|
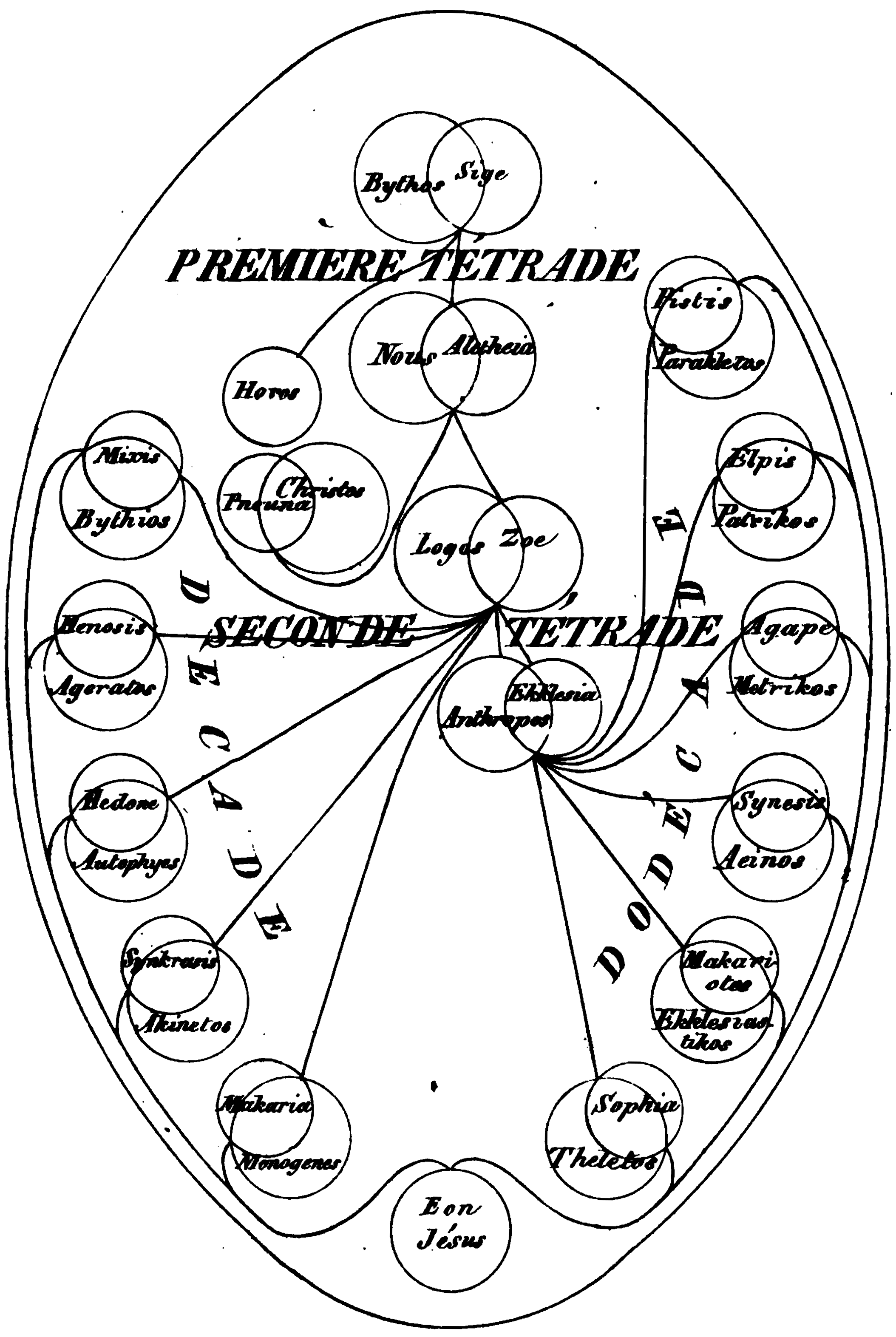
Bythos
In some Gnostic systems, the supreme being is known as the Monad, the One, the Absolute, Aiōn Teleos (the Perfect Aeon, ), Bythos (Depth or Profundity, ), Proarchē (Before the Beginning, ), Hē Archē (The Beginning, ), the Ineffable Parent, and/or the primal Father. The Monad is an adaptation of concepts of the monad in Greek philosophy to Christian belief systems. The ''Apocryphon of John'', written , gives the following description: {{blockquote, The Monad is a monarchy with nothing above it. It is he who exists as God and Father of everything, the invisible One who is above everything, who exists as incorruption, which is in the pure light into which no eye can look. "He is the invisible Spirit, of whom it is not right to think of him as a god, or something similar. For he is more than a god, since there is nothing above him, for no one lords it over him. For he does not exist in something inferior to him, since everything exists in him. For it is he who establishes himse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aeon (Gnosticism)
In many Gnosticism, Gnostic systems, there are various emanationism, emanations of God, who is known by such names as One, Monad (Gnosticism), Monad, ''Aion teleos'' (αἰών τέλεος "The Broadest Aeon"), Bythos (, "depth" or "profundity"), ''Arkhe'' (, "the beginning"). In Gnosticism these emanations of God are named as ''ARKHIRES'' (, "''before'' the beginning") and as Aeons (which are also often named and may be paired or grouped). In different systems these emanations are differently named, classified, and described (but emanation is common to all forms of 'Gnosticism'). In Basilidian Gnosis they are called sonships (υἱότητες ''huiotetes''; sing.: υἱότης ''huiotes''); according to Marcosians, Marcus, they are numbers and sounds; in Valentinianism they form male/female pairs called syzygies (, from σύζυγοι ''syzygoi'': lit. "yokings together"). This source of all being is an Aeon, in which an inner being dwells, known as ''Ennoea'' (, "thought, in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valentinus (Gnostic)
Valentinus ( Greek: Οὐαλεντῖνος; ) was the best known and, for a time, most successful early Christian Gnostic theologian. He founded his school in Rome. According to Tertullian, Valentinus was a candidate for bishop but started his own group when another was chosen. Valentinus produced a variety of writings, but only fragments survive, largely those quoted in rebuttal arguments in the works of his opponents, not enough to reconstruct his system except in broad outline. His doctrine is known only in the developed and modified form given to it by his disciples, the Valentinians. He taught that there were three kinds of people, the spiritual, psychical, and material; and that only those of a spiritual nature received the '' gnosis'' (knowledge) that allowed them to return to the divine Pleroma, while those of a psychic nature (ordinary Christians) would attain a lesser or uncertain form of salvation, and that those of a material nature were doomed to perish. Valentinu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sophia (Gnosticism)
Sophia ( "Wisdom", "the Sophia") is a figure, along with Knowledge ( ''gnosis'', ), among many of the early Christian knowledge theologies grouped by the Heresiology, heresiologist Irenaeus as (), "knowing". Gnosticism is a 17th-century term expanding the definition of Irenaeus' groups to include other Syncretism, syncretic faiths and the Greco-Roman mysteries. In Gnosticism, Sophia is a feminine figure, analogous to the human soul but also simultaneously one of the feminine aspects of God. Gnostics held that she was the ''syzygy'', or female twin, of Jesus, i.e. the Bride of Christ, and the Holy Spirit of the Trinity. She is occasionally referred to by the term (, ) and as (). In the Nag Hammadi library, Nag Hammadi texts, Sophia is the lowest aeon (Gnosticism), aeon or anthropic emanationism, emanation of the godhead. Gnostic mythos Many Gnostic systems, particularly those of the Gnosticism#Major Gnostic schools and their texts, Syrian or Egyptian, teach that the unive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gnostic
Gnosticism (from Ancient Greek: , romanized: ''gnōstikós'', Koine Greek: �nostiˈkos 'having knowledge') is a collection of religious ideas and systems that coalesced in the late 1st century AD among early Christian sects. These diverse groups emphasized personal spiritual knowledge ('' gnosis'') above the proto-orthodox teachings, traditions, and authority of religious institutions. Generally, in Gnosticism, the Monad is the supreme God who emanates divine beings; one, Sophia, creates the flawed demiurge who makes the material world, trapping souls until they regain divine knowledge. Consequently, Gnostics considered material existence flawed or evil, and held the principal element of salvation to be direct knowledge of the hidden divinity, attained via mystical or esoteric insight. Many Gnostic texts deal not in concepts of sin and repentance, but with illusion and enlightenment. Gnosticism likely originated in the late first and early second centuries around Alex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plotinus
Plotinus (; , ''Plōtînos''; – 270 CE) was a Greek Platonist philosopher, born and raised in Roman Egypt. Plotinus is regarded by modern scholarship as the founder of Neoplatonism. His teacher was the self-taught philosopher Ammonius Saccas, who belonged to the Platonic tradition. Historians of the 19th century invented the term "neoplatonism" and applied it to refer to Plotinus and his philosophy, which was vastly influential during late antiquity, the Middle Ages, and the Renaissance. Much of the biographical information about Plotinus comes from Porphyry's preface to his edition of Plotinus' most notable literary work, '' The Enneads''. In his metaphysical writings, Plotinus described three fundamental principles: the One, the Intellect, and the Soul. His works have inspired centuries of pagan, Jewish, Christian, Gnostic, and early Islamic metaphysicians and mystics, including developing precepts that influence mainstream theological concepts within religion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Testament
The Old Testament (OT) is the first division of the Christian biblical canon, which is based primarily upon the 24 books of the Hebrew Bible, or Tanakh, a collection of ancient religious Hebrew and occasionally Aramaic writings by the Israelites. The second division of Christian Bibles is the New Testament, written in Koine Greek. The Old Testament consists of many distinct books by various authors produced over a period of centuries. Christians traditionally divide the Old Testament into four sections: the first five books or Pentateuch (which corresponds to the Jewish Torah); the history books telling the history of the Israelites, from their conquest of Canaan to their defeat and exile in Babylon; the poetic and wisdom literature, which explore themes of human experience, morality, and divine justice; and the books of the biblical prophets, warning of the consequences of turning away from God. The Old Testament canon differs among Christian denominations. The Ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetragrammaton
The TetragrammatonPronounced ; ; also known as the Tetragram. is the four-letter Hebrew-language theonym (transliteration, transliterated as YHWH or YHVH), the name of God in the Hebrew Bible. The four Hebrew letters, written and read from right to left, are ''yodh, yod'', ''he (letter), he'', ''waw (letter), vav'', and ''he''.The word "tetragrammaton" originates from Greek 'four' + ( ) 'letter' The name may be derived from a verb that means 'to be', 'to exist', 'to cause to become', or 'to come to pass'. While there is no consensus about the structure and etymology of the name, the form ''Yahweh'' (with niqqud: ) is now almost universally accepted among Biblical and Semitic linguistics scholars,The form ''Yahweh'' is also dominant in Christianity, but is not used in Islam or Judaism. though the vocalization ''Jehovah'' continues to have wide usage, especially in Christian traditions. In modernity, Christianity is the only Abrahamic religion in which the Tetragrammaton is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hippolytus Of Rome
Hippolytus of Rome ( , ; Romanized: , – ) was a Bishop of Rome and one of the most important second–third centuries Christian theologians, whose provenance, identity and corpus remain elusive to scholars and historians. Suggested communities include Rome, Palestine, Egypt, Anatolia and other regions of the Middle East. The best historians of literature in the ancient church, including Eusebius and Jerome, openly confess they cannot name where Hippolytus the biblical commentator and theologian served in leadership. They had read his works but did not possess evidence of his community. Photios I of Constantinople describes him in his ''Bibliotheca (Photius), Bibliotheca'' (cod. 121) as a disciple of Irenaeus, who was said to be a disciple of Polycarp, and from the context of this passage it is supposed that he suggested that Hippolytus so styled himself. This assertion is doubtful. One older theory asserts he came into conflict with the popes of his time and seems to have heade ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dyad (Greek Philosophy)
The Dyad is a title used by the Pythagoreans for the number two, representing the principle of "twoness" or "otherness". Numenius of Apamea, a Neopythagorean philosopher in the latter 2nd century CE, said that Pythagoras gave the name of Monad to God, and the name of Dyad to matter. Aristotle equated matter as the formation of the elements (energies) into the material world as the static material was formed by the energies being acted upon by force or motion. Later Neoplatonic Philosophers and idealists like Plotinus treated the dyad as a second cause ( demiurge), which was the divine mind (nous ''Nous'' (, ), from , is a concept from classical philosophy, sometimes equated to intellect or intelligence, for the cognitive skill, faculty of the human mind necessary for understanding what is truth, true or reality, real. Alternative Eng ...) that via a reflective nature ( finiteness) causes matter to "appear" or become perceivable. See also * Monad * Tetrad References ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pythagoreanism
Pythagoreanism originated in the 6th century BC, based on and around the teachings and beliefs held by Pythagoras and his followers, the Pythagoreans. Pythagoras established the first Pythagorean community in the Ancient Greece, ancient Greek colony of Crotone, Kroton, in modern Calabria (Italy) circa 530 BC. Early Pythagorean communities spread throughout Magna Graecia. Already during Pythagoras' life it is likely that the distinction between the ''akousmatikoi'' ("those who listen"), who is conventionally regarded as more concerned with religious, and ritual elements, and associated with the oral tradition, and the ''mathematikoi'' ("those who learn") existed. The ancient biographers of Pythagoras, Iamblichus () and his master Porphyry (philosopher), Porphyry ( ) seem to make the distinction of the two as that of 'beginner' and 'advanced'. As the Pythagorean cenobites practiced an esoteric path, like the Greco-Roman mysteries, mystery schools of antiquity, the adherents, ''akou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deity
A deity or god is a supernatural being considered to be sacred and worthy of worship due to having authority over some aspect of the universe and/or life. The ''Oxford Dictionary of English'' defines ''deity'' as a God (male deity), god or goddess, or anything revered as divine. C. Scott Littleton defines a deity as "a being with powers greater than those of ordinary humans, but who interacts with humans, positively or negatively, in ways that carry humans to new Higher consciousness, levels of consciousness, beyond the grounded preoccupations of ordinary life". Religions can be categorized by how many deities they worship. Monotheism, Monotheistic religions accept only one deity (predominantly referred to as "God"), whereas Polytheism, polytheistic religions accept multiple deities. Henotheism, Henotheistic religions accept one God, supreme deity without denying other deities, considering them as aspects of the same divine principle. Nontheistic religions deny any supreme eter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Number
A number is a mathematical object used to count, measure, and label. The most basic examples are the natural numbers 1, 2, 3, 4, and so forth. Numbers can be represented in language with number words. More universally, individual numbers can be represented by symbols, called ''numerals''; for example, "5" is a numeral that represents the number five. As only a relatively small number of symbols can be memorized, basic numerals are commonly organized in a numeral system, which is an organized way to represent any number. The most common numeral system is the Hindu–Arabic numeral system, which allows for the representation of any Integer, non-negative integer using a combination of ten fundamental numeric symbols, called numerical digit, digits. In addition to their use in counting and measuring, numerals are often used for labels (as with telephone numbers), for ordering (as with serial numbers), and for codes (as with ISBNs). In common usage, a ''numeral'' is not clearly dist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |