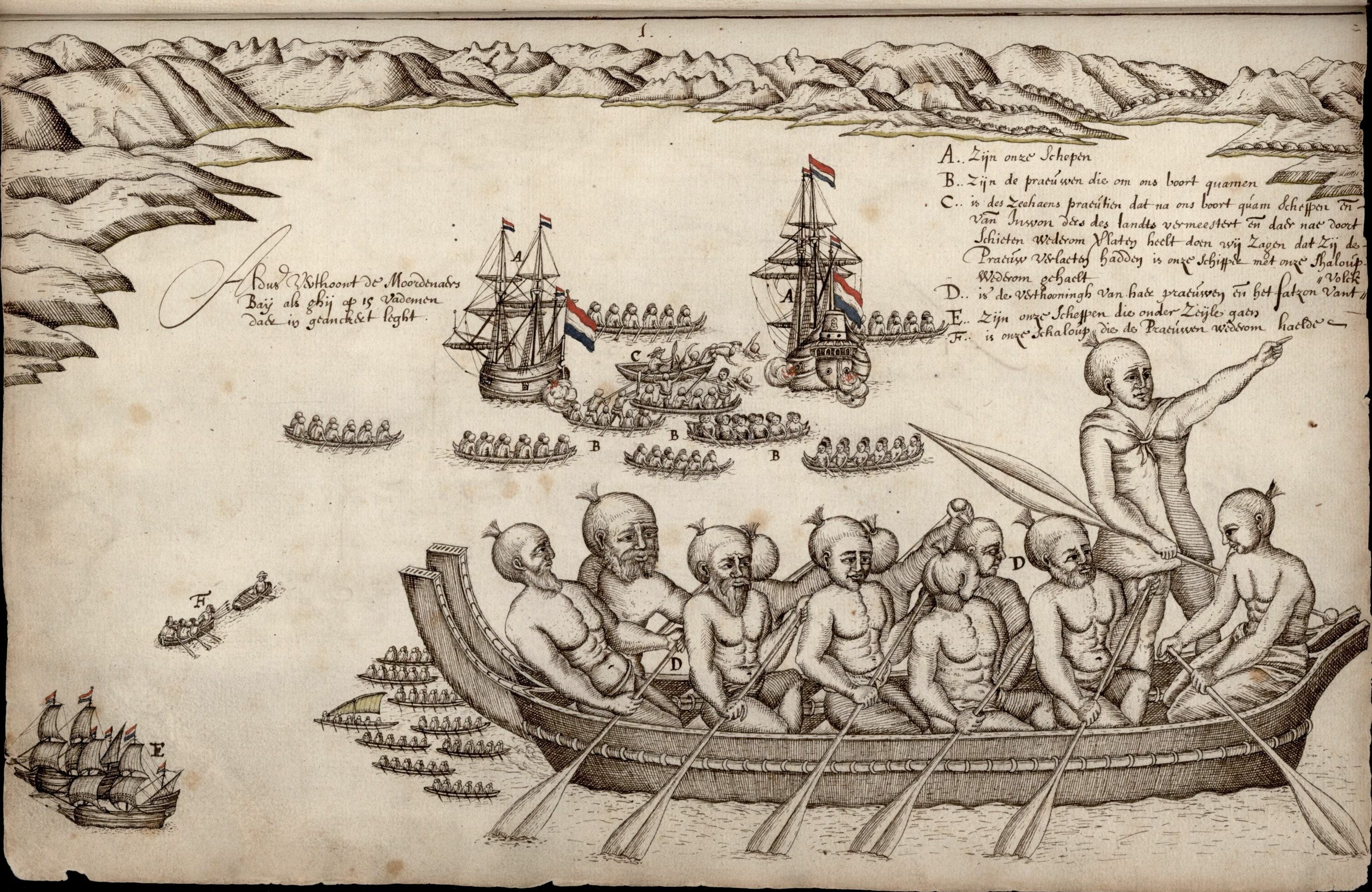
Ngāti Tūmatakōkiri
Ngāti Tūmatakōkiri is a Māori iwi (tribe) of New Zealand, who arrived on the '' Kurahaupō'' waka. In the 1600s the iwi settled northwestern South Island, becoming a major power in the region until the 1800s. In 1642, members of Ngāti Tūmatakōkiri made the first known contact between Europeans and Māori, when Dutch explorer Abel Tasman visited Golden Bay / Mohua. History The members of the '' Kurahaupō'' waka initially settled in the Bay of Plenty, and after several generations moved inland towards Taupō District and along the Whanganui River. In the late 1500s, the iwi began settling the Marlborough Sounds, however later moved westwards. By the 1600s, the rohe of Ngāti Tūmatakōkiri had expanded to include most of the northwest of the South Island, spanning from Māwhera (Greymouth) in the west to Whangarae ( Croisilles Harbour in the Marlborough Sounds), displacing Ngāti Wairangi ( Hauāuru Māori) to move south of Māwhera (Greymouth). Ngāti Tūmatakōkiri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Māori People
Māori () are the Indigenous peoples of Oceania, indigenous Polynesians, Polynesian people of mainland New Zealand. Māori originated with settlers from East Polynesia, who arrived in New Zealand in several waves of Māori migration canoes, canoe voyages between roughly 1320 and 1350. Over several centuries in isolation, these settlers developed Māori culture, a distinct culture, whose language, mythology, crafts, and performing arts evolved independently from those of other eastern Polynesian cultures. Some early Māori moved to the Chatham Islands, where their descendants became New Zealand's other indigenous Polynesian ethnic group, the Moriori. Early contact between Māori and Europeans, starting in the 18th century, ranged from beneficial trade to lethal violence; Māori actively adopted many technologies from the newcomers. With the signing of the Treaty of Waitangi, Treaty of Waitangi/Te Tiriti o Waitangi in 1840, the two cultures coexisted for a generation. Rising ten ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
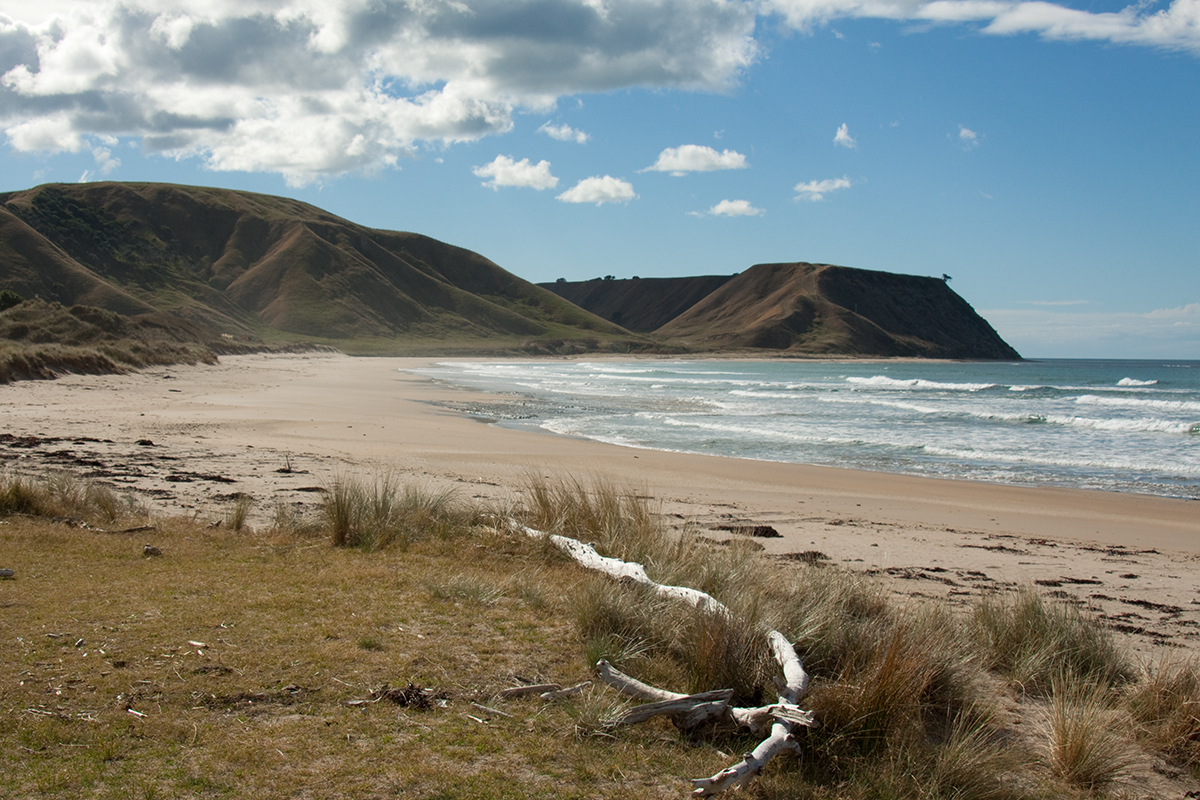
Golden Bay / Mohua
Golden Bay / Mohua is a large shallow bay in New Zealand's Tasman District, near the northern tip of the South Island. An arm of the Tasman Sea, the bay lies northwest of Tasman Bay / Te Tai-o-Aorere and Cook Strait. It is protected in the north by Farewell Spit, a arm of fine golden sand that is the country's longest sandspit. The Aorere River, Aorere and Tākaka River, Tākaka rivers are the major waterways to flow into the bay from the south and the west. The bay was once a resting area for migrating whales and dolphins such as southern right whales and humpback whales, and pygmy blue whales may be observed off the bay as well. The west and northern regions of the bay are largely unpopulated. Along its southern coast are the towns of Tākaka and Collingwood, New Zealand, Collingwood, and the Abel Tasman National Park. Separation Point / Te Matau, the natural boundary between Golden and Tasman Bays, is in the park. North-eastern parts of Kahurangi National Park are in Gol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Farewell Spit
Farewell Spit () is a narrow sand spit at the northern end of the Golden Bay, in the South Island of New Zealand. The spit includes around of stable land and another of mobile sand spit running eastwards from Cape Farewell, the northern-most point of the South Island. Farewell Spit is the longest sand spit in New Zealand, and is a legally protected Nature Reserve. The area is designated as a Ramsar wetland site and an East Asian–Australasian Flyway Shorebird Network site. Farewell Spit is administered by the Department of Conservation as a seabird and wildlife reserve. Apart from a small area at the base of the spit, it is closed to the public except through organised tours. Conservation initiatives are in progress towards eliminating mammalian predators from Farewell Spit, including a proposal for a predator-proof fence. The spit has been the site of many shipwrecks and vessel strandings, particularly in the era of merchant sailing vessels. A lighthouse with a tower c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dutch East India Company
The United East India Company ( ; VOC ), commonly known as the Dutch East India Company, was a chartered company, chartered trading company and one of the first joint-stock companies in the world. Established on 20 March 1602 by the States General of the Netherlands amalgamating Voorcompagnie, existing companies, it was granted a 21-year monopoly to carry out trade activities in Asia. Shares in the company could be purchased by any citizen of the Dutch Republic and subsequently bought and sold in open-air secondary markets (one of which became the Amsterdam Stock Exchange). The company possessed quasi-governmental powers, including the ability to wage war, imprison and execute convicts, negotiate treaties, strike Coinage of the Dutch East India Company, its own coins, and establish colonies. Also, because it traded across multiple colonies and countries from both the East and the West, the VOC is sometimes considered to have been the world's first multinational corporation. St ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Island
The South Island ( , 'the waters of Pounamu, Greenstone') is the largest of the three major islands of New Zealand by surface area, the others being the smaller but more populous North Island and Stewart Island. It is bordered to the north by Cook Strait, to the west by the Tasman Sea, to the south by the Foveaux Strait and Southern Ocean, and to the east by the Pacific Ocean. The South Island covers , making it the List of islands by area, world's 12th-largest island, constituting 56% of New Zealand's land area. At low altitudes, it has an oceanic climate. The most populous cities are Christchurch, Dunedin, Nelson, New Zealand, Nelson and Invercargill. Prior to European settlement, Te Waipounamu was sparsely populated by three major iwi – Kāi Tahu, Kāti Māmoe, and the historical Waitaha (South Island iwi), Waitaha – with major settlements including in Kaiapoi Pā near modern-day Christchurch. During the Musket Wars expanding iwi colonised Te Tau Ihu Māori, Te Tau Ihu, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abel Tasman
Abel Janszoon Tasman (; 160310 October 1659) was a Dutch sea explorer, seafarer and exploration, explorer, best known for his voyages of 1642 and 1644 in the service of the Dutch East India Company (VOC). He was the first European to reach New Zealand, which he named ''Staten Landt''. He was also the eponym of Tasmania. Likely born in 1602 or 1603 in Lutjegast, Netherlands, Tasman started his career as a merchant seaman and became a skilled navigator. In 1633, he joined the VOC and sailed to Batavia, Dutch East Indies, Batavia, now Jakarta, Indonesia. He participated in several voyages, including one to Japan. In 1642, Tasman was appointed by the VOC to lead an expedition to explore the uncharted regions of the Southern Pacific Ocean. His mission was to discover new trade routes and to establish trade relations with the native inhabitants. After leaving Batavia, Tasman sailed westward to Mauritius, then south to the Roaring Forties, then eastward, and reached the coast of Tasma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |