|
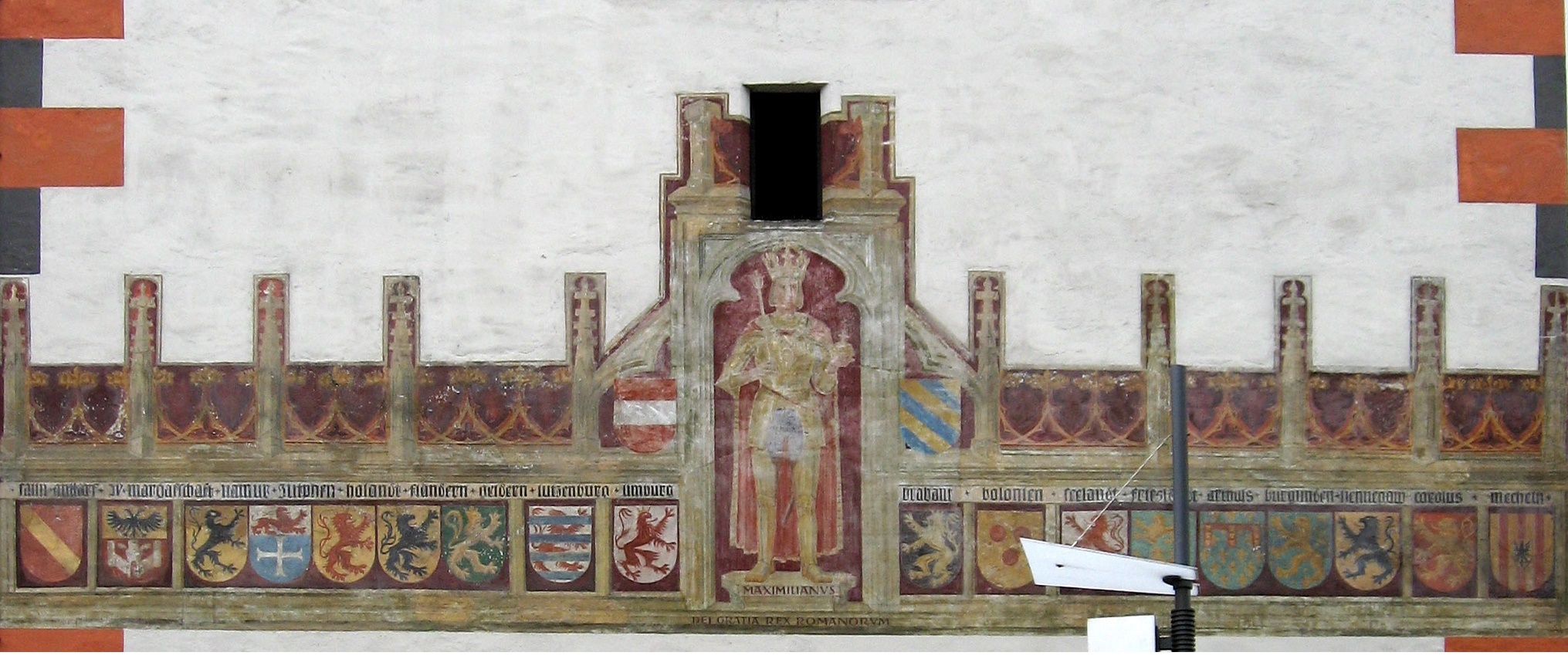
Burgundian Circle
The Burgundian Circle (german: Burgundischer Kreis, nl, Bourgondische Kreits, french: Cercle de Bourgogne) was an Imperial Circle of the Holy Roman Empire created in 1512 and significantly enlarged in 1548. In addition to the Free County of Burgundy (present-day administrative region of Franche-Comté), the Burgundian Circle roughly covered the Low Countries, i.e., the areas now known as the Netherlands, Belgium and Luxembourg and adjacent parts in the French administrative region of Nord-Pas-de-Calais. For most of its history, its lands were coterminous with the holdings of the Spanish Habsburgs in the Empire (Franche-Comté and the Habsburg Netherlands). The circle's territorial scope was reduced considerably in the 17th century with the secession of the Seven United Provinces in 1581 (recognized 1648 under the Treaty of Westphalia) and the annexation of the Free County of Burgundy by France in 1678. Consequently, in the 18th century the circle was known as Austrian Netherlan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lordship Of Groningen
The Lordship of Groningen ( nl, Heerlijkheid Groningen) was a lordship under the rule of the House of Habsburg between 1536 and 1594, which is the present-day province of Groningen. Before 1536 A distinction must be made between the City of Groningen and the surrounding countryside, known as the Ommelanden. The city of Groningen had already gained its independence from its formal landlord, the Bishop of Utrecht in the 12th century. The Ommelanden, together with their Frisian neighbours, enjoyed the Frisian freedom and had never had a Lord. Therefore, before 1536, the concept of a ''Lord of Groningen'' had never existed. Charles V After the Habsburg victory in the Battle of Heiligerlee (1536) during the Guelders Wars, the city of Groningen and the Ommelanden came under the rule of Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor. They were joined in the ''Lordship of Groningen'' and ruled by a Stadtholder, but with preservation of their ancient rights and privileges. Because of the predominant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lordship Of Friesland
The Lordship of Frisia or Lordship of Friesland ( fry, Hearlikheid Fryslân, nl, Heerlijkheid Friesland) was a feudal dominion in the Netherlands. It was formed in 1498 by Maximilian of Habsburg and reformed in 1524 when Emperor Charles V conquered Frisia. History The former Frisian kingdom (''Magna Frisia'') had been incorporated into Francia after the Frisian–Frankish wars, that ended with the victory of the Frankish troops led by ''majordomo'' Charles Martel at the Battle of the Boarn in 734. The remaining territory east of the Lauwers River was conquered by Charlemagne in the course of the Saxon Wars until 785. During the decline of the Carolingian Empire in the 9th century, the Frisian coast with the important trading place of Dorestad was strongly affected by Viking raids. In turn the Frankish emperor Louis the Pious and his successor Lothair I, ruler of Middle Francia since 843, tried to pacify the Viking leaders such as Harald Klak or Rorik of Dorestad by vesting the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
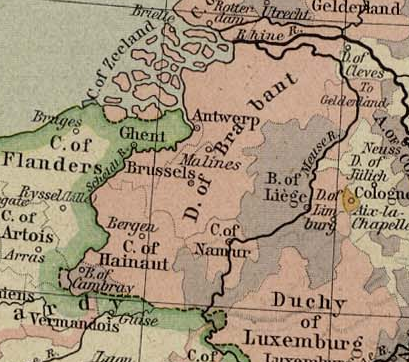
County Of Flanders
The County of Flanders was a historic territory in the Low Countries. From 862 onwards, the counts of Flanders were among the original twelve peers of the Kingdom of France. For centuries, their estates around the cities of Ghent, Bruges and Ypres formed one of the most affluent regions in Europe. Up to 1477, the area under French suzerainty was west of the Scheldt and was called "Royal Flanders" (Dutch: ''Kroon-Vlaanderen'', French: ''Flandre royale''). Aside from this, the counts, from the 11th century onward, held land east of the river as a fief of the Holy Roman Empire: "Imperial Flanders" (''Rijks-Vlaanderen'' or ''Flandre impériale''). Part of the Burgundian Netherlands from 1384, which had a complex relation with France, the whole county fell to the Empire after the Peace of Madrid in 1526 and the Peace of the Ladies in 1529. Having already regained much, by 1795, the rest – within the Austrian Netherlands – was acquired likewise by France under the Fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duchy Of Brabant
The Duchy of Brabant was a State of the Holy Roman Empire established in 1183. It developed from the Landgraviate of Brabant and formed the heart of the historic Low Countries, part of the Burgundian Netherlands from 1430 and of the Habsburg Netherlands from 1482, until it was partitioned after the Dutch revolt. Present-day North Brabant (''Noord-Brabant'') was ceded to the Generality Lands of the Dutch Republic according to the 1648 Peace of Westphalia, while the reduced duchy remained part of the Habsburg Netherlands until it was conquered by French Revolutionary forces in 1794, which was recognized by treaty in 1797. Today all the duchy's former territories, apart from exclaves, are in Belgium except for the Dutch province of North Brabant. Geography The Duchy of Brabant (adjective: ''Brabantian'' or '' Brabantine'') was historically divided into four parts, each with its own capital. The four capitals were Leuven, Brussels, Antwerp and 's-Hertogenbosch. Before 's-Herto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treaty Of The Pyrenees
The Treaty of the Pyrenees (french: Traité des Pyrénées; es, Tratado de los Pirineos; ca, Tractat dels Pirineus) was signed on 7 November 1659 on Pheasant Island, and ended the Franco-Spanish War that had begun in 1635. Negotiations were conducted on Pheasant Island, situated in the middle of the Bidasoa River on the border between the two countries, which has remained a French-Spanish condominium ever since. It was signed by Louis XIV of France and Philip IV of Spain, as well as their chief ministers, Cardinal Mazarin and Don Luis Méndez de Haro. Background France entered the Thirty Years' War after the Spanish Habsburg victories in the Dutch Revolt in the 1620s and at the Battle of Nördlingen against Sweden in 1634. By 1640, France began to interfere in Spanish politics, aiding the revolt in Catalonia, while Spain responded by aiding the Fronde revolt in France in 1648. During the negotiations for the Peace of Westphalia in 1648, France gained the Sundgau an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treaty Of Senlis
The Treaty of Senlis concerning the Burgundian succession was signed at Senlis, Oise on 23 May 1493 between Maximilian I of Habsburg and his son Philip "the Handsome", Archduke of Austria, and King Charles VIII of France. Background After the last Valois Duke of Burgundy, Charles the Bold, had died without male heir at the 1477 Battle of Nancy, his cousin Louis XI of France was determined to come into his inheritance, especially the Burgundian Netherlands with the thriving County of Flanders. However, Mary the Rich, daughter of Charles the Bold, and her husband Maximilian also claimed their rights, which led to clashes of arms culminating at the 1479 Battle of Guinegate, concluded in favour of Mary and Maximilian. Nevertheless, Mary died in 1482 and according to the Treaty of Arras, Maximilian had to cede Burgundy, the County of Artois including the City of Arras and several minor lordships to France as dowry for the proposed marriage of their daughter, Margaret, with Louis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
County Of Artois
The County of Artois (, ) was a historic province of the Kingdom of France, held by the Dukes of Burgundy from 1384 until 1477/82, and a state of the Holy Roman Empire from 1493 until 1659. Present Artois lies in northern France, on the border with Belgium. Its territory has an area of around 4000 km² and a population of about one million. Its principal cities are Arras (Atrecht), Calais (Kales), Boulogne-sur-Mer (Bonen), Saint-Omer (Sint-Omaars), Lens and Béthune. It forms the interior of the French département Pas-de-Calais. Originally a feudal county itself, Artois was annexed by the county of Flanders. It came to France in 1180 as a dowry of a Flemish princess, Isabelle of Hainaut, and was again made a separate county in 1237 for Robert, a grandson of Isabelle. Through inheritance, Artois came under the rule of the dukes of Burgundy in 1384. At the death of the fourth duke, Charles the Bold, Artois was inherited by the Habsburgs and passed to the dynasty's Spani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Margraviate Of Antwerp
The Margraviate of Antwerp (or Mark of Antwerp) consisted since the eleventh century of the area around the cities of Antwerp and Breda. Origin Under Otto II, emperor of the Holy Roman Empire, several marches were created along the border with West Francia (this border coincided with the river Scheldt). Originally the mark was restricted to the borders of the Scheldt, in 994 Ansfried of Utrecht added Toxandria to the mark. History In the 11th century the mark of Antwerp was one of the fiefs of the duke of Lower Lorraine. Godfrey of Bouillon received the mark in 1076 from emperor Henry IV. After his death in the Crusader state of Jerusalem in 1100, Henry I of Limburg was appointed as margrave. In 1106 the duchy of Lower Lorraine and the margraviate were united. After the abolishment of the duchy in 1190 during the Diet of Schwäbisch Hall by Emperor Henry VI only its titles remained and these were given to the duke of Brabant. Composition The margraviate consisted (a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
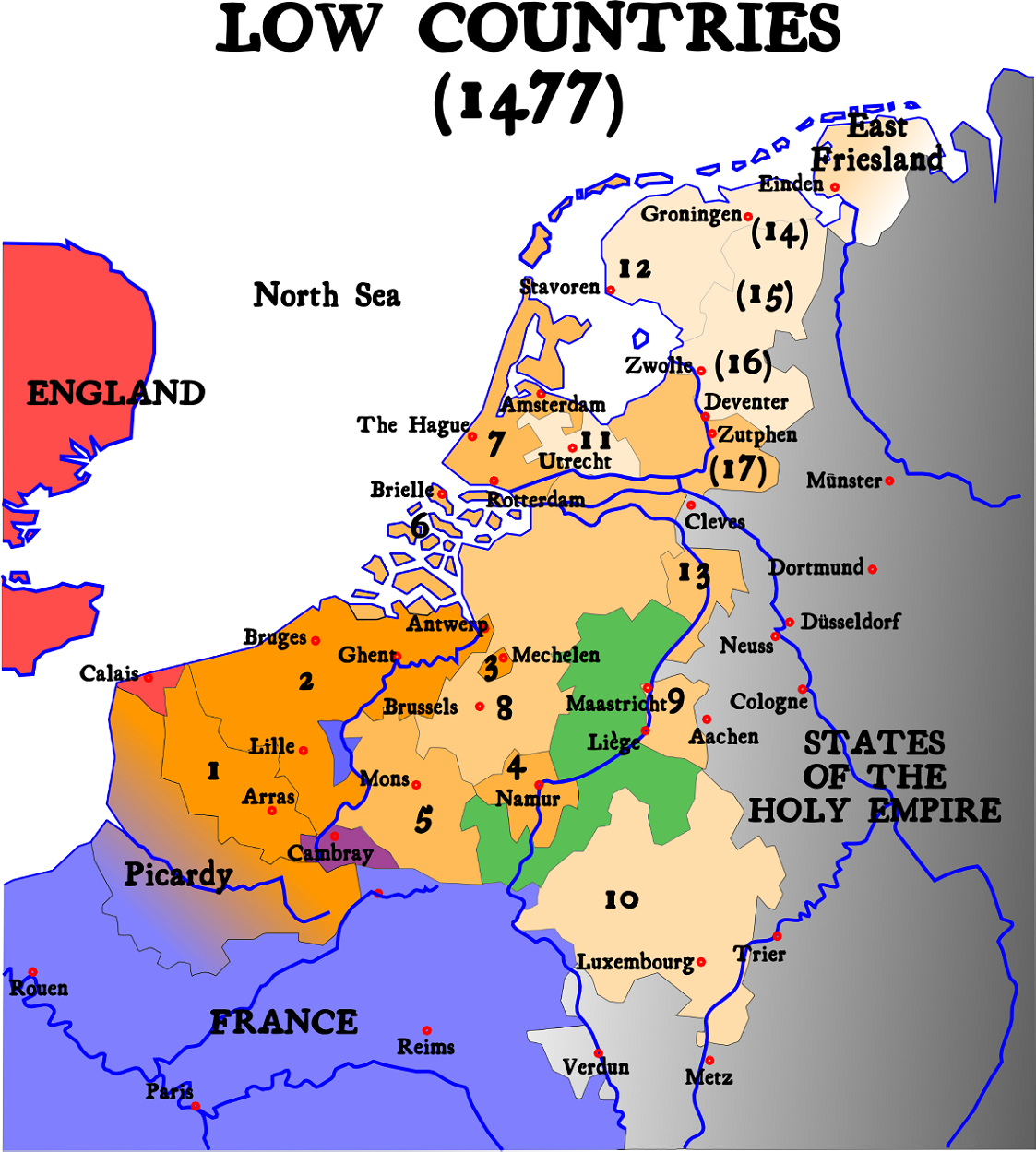
Seventeen Provinces
The Seventeen Provinces were the Imperial states of the Habsburg Netherlands in the 16th century. They roughly covered the Low Countries, i.e., what is now the Netherlands, Belgium, Luxembourg, and most of the French departments of Nord (French Flanders and French Hainaut) and Pas-de-Calais (Artois). Also within this area were semi-independent fiefdoms, mainly ecclesiastical ones, such as Liège, Cambrai and Stavelot-Malmedy. The Seventeen Provinces arose from the Burgundian Netherlands, a number of fiefs held by the House of Valois-Burgundy and inherited by the Habsburg dynasty in 1482, and held by Habsburg Spain from 1556. Starting in 1512, the Provinces formed the major part of the Burgundian Circle. In 1581, the Seven United Provinces seceded to form the Dutch Republic. Composition After the Habsburg emperor Charles V had re-acquired the Duchy of Guelders from Duke William of Jülich-Cleves-Berg by the 1543 Treaty of Venlo, the Seventeen Provinces comprised: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diet Of Augsburg
The Diet of Augsburg were the meetings of the Imperial Diet of the Holy Roman Empire held in the German city of Augsburg. Both an Imperial City and the residence of the Augsburg prince-bishops, the town had hosted the Estates in many such sessions since the 10th century. In 1282, the diet of Augsburg assigned the control of Austria to the House of Habsburg. In the 16th century, twelve of thirty-five imperial diets were held in Augsburg, a result of the close financial relationship between the Augsburg-based banking families such as the Fugger and the reigning Habsburg emperors, particularly Maximilian I and his grandson Charles V. Nevertheless, the meetings of 1518, 1530, 1547/48 and 1555, during the Reformation and the ensuing religious war between the Catholic emperor and the Protestant Schmalkaldic League, are especially noteworthy. With the Peace of Augsburg, the principle let each prince decide the religion of his subjects and inhabitants who could not conform could ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.png)