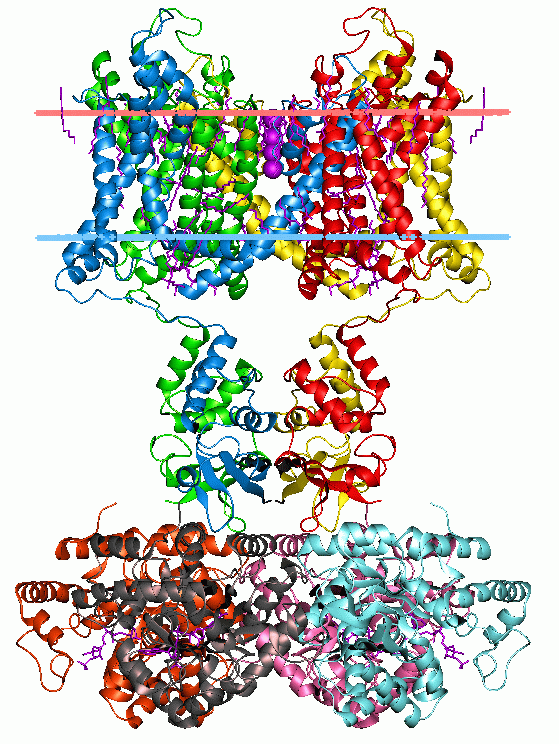
|
Butyrophilin
Butyrophilins are membrane proteins belonging to the immunoglobulin superfamily (Ig). Butyrophilin (Btn) genes constitute a subgroup of at least 10 genes in the Ig superfamily identified in human, mouse, cow, goat and other species. The eponymous Btn gene (BTN1A1 in humans; Btn1a1 in mouse) is highly expressed in the secretory epithelium of the mammary gland during lactation. Other homologues are predominantly expressed in skeletal muscle and the intestine and erythroid cells. In contrast, BTN2A1 and 2 and BTN3A1, 2, and 3 are widely expressed in many tissues, suggesting that the structural domains of Btn proteins may have both universal and tissue-specific functions. Types include: * BTN1A1 - Regulates secretion of milk-lipid droplets * BTN2A2 - Involved in lipid, fatty-acid, and sterol metabolism * BTN3A1 - Presents phosphoantigens to Gamma delta T cells Gamma (uppercase , lowercase ; ''gámma'') is the third letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Butyrophilin, Subfamily 1, Member A1
Butyrophilin subfamily 1 member A1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''BTN1A1'' gene. Butyrophilin (BTN) is the major protein associated with fat droplets in the milk. It is a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily. It may have a cell surface receptor function. The human butyrophilin gene is localized in the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I region of 6p and may have arisen relatively recently in evolution by the shuffling of exons between 2 ancestral gene families Function Btn1a1 regulates the amount of lipids and size of droplets expressed in milk. When the gene is compromised in laboratory mice, approximately half the pups died within the first 20 days and the remainder were significantly under-weight. Link to multiple sclerosis Butyrophilin has been presented as a potential antigen which may be similar enough to myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein Myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein (MOG) is a glycoprotein believed to be important in the myelina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Butyrophilin, Subfamily 2, Member A2
Butyrophilin subfamily 2 member A2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''BTN2A2'' gene. Function Butyrophilin is the major protein associated with fat droplets in the milk. This gene is a member of the BTN2 subfamily of genes, which encode proteins belonging to the butyrophilin protein family. The gene is located in a cluster on chromosome 6, consisting of seven genes belonging to the expanding B7/butyrophilin-like group, a subset of the immunoglobulin gene superfamily. The encoded protein is a type 1 receptor glycoprotein involved in lipid, fatty-acid and sterol metabolism. Several alternatively spliced transcript variants Alternative splicing, or alternative RNA splicing, or differential splicing, is an alternative splicing process during gene expression that allows a single gene to code for multiple proteins. In this process, particular exons of a gene may be ... of this gene have been described, but the full-length nature of some variants has not been determ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Butyrophilin, Subfamily 3, Member A1
Butyrophilin subfamily 3 member A1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''BTN3A1'' gene In biology, the word gene (from , ; "... Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a b .... References External links * Further reading * * * * * * * {{gene-6-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immunoglobulin Superfamily
The immunoglobulin superfamily (IgSF) is a large protein superfamily of cell surface and soluble proteins that are involved in the recognition, binding, or adhesion processes of cells. Molecules are categorized as members of this superfamily based on shared structural features with immunoglobulins (also known as antibodies); they all possess a domain known as an immunoglobulin domain or fold. Members of the IgSF include cell surface antigen receptors, co-receptors and co-stimulatory molecules of the immune system, molecules involved in antigen presentation to lymphocytes, cell adhesion molecules, certain cytokine receptors and intracellular muscle proteins. They are commonly associated with roles in the immune system. Otherwise, the sperm-specific protein IZUMO1, a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily, has also been identified as the only sperm membrane protein essential for sperm-egg fusion. Immunoglobulin domains Proteins of the IgSF possess a structural domain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Membrane Protein
Membrane proteins are common proteins that are part of, or interact with, biological membranes. Membrane proteins fall into several broad categories depending on their location. Integral membrane proteins are a permanent part of a cell membrane and can either penetrate the membrane ( transmembrane) or associate with one or the other side of a membrane ( integral monotopic). Peripheral membrane proteins are transiently associated with the cell membrane. Membrane proteins are common, and medically important—about a third of all human proteins are membrane proteins, and these are targets for more than half of all drugs. Nonetheless, compared to other classes of proteins, determining membrane protein structures remains a challenge in large part due to the difficulty in establishing experimental conditions that can preserve the correct conformation of the protein in isolation from its native environment. Function Membrane proteins perform a variety of functions vital to the su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gamma Delta T Cell
Gamma delta T cells (γδ T cells) are T cells that have a γδ T-cell receptor (TCR) on their surface. Most T cells are αβ (alpha beta) T cells with TCR composed of two glycoprotein chains called α (alpha) and β (beta) TCR chains. In contrast, γδ T cells have a TCR that is made up of one γ (gamma) chain and one δ (delta) chain. This group of T cells is usually less common than αβ T cells, but are at their highest abundance in the gut mucosa, within a population of lymphocytes known as intraepithelial lymphocytes (IELs). The antigenic molecules that activate gamma delta T cells are still largely unknown. However, γδ T cells are peculiar in that they do not seem to require antigen processing and major-histocompatibility-complex (MHC) presentation of peptide epitopes, although some recognize MHC class Ib molecules. γδ T cells are believed to have a prominent role in recognition of lipid antigens. They are of an invariant nature and may be triggered by alarm signals, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Proteins
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') are the most abundant and widespread species of primate, characterized by bipedalism and exceptional cognitive skills due to a large and complex brain. This has enabled the development of advanced tools, culture, and language. Humans are highly social and tend to live in complex social structures composed of many cooperating and competing groups, from families and kinship networks to political states. Social interactions between humans have established a wide variety of values, social norms, and rituals, which bolster human society. Its intelligence and its desire to understand and influence the environment and to explain and manipulate phenomena have motivated humanity's development of science, philosophy, mythology, religion, and other fields of study. Although some scientists equate the term ''humans'' with all members of the genus ''Homo'', in common usage, it generally refers to ''Homo sapiens'', the only extant member. Anatomically modern h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |