|
Byzantine Venetia
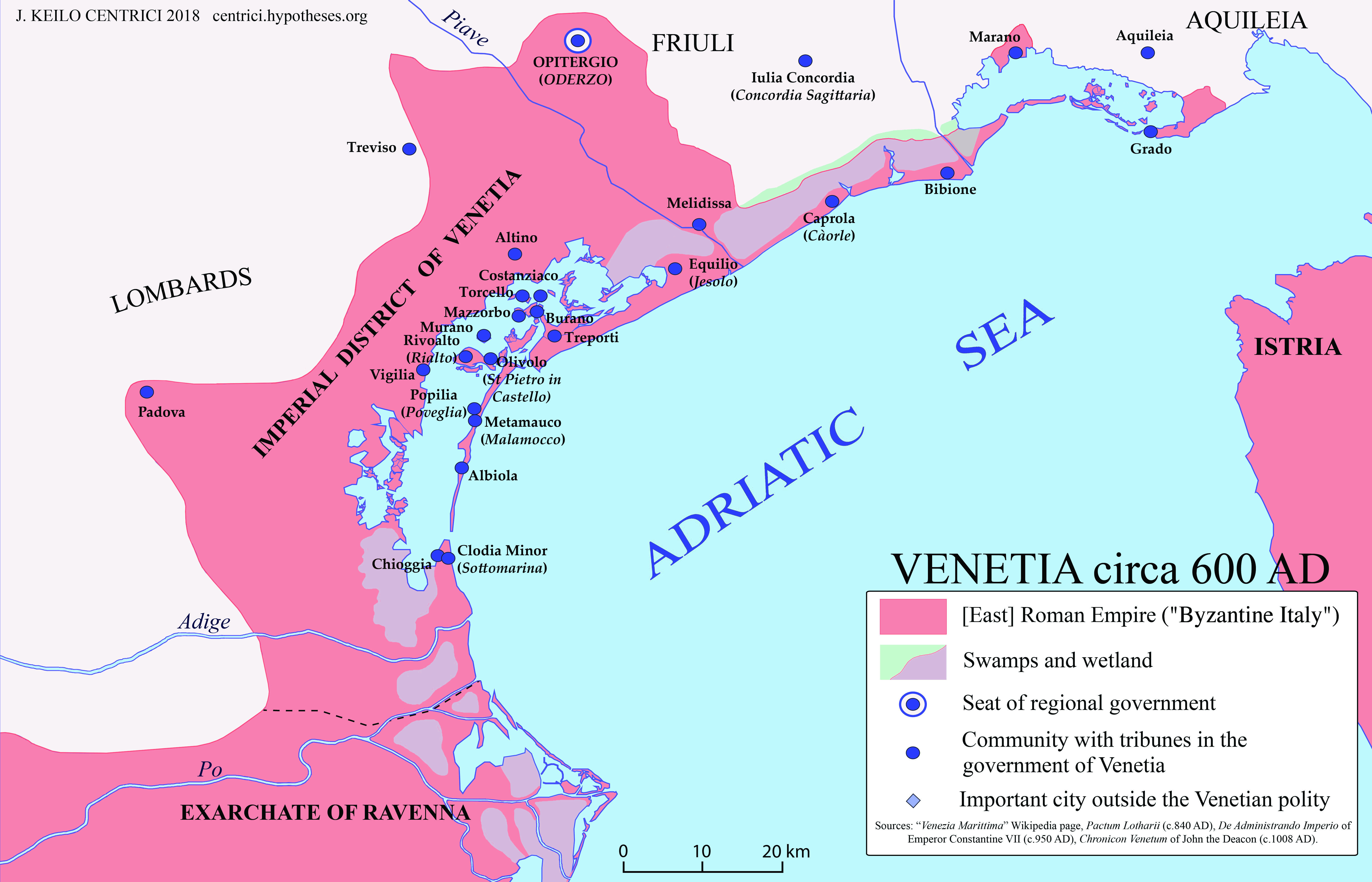
Byzantine Venetia (), also known as the Byzantine Maritime Venetia (), or Maritime Venice (), was a territory of the Byzantine Empire, within the Exarchate of Ravenna, that existed from the middle of the 6th century, up to the second half of the 7th century. Its territory was corresponding to the coastal belt of ancient Venetia and Istria, encompassing coastal regions of present-day Veneto, and Friuli-Venezia Giulia, including the Venetian Lagoon. Its territory did not include hinterland of the old Venetian province, which was conquered by the Lombards. Within Byzantine domains in Byzantine Italy, Italy, Maritime Venetia had a peripheral position, characterized by a patchwork of settlements without major Urban area, urban centers, besides Oderzo (), the capital city of the province. History During the Gothic War (535–554), Gothic War (535–554), Byzantine rule was established on the entire territory of the ancient Roman province of Venetia and Istria, with its traditional ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Venetia C 600 AD
''The'' is a grammatical article in English, denoting nouns that are already or about to be mentioned, under discussion, implied or otherwise presumed familiar to listeners, readers, or speakers. It is the definite article in English. ''The'' is the most frequently used word in the English language; studies and analyses of texts have found it to account for seven percent of all printed English-language words. It is derived from gendered articles in Old English which combined in Middle English and now has a single form used with nouns of any gender. The word can be used with both singular and plural nouns, and with a noun that starts with any letter. This is different from many other languages, which have different forms of the definite article for different genders or numbers. Pronunciation In most dialects, "the" is pronounced as (with the voiced dental fricative followed by a schwa) when followed by a consonant sound, and as (homophone of the archaic pronoun ''thee'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autonomy
In developmental psychology and moral, political, and bioethical philosophy, autonomy is the capacity to make an informed, uncoerced decision. Autonomous organizations or institutions are independent or self-governing. Autonomy can also be defined from a human resources perspective, where it denotes a (relatively high) level of discretion granted to an employee in his or her work. In such cases, autonomy is known to generally increase job satisfaction. Self-actualized individuals are thought to operate autonomously of external expectations. In a medical context, respect for a patient's personal autonomy is considered one of many fundamental ethical principles in medicine. Sociology In the sociology of knowledge, a controversy over the boundaries of autonomy inhibited analysis of any concept beyond relative autonomy, until a typology of autonomy was created and developed within science and technology studies. According to it, the institution of science's existing autonom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Santa Fosca , also dedicated to Fusca of Ravenna
{{disambig ...
Santa Fosca may refer to: * Fusca of Ravenna (died c. 250), a child saint of the Roman Catholic Church * Santa Fosca, Venice, a church named after and dedicated to Fusca of Ravenna * Church of Santa Fosca, a different church in Venice that is part of the Torcello Cathedral The Church of Santa Maria Assunta () is a basilica church on the island of Torcello, Venice, northern Italy. It is a notable example of Late Paleochristian architecture, one of the most ancient religious edifices in the Veneto, and containing th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Republic Of Venice
The Republic of Venice, officially the Most Serene Republic of Venice and traditionally known as La Serenissima, was a sovereign state and Maritime republics, maritime republic with its capital in Venice. Founded, according to tradition, in 697 by Paolo Lucio Anafesto, over the course of its History of the Republic of Venice, 1,100 years of history it established itself as one of the major European commercial and naval powers. Initially extended in the ''Dogado'' area (a territory currently comparable to the Metropolitan City of Venice), during its history it annexed a large part of Northeast Italy, Istria, Dalmatia, the coasts of present-day Montenegro and Albania as well as numerous islands in the Adriatic Sea, Adriatic and eastern Ionian Sea, Ionian seas. At the height of its expansion, between the 13th and 16th centuries, it also governed Crete, Cyprus, the Peloponnese, a number of List of islands of Greece, Greek islands, as well as several cities and ports in the eastern Me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Doge Of Venice
The Doge of Venice ( ) – in Italian, was the doge or highest role of authority within the Republic of Venice (697–1797). The word derives from the Latin , meaning 'leader', and Venetian Italian dialect for 'duke', highest official of the republic of Venice for over 1,000 years. In standard Italian, the cognate is '' duce'' ( , ), one of National Fascist Party leader Benito Mussolini's titles. Originally referring to any military leader, it became in the Late Roman Empire the title for a leader of an expeditionary force formed by detachments () from the frontier army (), separate from, but subject to, the governor of a province, authorized to conduct operations beyond provincial boundaries. The Doge of Venice acted as both the head of state and head of the Venetian oligarchy. Doges were elected for life through a complex voting process. History The office and title of doge, in relation to Venetia (region) and Venice (city), emerged from older ducal offices (lat. D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paolo Lucio Anafesto
Paolo Lucio Anafesto () was, according to Venetian chronicler John the Deacon and other later traditions, the first Doge of Venice, serving (allegedly) from 697 to 717. Since he is not known from contemporary sources, various scholars have raised several questions regarding his personal ( prosopographical) historicity and reliability of late accounts, provided by John the Deacon, who died sometime after 1018. Traditional accounts Traditional accounts on ''Anafesto'' are based on John the Deacon's work, known as Chronicon Venetum et Gradense, written at the beginning of the 11th century, and also on several other, much later traditions. According to such sources, ''Anafesto'' was a nobleman from Eraclea, then the main town in the region. He was elected in 697 as duke, with official jurisdiction over the entire Venetian lagoon. His job was to both put an end to the conflicts between the various tribunes who until then had governed the differing towns, and to coordinate the defe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rialto
The Rialto is a central area of Venice, Italy, in the ''sestiere'' of San Polo. It is, and has been for many centuries, the financial and commercial heart of the city. Rialto is known for its prominent markets as well as for the monumental Rialto Bridge across the Grand Canal. History The area was settled by the ninth century, when a small area in the middle of the Realtine Islands on either side of the Rio Businiacus was known as the , or "high bank". Eventually the Businiacus became known as the Grand Canal, and the district the Rialto, referring only to the area on the left bank. The Rialto became an important district in 1097, when Venice's market moved there, and in the following century a boat bridge was set up across the Grand Canal providing access to it. This was soon replaced by the Rialto Bridge. The market grew, both as a retail and as a wholesale market. Warehouses were built, including the famous Fondaco dei Tedeschi on the other side of the bridge. Meanwhi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ruling Class
In sociology, the ruling class of a society is the social class who set and decide the political and economic agenda of society. In Marxist philosophy, the ruling class are the class who own the means of production in a given society and apply their cultural hegemony to determine and establish the dominant ideology (ideas, culture, mores, Norms (sociology), norms, Tradition, traditions) of the society. In the case of the Capitalist mode of production (Marxist theory), capitalist mode of production, that class is the capitalist class, also known as the bourgeoisie. In the 21st century, the worldwide political economy established by globalization has created a transnational capitalist class who are not native to any one country. Background In previous mode of production, modes of production, such as feudalism (inheritable property and rights), the feudal lords of the manor were the ruling class; in an economy based upon Slavery, chattel slavery, the slave owners were the rulin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Doge (title)
A doge ( , ; plural dogi or doges; see #Usage, below) was an elected lord and head of state in several Italy, Italian city-states, notably Republic of Venice, Venice and Republic of Genoa, Genoa, during the medieval and Renaissance periods. Such states were referred to as crowned republics. Doges wore a special hat, the Corno ducale and usually ruled life-long. The office of the doge in English is termed a ''dogeship''. Etymology The word ''doge'' comes from Venetian language, Venetian Italian, and, like its standard Italian language , Italian cognate ''duce'' (as in Benito Mussolini , Mussolini's title "Il Duce"), is derived from the Latin ', meaning either "spiritual leader" or "military commander". The political term ''doge'' reached English language, English via French language, French, along with the related English derivation ''duke''. In standard Italian language, Italian, the two derivations from the Latin word ''dux'' – ' and ' (both masculine; feminine: ') – a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Italian Language
Italian (, , or , ) is a Romance language of the Indo-European language family. It evolved from the colloquial Latin of the Roman Empire. Italian is the least divergent language from Latin, together with Sardinian language, Sardinian. It is spoken by about 68 million people, including 64 million native speakers as of 2024. Italian is an official language in Languages of Italy, Italy, Languages of San Marino, San Marino, Languages of Switzerland, Switzerland (Ticino and the Grisons), and Languages of Vatican City, Vatican City; it has official Minority language, minority status in Minority languages of Croatia, Croatia, Slovene Istria, Romania, Bosnia and Herzegovina, and the municipalities of Santa Teresa, Espírito Santo, Santa Tereza, Encantado, Rio Grande do Sul, Encantado, and Venda Nova do Imigrante in Languages of Brazil#Language co-officialization, Brazil. Italian is also spoken by large Italian diaspora, immigrant and expatriate communities in the Americas and Austral ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |