|
Butler Lampson
Butler W. Lampson (born December 23, 1943) is an American computer scientist best known for his contributions to the development and implementation of distributed personal computing. Education and early life After graduating from the Lawrenceville School (where in 2009 he was awarded the Aldo Leopold Award, also known as the Lawrenceville Medal, Lawrenceville's highest award to alumni), Lampson received an A.B. in physics (''magna cum laude'' with highest honors in the discipline) from Harvard University in 1964 and a PhD in electrical engineering and computer science from the University of California, Berkeley in 1967. Career and research During the 1960s, Lampson and others were part of Project GENIE at UC Berkeley. In 1965, several Project GENIE members, specifically Lampson and Peter Deutsch, developed the Berkeley Timesharing System for Scientific Data Systems' SDS 940 computer. After completing his doctorate, Lampson stayed on at UC Berkeley as an assistant professo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer Science
Computer science is the study of computation, information, and automation. Computer science spans Theoretical computer science, theoretical disciplines (such as algorithms, theory of computation, and information theory) to Applied science, applied disciplines (including the design and implementation of Computer architecture, hardware and Software engineering, software). Algorithms and data structures are central to computer science. The theory of computation concerns abstract models of computation and general classes of computational problem, problems that can be solved using them. The fields of cryptography and computer security involve studying the means for secure communication and preventing security vulnerabilities. Computer graphics (computer science), Computer graphics and computational geometry address the generation of images. Programming language theory considers different ways to describe computational processes, and database theory concerns the management of re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Stark Draper Prize
The U.S. National Academy of Engineering annually awards the Draper Prize, which is given for the advancement of engineering and the education of the public about engineering. It is one of three prizes that constitute the "Nobel Prizes of Engineering"—the others are the Academy's Russ and Gordon Prizes. The Draper Prize is awarded biennially and the winner of each of these prizes receives $500,000. The Draper prize is named for Charles Stark Draper, the "father of inertial navigation", an MIT professor and founder of Draper Laboratory. Past winners * 1989: Jack S. Kilby and Robert N. Noyce for their independent development of the monolithic integrated circuit * 1991: Sir Frank Whittle and Hans von Ohain for their independent development of the turbojet engine * 1993: John Backus for his development of FORTRAN, the first widely used, general purpose, high-level computer language * 1995: John R. Pierce and Harold A. Rosen for their development of communication satellite ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xerox Star
The Xerox Star workstation, officially named Xerox Star 8010 Information System, is the first commercial personal computer to incorporate technologies that have since become standard in personal computers, including a bitmapped display, a window-based graphical user interface, icons, folders, mouse (two-button), Ethernet networking, file servers, print servers, and email. Introduced by Xerox Corporation on April 27, 1981, the name ''Star'' technically refers only to the software sold with the system for the office automation market. The 8010 workstations were also sold with software based on the programming languages Lisp and Smalltalk for the smaller research and software development market. History The Xerox Alto The Xerox Star system's concept owes much to the Xerox Alto, an experimental workstation designed by the Xerox Palo Alto Research Center (PARC). The first Alto became operational in 1972. The Alto had been strongly influenced by what its designers had seen previ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer Monitor
A computer monitor is an output device that displays information in pictorial or textual form. A discrete monitor comprises a electronic visual display, visual display, support electronics, power supply, Housing (engineering), housing, electrical connectors, and external user controls. The display in modern monitors is typically an Liquid-crystal display, LCD with LED-backlit LCD, LED backlight, having by the 2010s replaced cold-cathode fluorescent lamp, CCFL Backlight, backlit LCDs. Before the mid-2000s, most monitors used a cathode-ray tube, cathode-ray tube (CRT) as the image output technology. A monitor is typically connected to its host computer via DisplayPort, HDMI, USB-C, Digital Visual Interface, DVI, or VGA connector, VGA. Monitors sometimes use other proprietary connectors and signals to connect to a computer, which is less common. Originally computer monitors were used for data processing while television sets were used for video. From the 1980s onward, computers ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
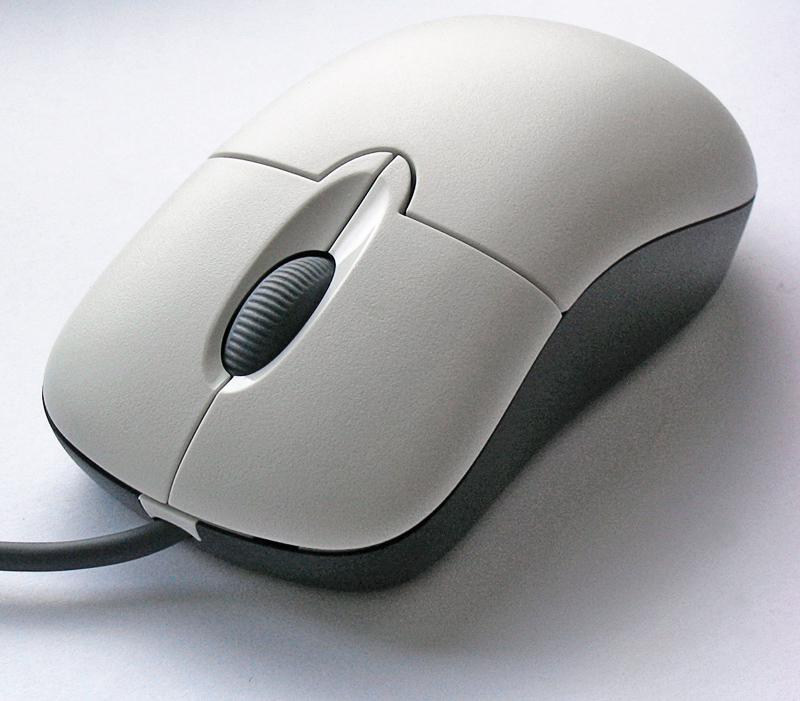
Computer Mouse
A computer mouse (plural mice; also mouses) is a hand-held pointing device that detects Plane (mathematics), two-dimensional motion relative to a surface. This motion is typically translated into the motion of the Cursor (user interface)#Pointer, pointer (called a cursor) on a computer monitor, display, which allows a smooth control of the graphical user interface of a computer. The first public demonstration of a mouse controlling a computer system was done by Doug Engelbart in 1968 as part of the Mother of All Demos. Mice originally used two separate wheels to directly track movement across a surface: one in the x-dimension and one in the Y. Later, the standard design shifted to use a ball rolling on a surface to detect motion, in turn connected to internal rollers. Most modern mice use optical mouse, optical movement detection with no moving parts. Though originally all mice were connected to a computer by a cable, many modern mice are cordless, relying on short-range rad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scientific Data Systems
Scientific Data Systems (SDS), was an American computer company founded in September 1961 by Max Palevsky, Arthur Rock and Robert Beck, veterans of Packard Bell Corporation and Bendix, along with eleven other computer scientists. SDS was the first to employ silicon transistors, and was an early adopter of integrated circuits in computer design. The company concentrated on larger scientific workload focused machines and sold many machines to NASA during the Space Race. Most machines were both fast and relatively low-priced. The company was sold to Xerox in 1969, but dwindling sales due to the oil crisis of 1973–74 caused Xerox to close the division in 1975 at a loss of hundreds of millions of dollars. During the Xerox years the company was officially Xerox Data Systems (XDS), whose machines were the Xerox 500 series. History Early machines Throughout the majority of the 1960s the US computer market was dominated by "Snow White", IBM, and the "Seven Dwarves", Burroughs, UN ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Berkeley Timesharing System
The Berkeley Timesharing System was a pioneering time-sharing operating system implemented between 1964 and 1967 at the University of California, Berkeley. It was designed as part of Project Genie and marketed by Scientific Data Systems for the SDS 940 computer system. It was the first commercial time-sharing which allowed general-purpose user programming, including machine language. History In the mid-1960s, most computers used batch processing: one user at a time with no interactivity. A few pioneering systems such as the Atlas Supervisor at the University of Manchester, Compatible Time-Sharing System at MIT, and the Dartmouth Time-Sharing System at Dartmouth College required large expensive machines. Implementation started in 1964 with the arrival of the SDS 930 which was modified slightly, and an operating system was written from scratch. Students who worked on the Berkeley Timesharing System included undergraduates Chuck Thacker and L. Peter Deutsch and doctoral student B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Project Genie
Project Genie was a computer research project started in 1964 at the University of California, Berkeley. It produced an early time-sharing system including the Berkeley Timesharing System, which was then commercialized as the SDS 940. History Project Genie was funded by J. C. R. Licklider, the head of ARPA's Information Processing Techniques Office at that time. The project was a smaller counterpart to MIT's Project MAC. The Scientific Data Systems SDS 940 was created by modifying an SDS 930 24-bit commercial computer so that it could be used for timesharing. The work was funded by ARPA and directed by Melvin W. Pirtle and Wayne Lichtenberger at UC Berkeley. Butler Lampson, Chuck Thacker, and L. Peter Deutsch were among the young technical leaders of that project. When completed and in service, the first 940 ran reliably in spite of its array of tricky mechanical issues such as a huge disk drive driven by hydraulic arms. It served about forty or fifty users at a time and stil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Professional Developers Conference 2009 Technical Leaders Panel 6
A professional is a member of a profession or any person who works in a specified professional activity. The term also describes the standards of education and training that prepare members of the profession with the particular knowledge and skills necessary to perform their specific role within that profession. In addition, most professionals are subject to strict codes of conduct, enshrining rigorous ethical and moral obligations. Professional standards of practice and ethics for a particular field are typically agreed upon and maintained through widely recognized professional associations, such as the IEEE. Some definitions of "professional" limit this term to those professions that serve some important aspect of public interest and the general good of society.Sullivan, William M. (2nd ed. 2005). ''Work and Integrity: The Crisis and Promise of Professionalism in America''. Jossey Bass.Gardner, Howard and Shulman, Lee S., The Professions in America Today: Crucial but Fragile. Da ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrical Engineering
Electrical engineering is an engineering discipline concerned with the study, design, and application of equipment, devices, and systems that use electricity, electronics, and electromagnetism. It emerged as an identifiable occupation in the latter half of the 19th century after the commercialization of the electric telegraph, the telephone, and electrical power generation, distribution, and use. Electrical engineering is divided into a wide range of different fields, including computer engineering, systems engineering, power engineering, telecommunications, radio-frequency engineering, signal processing, instrumentation, photovoltaic cells, electronics, and optics and photonics. Many of these disciplines overlap with other engineering branches, spanning a huge number of specializations including hardware engineering, power electronics, Electromagnetism, electromagnetics and waves, microwave engineering, nanotechnology, electrochemistry, renewable energies, mechatronics/control ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physics
Physics is the scientific study of matter, its Elementary particle, fundamental constituents, its motion and behavior through space and time, and the related entities of energy and force. "Physical science is that department of knowledge which relates to the order of nature, or, in other words, to the regular succession of events." It is one of the most fundamental scientific disciplines. "Physics is one of the most fundamental of the sciences. Scientists of all disciplines use the ideas of physics, including chemists who study the structure of molecules, paleontologists who try to reconstruct how dinosaurs walked, and climatologists who study how human activities affect the atmosphere and oceans. Physics is also the foundation of all engineering and technology. No engineer could design a flat-screen TV, an interplanetary spacecraft, or even a better mousetrap without first understanding the basic laws of physics. (...) You will come to see physics as a towering achievement of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lawrenceville School
The Lawrenceville School is a Private school, private, coeducational College-preparatory school, preparatory school for boarding and day students located in the Local government in New Jersey, unincorporated community of Lawrenceville, New Jersey, Lawrenceville within Lawrence Township, Mercer County, New Jersey, Lawrence Township in Mercer County, New Jersey, Mercer County, in the U.S. state of New Jersey. Lawrenceville is a member of the Eight Schools Association and the Ten Schools Admission Organization. History 19th century Lawrenceville School was founded in 1810 as the Maidenhead Academy by Presbyterianism, Presbyterian clergyman Isaac Van Arsdale Brown. One of the oldest University-preparatory school, preparatory schools in the United States, it has had several names, including Lawrenceville Classical and Commercial High School and Lawrenceville Academy. In 1883, the John Cleve Green Foundation purchased the school from its aging headmaster Samuel McClintock Hamill, Sam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |