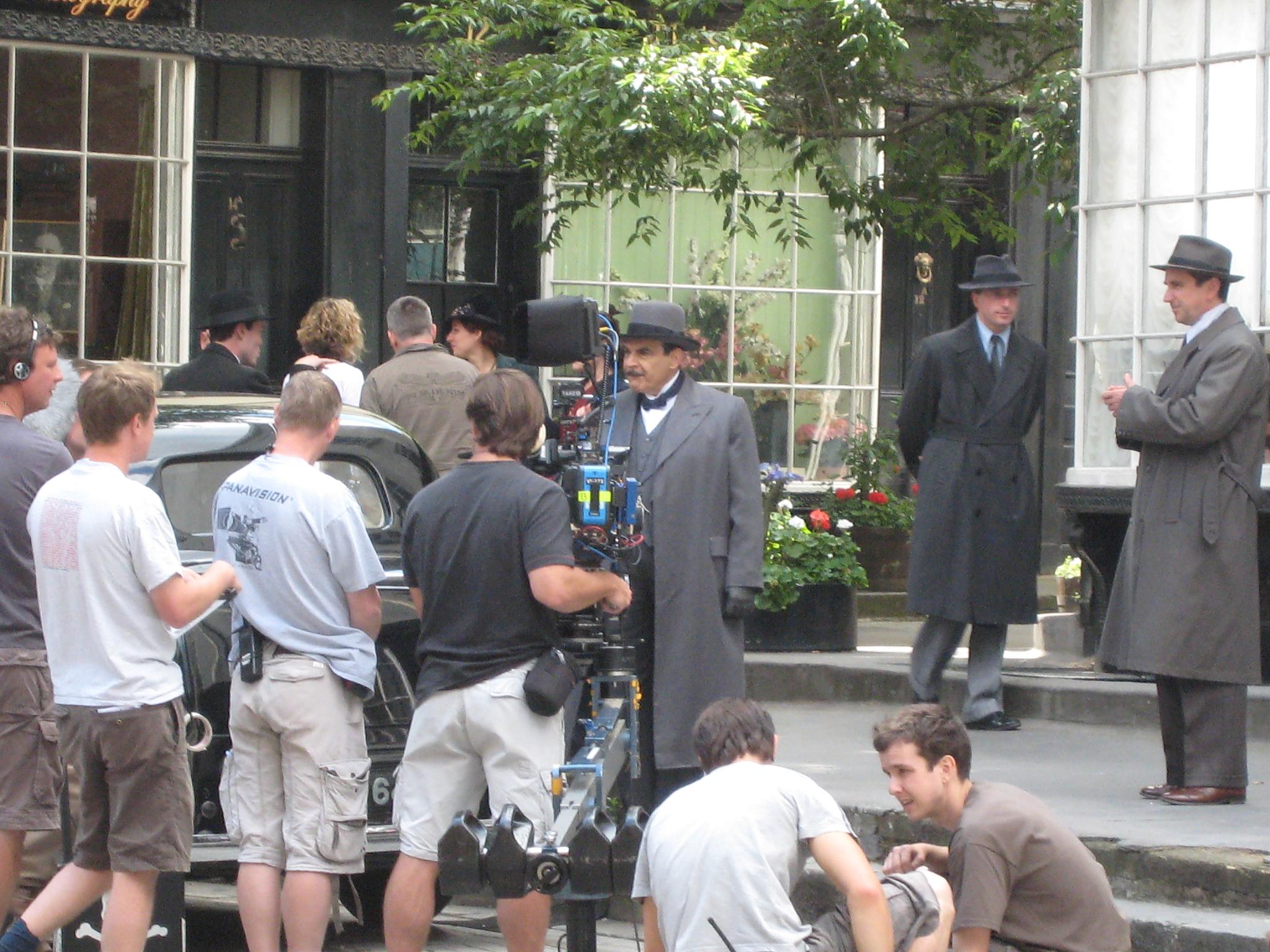|
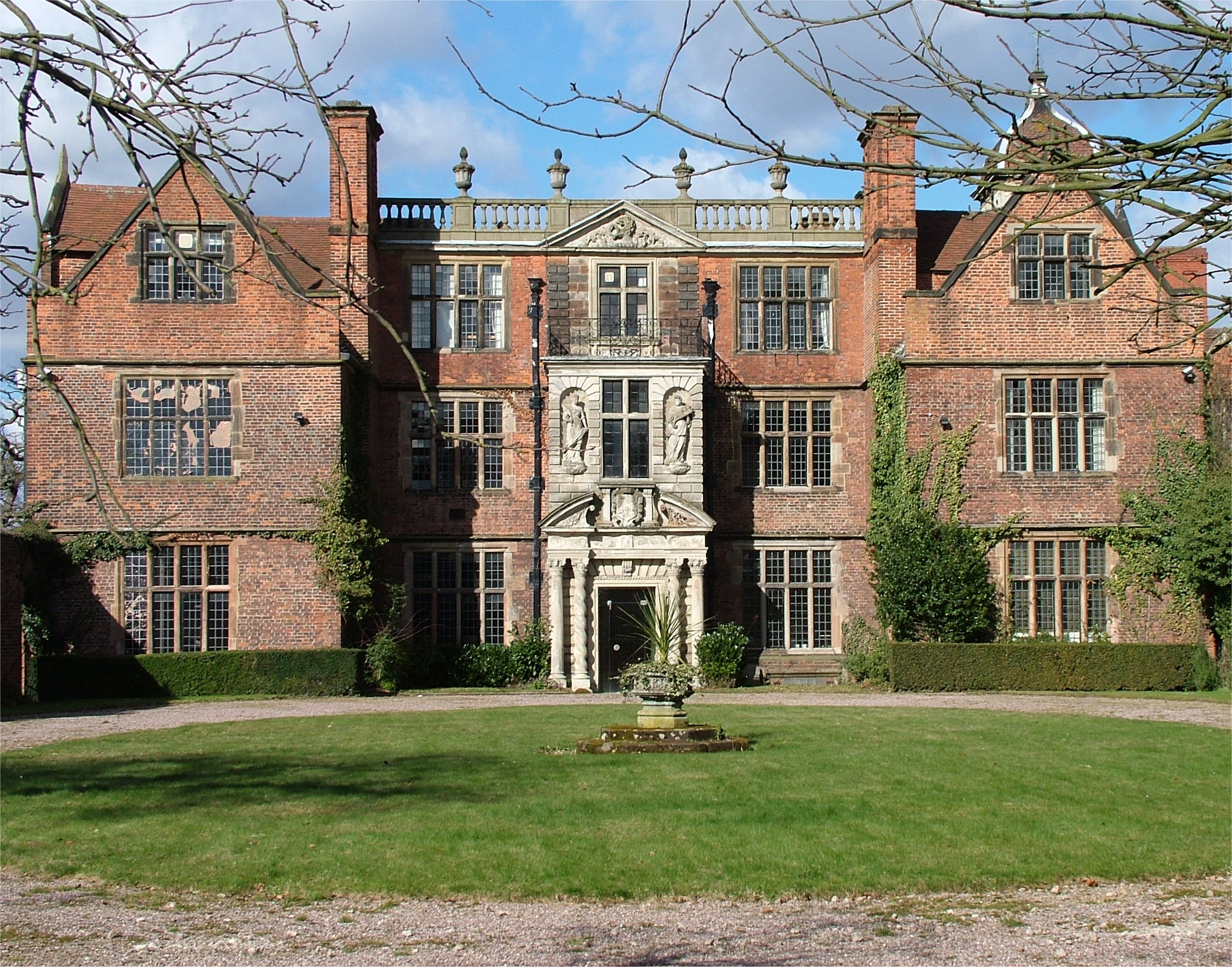
Byfleet Manor
Byfleet Manor is a Grade II* listed house in Byfleet, Surrey, England. Byfleet Manor has been used as a filming location in three television series, most notably ''Downton Abbey''. History Byfleet Manor's precursor was a royal hunting lodge given by Edward II to Piers Gaveston, his reputed lover. Anne of Denmark, wife of King James I, the house's last royal owner, commissioned a fresh house here in 1617. She kept horses sent by her brother Christian IV in the park, and spent at least £250 on the house. However, she died before the work was finished. According to John Aubrey, the house was completed by the courtier James Fullerton. The front walls and gate piers, which can still be seen today, date from that time. A detailed ownership and account of royal rights is set out in sources covering this period of history, such as the Feet of Fines and the Assize Rolls kept in the royal collections and The National Archives, but which is well summarised in, for example, the Victori ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
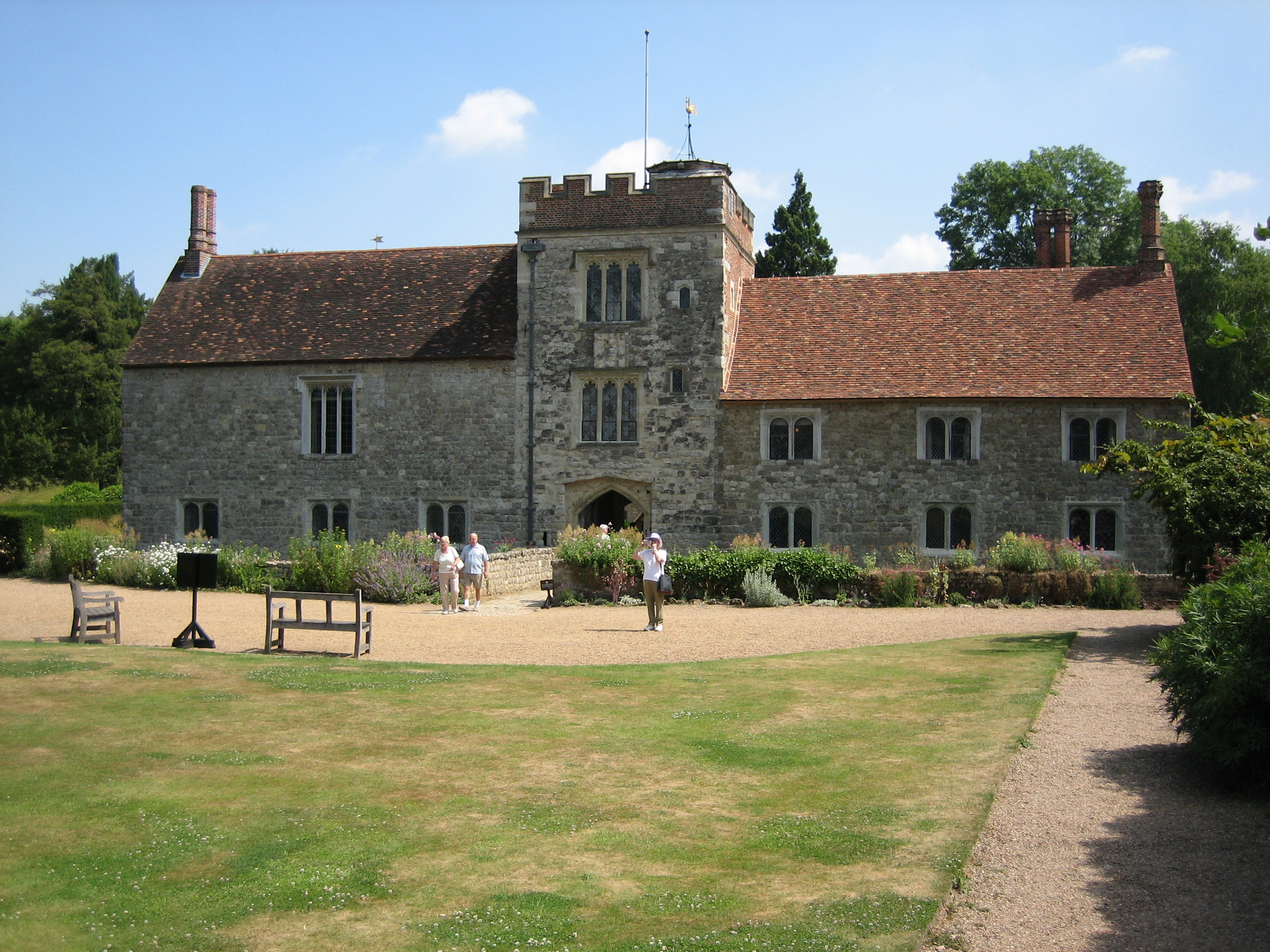
Byfleet
Byfleet is a village in Surrey, England. It is located in the far east of the borough of Woking, around east of West Byfleet, from which it is separated by the M25 motorway and the Wey Navigation. The village is of medieval origin. Its winding main street, High Road, contains old large public houses and several timber-framed houses, as well as other 16th and 17th century houses with listed status . The former Brooklands motor racing circuit is located just to the north, while to the east, across the River Wey, is the former Silvermere estate, now a golf club. Byfleet is served by Byfleet & New Haw railway station, on the South West Main Line. In July 2012, its northern bypass hosted the long-distance cycling road races for the 2012 Summer Olympics. History The village was in the Godley hundred, a Saxon division for strategic and taxation purposes. Byfleet appears in Domesday Book as ''Byeflete''. It was held by Ulwin (Wulfwin) from Chertsey Abbey. Its domesday assets ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jacobean Architecture
The Jacobean style is the second phase of Renaissance architecture in England, following the Elizabethan style. It is named after King James VI and I, with whose reign (1603–1625 in England) it is associated. At the start of James's reign, there was little stylistic break in architecture, as Elizabethan trends continued their development. However, his death in 1625 came as a decisive change towards more classical architecture, with Italian influence, was in progress, led by Inigo Jones. The style this began is sometimes called Stuart architecture, or English Baroque (though the latter term may be regarded as starting later). Courtiers continued to build large prodigy houses, even though James spent less time on summer progresses around his realm than Elizabeth had. The influence of Flemish and German Northern Mannerism increased, now often executed by recruited craftsmen and artists, rather than obtained from books as in the previous reign. There continued to be very little b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Into The Woods (film)
''Into the Woods'' is a 2014 American musical fantasy film directed by Rob Marshall, with a screenplay by James Lapine based on his and Stephen Sondheim's 1987 Broadway musical of the same name. Produced by Walt Disney Pictures, it features an ensemble cast that includes Meryl Streep, Emily Blunt, James Corden, Anna Kendrick, Chris Pine, Tracey Ullman, Christine Baranski, and Johnny Depp. The film is centered on a childless couple who set out to end a curse placed on them by a vengeful witch, and the characters are forced to experience the consequences of their actions. It is inspired by the Grimm Brothers' fairy-tales of " Little Red Riding Hood", "Cinderella", " Jack and the Beanstalk", and " Rapunzel". After several unsuccessful attempts by other studios and producers to adapt the musical to film, Disney announced in 2012 that it was producing an adaptation, with Marshall directing and John DeLuca serving as producer. Principal photography commenced in September 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cranford (TV Series)
''Cranford'' is a British television series directed by Simon Curtis and Steve Hudson. The teleplay by Heidi Thomas was adapted from three novellas by Elizabeth Gaskell published between 1849 and 1858: '' Cranford'', '' My Lady Ludlow'' and '' Mr Harrison's Confessions''. " The Last Generation in England" was also used as a source. The series was transmitted in five parts in the UK by BBC One in November and December 2007. In the United States, it was broadcast in three episodes by PBS as part of its ''Masterpiece Theatre'' series in May 2008. ''Cranford'' returned with a two-part Christmas special '' Return to Cranford'' in 2009. Plot Set in the early 1840s in the fictional village of Cranford in the county of Cheshire in North West England, the story focuses primarily on the town's single and widowed middle class female inhabitants who are comfortable with their traditional way of life and place great store in propriety and maintaining an appearance of gentility. Among the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
After The Funeral
''After the Funeral'' is a work of detective fiction by Agatha Christie and first published in the US by Dodd, Mead and Company in March 1953 under the title of ''Funerals are Fatal'' and in UK by the Collins Crime Club on 18 May of the same year under Christie's original title. The US edition retailed at $2.50 and the UK edition at ten shillings and sixpence (10/6). A 1963 UK paperback issued by Fontana Books changed the title to ''Murder at the Gallop'' to tie in with the film version. The book features the author's Belgian detective Hercule Poirot, but the ''Murder at the Gallop'' film adaptation instead featured her amateur sleuth, Miss Marple. A wealthy man dies at home. His relatives gather after his funeral for the reading of his will, during which his sister states that he was murdered. The next day, she herself is found murdered. Poirot is called in to solve the mystery. Plot summary Following the funeral of Richard Abernethie, his family assembles at Enderby Hall fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agatha Christie's Poirot
''Agatha Christie's Poirot'', or simply ''Poirot'' (), is a British mystery drama television programme that aired on ITV from 8 January 1989 to 13 November 2020. The ITV show is based on many of Agatha Christie's famous crime fiction series, which revolves around the fictional private investigator Hercule Poirot. David Suchet stars as the title character. Initially produced by LWT, the series was later produced by ITV Studios. The series also aired on VisionTV in Canada, and on PBS and A&E in the US. The programme ran for 13 series and 70 episodes in total. Each episode was adapted from a novel or short story by Christie that featured Poirot. In each episode Poirot is both the main detective in charge of the investigation of a crime (usually murder) and the protagonist at the centre of most of the episode's action. At the programme's conclusion, which finished with " Curtain: Poirot's Last Case", based on the 1975 novel of the same name, every major literary work by Christi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Filming Location
A filming location is a place where some or all of a film or television series is produced, instead of or in addition to using sets constructed on a movie studio backlot or soundstage. In filmmaking, a location is any place where a film crew will be filming actors ''and'' recording their dialog. A location where dialog is not recorded may be considered a second unit photography site. Filmmakers often choose to shoot on location because they believe that greater realism can be achieved in a "real" place; however, location shooting is often motivated by the film's budget. Many films shoot interior scenes on a sound stage and exterior scenes on location. Types of locations There are two main types of locations: * Location shooting, the practice of filming in an actual setting * Studio shoots, on either a sound stage or back lot History Video cameras originally designed for television broadcast were large and heavy, mounted on special pedestals and wired to remote recorders in se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manorial Rights
Manorialism, also known as seigneurialism, the manor system or manorial system, was the method of land ownership (or "tenure") in parts of Europe, notably France and later England, during the Middle Ages. Its defining features included a large, sometimes fortified manor house in which the lord of the manor and his dependants lived and administered a rural estate, and a population of labourers or serfs who worked the surrounding land to support themselves and the lord. These labourers fulfilled their obligations with labour time or in-kind produce at first, and later by cash payment as commercial activity increased. Manorialism was part of the feudal system. Manorialism originated in the Roman villa system of the Late Roman Empire, and was widely practised in medieval western Europe and parts of central Europe. An essential element of feudal society, manorialism was slowly replaced by the advent of a money-based market economy and new forms of agrarian contract. Manorialism fad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Common Land
Common land is collective land (sometimes only open to those whose nation governs the land) in which all persons have certain common rights, such as to allow their livestock to graze upon it, to collect wood, or to cut turf for fuel. A person who has a right in, or over, common land jointly with another or others is usually called a commoner. In Great Britain, common land or former common land is usually referred to as a common; for instance, Clapham Common and Mungrisdale Common. Due to enclosure, the extent of common land is now much reduced from the hundreds of square kilometres that existed until the 17th century, but a considerable amount of common land still exists, particularly in upland areas. There are over 8,000 registered commons in England alone. Origins Originally in medieval England the common was an integral part of the manor, and was thus part of the estate held by the lord of the manor under a grant from the Crown or a superior peer (who in turn held hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parish
A parish is a territorial entity in many Christianity, Christian denominations, constituting a division within a diocese. A parish is under the pastoral care and clerical jurisdiction of a priest#Christianity, priest, often termed a parish priest, who might be assisted by one or more curates, and who operates from a parish church. Historically, a parish often covered the same geographical area as a Manorialism, manor. Its association with the parish church remains paramount. By extension the term ''parish'' refers not only to the territorial entity but to the people of its community or congregation as well as to church property within it. In England this church property was technically in ownership of the parish priest ''Ex officio member, ex officio'', vested in him on his institution to that parish. Etymology and use First attested in English in the late 13th century, the word ''parish'' comes from the Old French , in turn from , the Romanization of Greek, Romanisation of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enclosure
Enclosure or inclosure is a term, used in English landownership, that refers to the appropriation of "waste" or "common land", enclosing it, and by doing so depriving commoners of their traditional rights of access and usage. Agreements to enclose land could be either through a formal or informal process. The process could normally be accomplished in three ways. First there was the creation of "closes", taken out of larger common fields by their owners. Secondly, there was enclosure by proprietors, owners who acted together, usually small farmers or squires, leading to the enclosure of whole parishes. Finally there were inclosure act, enclosures by acts of Parliament. The stated justification for enclosure was to improve the efficiency of agriculture. However, there were other motives too, one example being that the value of the land enclosed would be substantially increased. There were social consequences to the policy, with many protests at the removal of rights from the comm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lord Of The Manor
Lord of the manor is a title that, in Anglo-Saxon England and Norman England, referred to the landholder of a historical rural estate. The titles date to the English Feudalism, feudal (specifically English feudal barony, baronial) system. The lord enjoyed Manorialism, manorial rights (the rights to establish and occupy a residence, known as the manor house and demesne) as well as seignory, the right to grant or draw benefit from the estate (for example, as a landlord). The title is not a peerage or title of upper nobility (although the holder could also be a peer) but was a relationship to land and how it could be used and those living on the land (tenants) may be deployed, and the broad estate and its inhabitants administered. The title continues in modern England and Wales as a legally recognised form of property that can be held independently of its historical rights. It may belong entirely to one person or be a moiety title, moiety shared with other people. The title is know ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |