|
Byblos Necropolis Graffito
The Byblos Necropolis graffito is a Phoenician inscription situated in the Royal necropolis of Byblos. The graffito of Ahiram's tomb was found on the south wall of the shaft leading to the hypogeum, about three meters from the opening. The three-line graffito with William F. Albright's translation: René Dussaud, who found the text, translated it as "''Avis, voici ta perte (est) ci-dessous''" ("Beware, here is your loss (is) below"). The fourth sign of the second line (now considered to be a pē, 𐤐), is not very clear, a bēt (𐤁) seems to have been engraved on top of a qōp (𐤒), or vice versa. Pierre Montet Jean Pierre Marie Montet (27 June 1885 – 19 June 1966) was a French Egyptologist. Biography Montet was born in Villefranche-sur-Saône, Rhône, and began his studies under Victor Loret at the University of Lyon. He excavated at Byblos i ..., the archaeologist who excavated the royal necropolis 1922, made the following comment: Since the graffiti is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ahiram Sarcophagus
The Ahiram sarcophagus (also spelled Ahirom; Phoenician: ) was the sarcophagus of a Phoenician King of Byblos (c. 1000 BC), discovered in 1923 by the French excavator Pierre Montet in tomb V of the royal necropolis of Byblos. The sarcophagus is famed for its bas relief carvings, and its Phoenician inscription. One of five known Byblian royal inscriptions, the inscription is considered to be the earliest known example of the fully developed Phoenician alphabet.Cook, p1 The Phoenician alphabet is believed to be the parent alphabet for a wide number of the world's current writing systems; including the Greek, Latin and Cyrillic Alphabets, and the Hebrew, Arabic and Urdu Abjads. For some scholars it represents the ''terminus post quem'' of the transmission of the alphabet to Europe. Ahirom is not attested in any other Ancient Oriental source, although some scholars have suggested a possible connection to the contemporaneous King Hiram mentioned in the Hebrew Bible (see Hiram I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pierre Montet
Jean Pierre Marie Montet (27 June 1885 – 19 June 1966) was a French Egyptologist. Biography Montet was born in Villefranche-sur-Saône, Rhône, and began his studies under Victor Loret at the University of Lyon. He excavated at Byblos in Lebanon between 1921 and 1924, excavating tombs of rulers from Middle Kingdom of Egypt, Middle Kingdom times. Between 1929 and 1939, he excavated at Tanis, Egypt, finding the royal necropolis of the Twenty-first Dynasty of Egypt, Twenty-first and Twenty-second Dynasty of Egypt, Twenty-second Dynasties: those finds almost equalled that of Tutankhamun's tomb in the Valley of the Kings. In the 1939–1940 Egypt excavation season, he discovered the completely-intact tombs of three Egyptian pharaohs at Tanis: Psusennes I, Amenemope (pharaoh), Amenemope, and Shoshenq II along with the partially plundered tomb of Takelot I. The latter tomb contained a gold bracelet of Osorkon I, Takelot's father, as well as a heart scarab. He also found the f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phoenician Funerary Practices
Phoenician may refer to: * Phoenicia, an ancient civilization * Phoenician alphabet **Phoenician (Unicode block) * Phoenicianism, a form of Lebanese nationalism * Phoenician language * List of Phoenician cities See also * Phoenix (mythology) * Phoenix (other) * Phoenicia (other) Phoenicia, or Phœnicia, was an ancient civilization in the north of Canaan in parts of Lebanon, Syria, and Palestine. Phoenicia may also refer to: Historical places *Phoenice (Roman province), a province of the Roman Empire encompassing the reg ... * {{disambiguation Language and nationality disambiguation pages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Byblos
Byblos ( ; ), also known as Jebeil, Jbeil or Jubayl (, Lebanese Arabic, locally ), is an ancient city in the Keserwan-Jbeil Governorate of Lebanon. The area is believed to have been first settled between 8800 and 7000BC and continuously inhabited since 5000BC. During its history, Byblos was part of numerous cultures including Old Kingdom of Egypt, Egyptian, Phoenician, Assyrian, Achaemenid Empire, Persian, Hellenistic period, Hellenistic, Roman Empire, Roman, Genoese Republic, Genoese, Mamluk Sultanate, Mamluk and Ottoman Empire, Ottoman. Urbanisation is thought to have begun during the third millennium BC when it developed into a city, making it one of the List of oldest continuously inhabited cities, oldest cities in the world, if not the oldest. It is a UNESCO World Heritage Site. It was in Ancient Byblos that the Phoenician alphabet, likely the ancestor of the Greek alphabet, Greek, Latin and all other Western alphabets, was developed. Etymology The name appears as ''Keb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
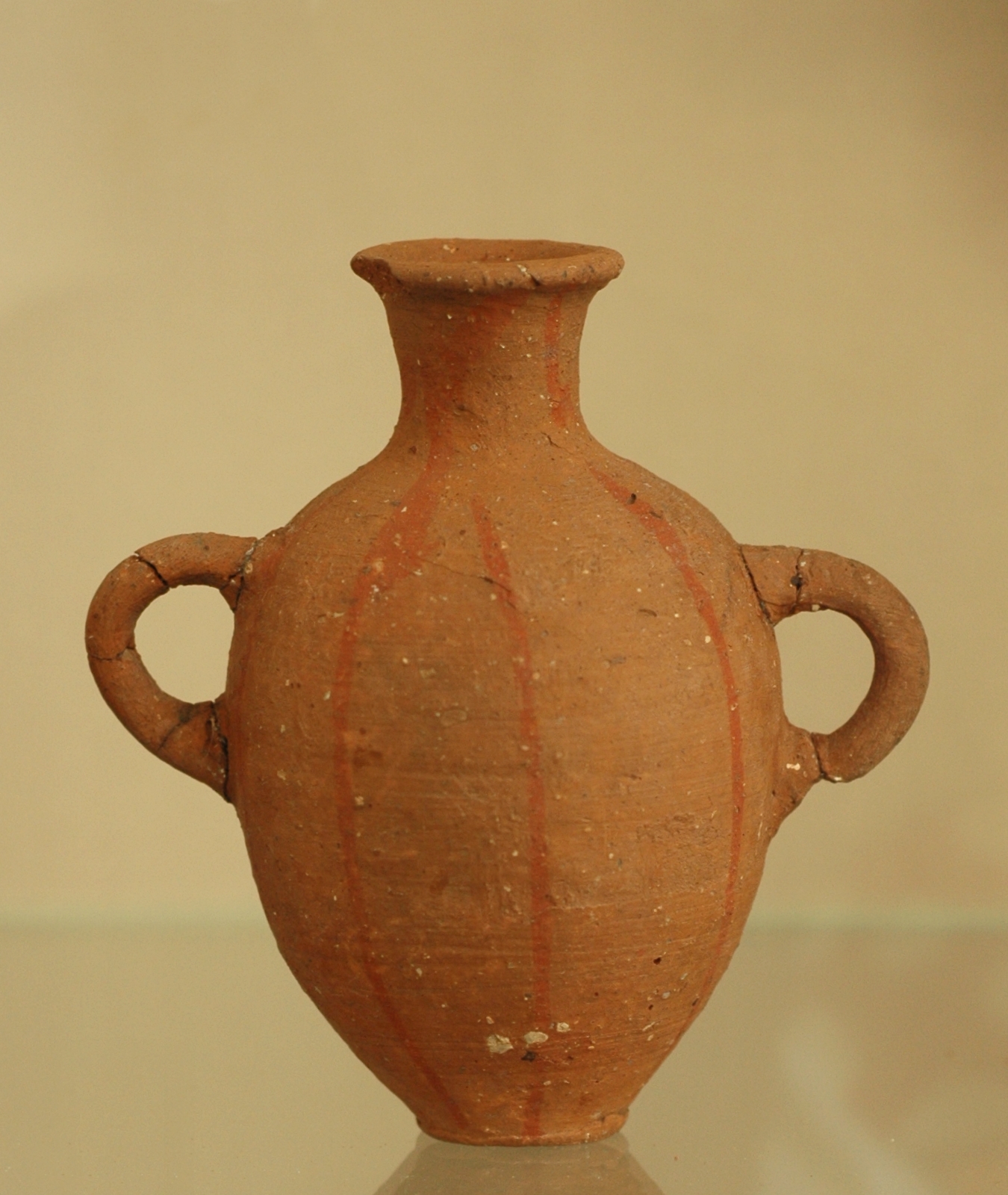
Archaeological Artifacts
An artifact or artefact (British English) is a general term for an item made or given shape by humans, such as a tool or a work of art, especially an object of archaeological interest. In archaeology, the word has become a term of particular nuance; it is defined as an object recovered by archaeological endeavor, including cultural artifacts (of cultural interest). "Artifact" is the general term used in archaeology, while in museums the equivalent general term is normally "object", and in art history perhaps artwork or a more specific term such as "carving". The same item may be called all or any of these in different contexts, and more specific terms will be used when talking about individual objects, or groups of similar ones. Artifacts exist in many different forms and can sometimes be confused with ecofacts and features; all three of these can sometimes be found together at archaeological sites. They can also exist in different types of context depending on the processes th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeological Sites In Lebanon
Archaeology or archeology is the study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of Artifact (archaeology), artifacts, architecture, biofact (archaeology), biofacts or ecofacts, archaeological site, sites, and cultural landscapes. Archaeology can be considered both a social science and a branch of the humanities. It is usually considered an independent academic discipline, but may also be classified as part of anthropology (in North America – the four-field approach), history or geography. The discipline involves Survey (archaeology), surveying, Archaeological excavation, excavation, and eventually Post excavation, analysis of data collected, to learn more about the past. In broad scope, archaeology relies on cross-disciplinary research. Archaeologists study human prehistory and history, from the development of the first stone tools at Lomekwi in East Africa 3.3 million years ago up until recent decades. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graffiti (archaeology)
Graffiti (singular ''graffiti'', or ''graffito'' only in Graffito (archaeology), graffiti archeology) is writing or drawings made on a wall or other surface, usually without permission and within public view. Graffiti ranges from simple written Moniker (graffiti), "monikers" to elaborate wall paintings, and has existed Graffito (archaeology), since ancient times, with examples dating back to ancient Egypt, ancient Greece, and the Roman Empire. Modern graffiti is a controversial subject. In most countries, marking or painting property without permission is considered vandalism. Modern graffiti began in the New York City Subway nomenclature, New York City subway system and Philadelphia in the early 1970s and later spread to the rest of the United States and throughout the world. Etymology "Graffiti" (usually both singular and plural) and the rare singular form "graffito" are from the Italian word ''graffiato'' ("scratched"). In ancient times graffiti were carved on walls with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phoenician Inscriptions
The Canaanite and Aramaic inscriptions, also known as Northwest Semitic inscriptions, are the primary extra-Biblical source for understanding of the societies and histories of the ancient Phoenicians, Ancient Hebrews, Hebrews and Arameans. Semitic inscriptions may occur on stone slabs, pottery ostraca, ornaments, and range from simple names to full texts. The older inscriptions form a Canaanite languages, Canaanite–Aramaic dialect continuum, exemplified by writings which scholars have struggled to fit into either category, such as the Stele of Zakkur and the Deir Alla Inscription. The Northwest Semitic languages are a language group that contains the Aramaic, Aramaic language, as well as the Canaanite languages including Phoenician language, Phoenician and Hebrew language, Hebrew. Languages The old Aramaic period (850 to 612 BC) saw the production and dispersal of inscriptions due to the rise of the Arameans as a major force in Ancient Near East. Their language was adopted a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qoph
Qoph is the nineteenth letter of the Semitic abjads, including Phoenician ''qōp'' 𐤒, Hebrew ''qūp̄'' , Aramaic ''qop'' 𐡒, Syriac ''qōp̄'' ܩ, and Arabic ''qāf'' . It is also related to the Ancient North Arabian , South Arabian , and Ge'ez . Its original sound value was a West Semitic emphatic stop, presumably . In Hebrew numerals, it has the numerical value of 100. Origins The origin of the glyph shape of ''qōp'' () is uncertain. It is usually suggested to have originally depicted either a sewing needle, specifically the eye of a needle (Hebrew ''quf'' and Aramaic ''qopɑʔ'' both refer to the eye of a needle), or the back of a head and neck (''qāf'' in Arabic meant " nape"). According to an older suggestion, it may also have been a picture of a monkey and its tail (the Hebrew means "monkey"). Besides Aramaic ''Qop'', which gave rise to the letter in the Semitic abjads used in classical antiquity, Phoenician ''qōp'' is also the origin of the Latin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canaanite And Aramaic Inscriptions
The Canaanite and Aramaic inscriptions, also known as Northwest Semitic inscriptions, are the primary extra-Biblical source for understanding of the societies and histories of the ancient Phoenicians, Ancient Hebrews, Hebrews and Arameans. Semitic inscriptions may occur on stone slabs, pottery ostraca, ornaments, and range from simple names to full texts. The older inscriptions form a Canaanite languages, Canaanite–Aramaic dialect continuum, exemplified by writings which scholars have struggled to fit into either category, such as the Stele of Zakkur and the Deir Alla Inscription. The Northwest Semitic languages are a language group that contains the Aramaic, Aramaic language, as well as the Canaanite languages including Phoenician language, Phoenician and Hebrew language, Hebrew. Languages The old Aramaic period (850 to 612 BC) saw the production and dispersal of inscriptions due to the rise of the Arameans as a major force in Ancient Near East. Their language was adopted a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bet (letter)
Bet, Beth, Beh, or Vet is the second Letter (alphabet), letter of the Semitic abjads, including Phoenician language, Phoenician ''bēt'' 𐤁 , Hebrew language, Hebrew ''bēt'' , Aramaic language, Aramaic ''bēṯ'' 𐡁, Syriac alphabet, Syriac ''bēṯ'' ܒ and Arabic Alphabet, Arabic ''bāʾ'' . It is also related to the Ancient North Arabian 𐪈, Ancient South Arabian script, South Arabian , and Ge'ez . Its sound value is the voiced bilabial stop ⟨b⟩ or the voiced labiodental fricative ⟨v⟩. The letter's name means "house" in various Semitic languages (Arabic '':wikt:بيت#Arabic, bayt'', Akkadian '':wikt:𒂍#Akkadian, bītu, bētu'', Hebrew: '':wikt:בית#Hebrew, bayīṯ'', Phoenician '':wikt:𐤁𐤉𐤕#Phoenician, bēt'' etc.; ultimately all from Proto-Semitic '':wikt:Reconstruction:Proto-Semitic/bayt-, *bayt-''), and appears to derive from an Egyptian hieroglyph of a house by acrophony. O1 The Phoenician letter gave rise to, among others, the Greek al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pe (Semitic Letter)
Pe is the seventeenth Letter (alphabet), letter of the Semitic abjads, including Arabic alphabet, Arabic ''fāʾ'' , Aramaic alphabet, Aramaic ''pē'' 𐡐, Hebrew alphabet, Hebrew ''pē'' , Phoenician alphabet, Phoenician ''pē'' 𐤐, and Syriac alphabet, Syriac ''pē'' ܦ. (in abjadi order). It is related to the Ancient North Arabian 𐪐, Ancient South Arabian script, South Arabian , and Geʽez script, Ge'ez . The original sound value is a voiceless bilabial plosive and it retains this value in most Semitic languages, except for Arabic, where the sound changed into the voiceless labiodental fricative , carrying with it the pronunciation of the letter. However, the sound in Arabic is used in loanwords with the letter ''pe (Persian letter), pe'' as an alternative. Under the Persian influence, many Arabic dialects in the Persian Gulf, as well as in Egyptian Arabic, Egypt and in some of the Maghreb under the Ottoman influence uses the letter ''pe'' to represent the sound wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |