|
Buta Ul
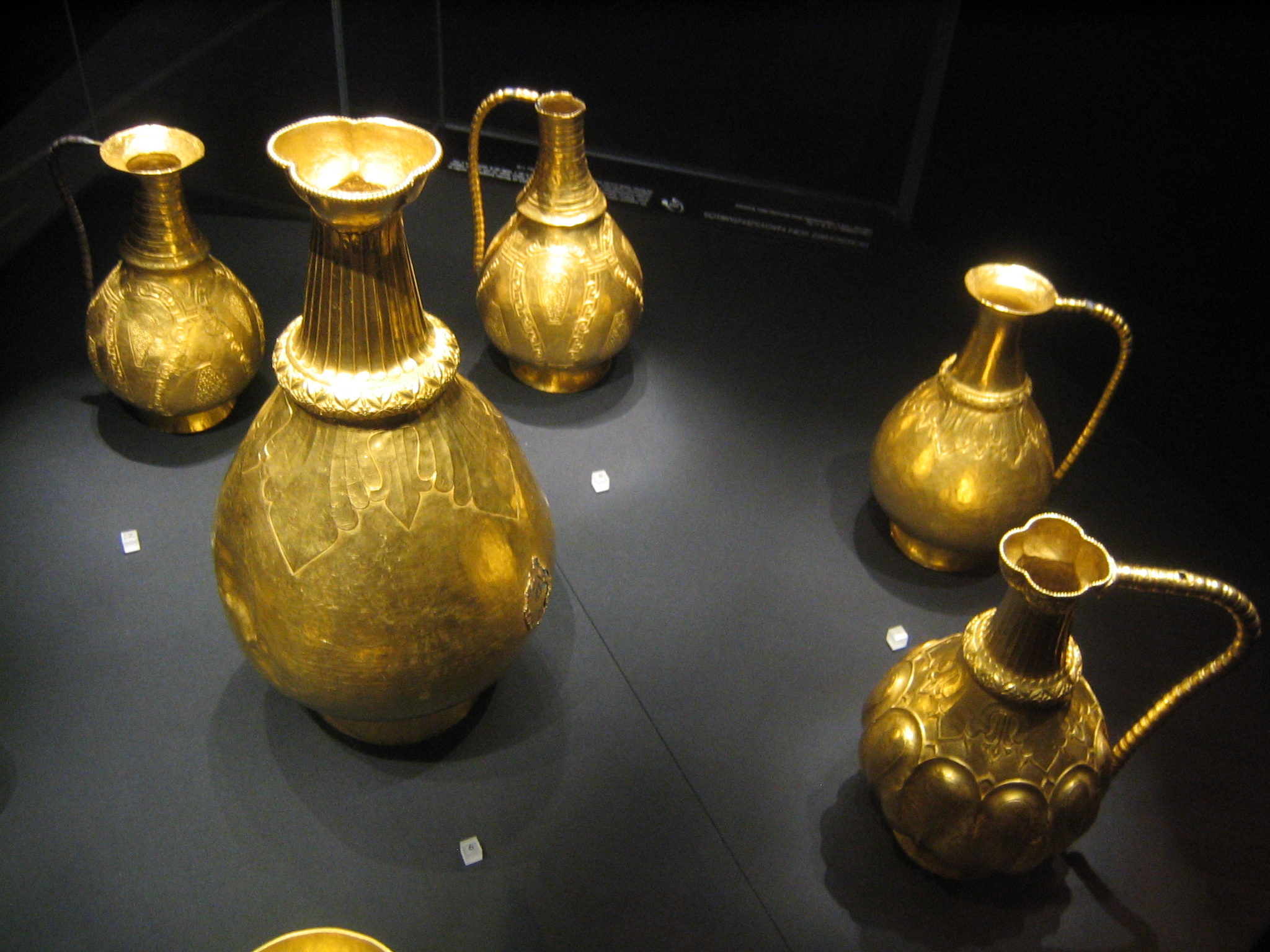
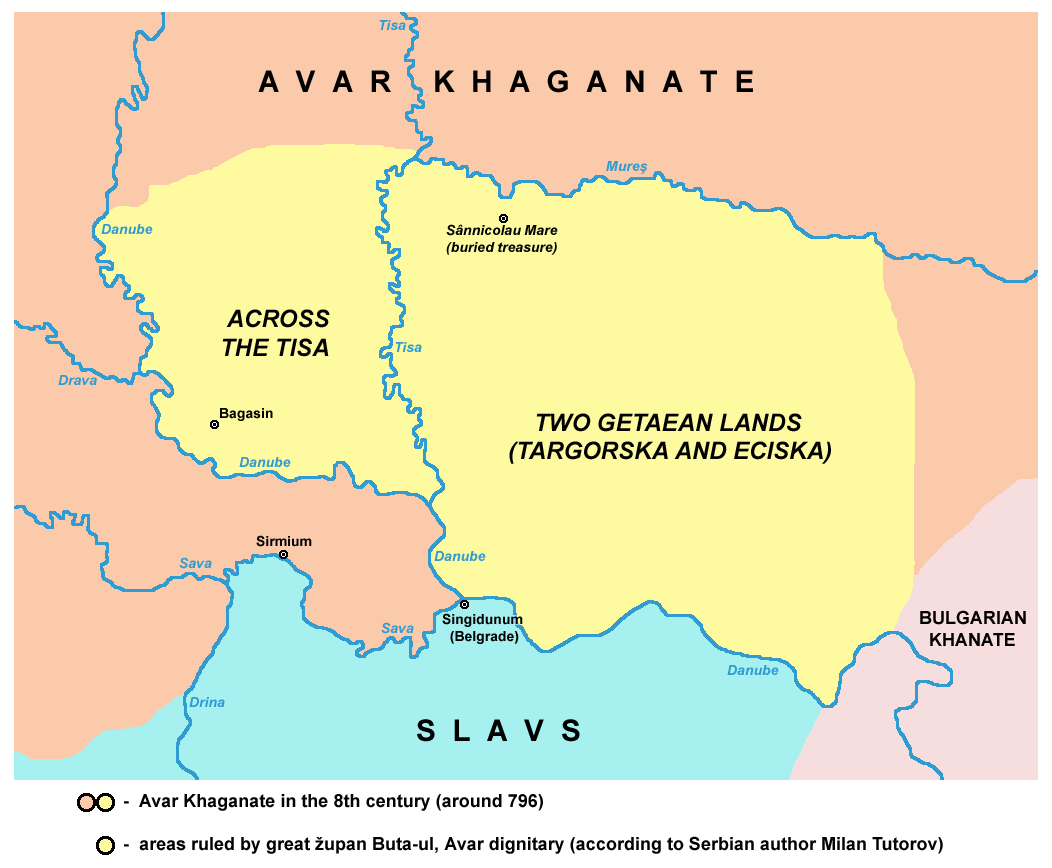
Butaul (also spelled ''Buta-ul'', with possible meaning "the son of Buta") is a name mentioned in an inscription contained in a treasure trove of gold artifacts found in 1799 in Sânnicolau Mare, in northern Banat (then under administration of Habsburg monarchy, today in Timiș County in western Romania). According to various interpretations of the inscription, Butaul was an '' župan'', a sort of local chieftain. It is possible that Butaul is linked to the runiform on the chalice of Kiskőrös-Vágóhíd, which may be transliterated as /put'ə/ (Oghur Turkic for 'louse') or /Buta/ ghur Turkic for (camel's) foal The inscription Buta-ul and Buyla are names preserved by an inscription on one of the vessels found in the hoard. The inscription is written in the Greek alphabet and reads: :BOYHΛA.ZOAΠAN.TECH.ΔYΓΕTOIΓH.BOYTAOYΛ.ZΩAΠAN.TAΓPOΓH.HTZIΓH.TAICH ::(Transliteration: ''bouēla zoapan tesē dygetoigé boutaoul zōapan tagrogē ētzigē taisē''). The languag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treasure Of Nagyszentmiklós
The Treasure of Nagyszentmiklós ( hu, Nagyszentmiklósi kincs; german: Schatz von Nagyszentmiklós; ro, Tezaurul de la Sânnicolau Mare) is an important hoard of 23 early medieval gold vessels, in total weighing 9.945 kg (about 22 lbs), found in 1799 near Nagyszentmiklós, Kingdom of Hungary (german: Groß-Sankt-Niklaus, today Sânnicolau Mare, Romania), meaning "Great St Nicholas". After the excavation, the treasure was transferred to Vienna, the dynastic capital of the Habsburg Monarchy. Ever since, it has been in the possession of the Kunsthistorisches Museum there, where it is on permanent display. A wide range of views continue to be held as to the dating and the origins of the styles of the pieces, and the context in which they were made, which may well vary between the pieces. Unusually, the inscriptions on some pieces have increased the complexity of the arguments rather than reduced them. In 2008 Romanian officials asked the Austrian government for the treas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bačka
Bačka ( sr-cyrl, Бачка, ) or Bácska () is a geographical and historical area within the Pannonian Plain bordered by the river Danube to the west and south, and by the river Tisza to the east. It is divided between Serbia and Hungary. Most of the area is located within the Vojvodina region in Serbia and Novi Sad, the capital of Vojvodina, lies on the border between Bačka and Syrmia. The smaller northern part of the geographical area is located within Bács-Kiskun County in Hungary. Name According to Serbian historians, Bačka is a typical Slavic name form, created from "Bač" (name of historical town in Bačka) and suffix "ka" (which designates "the land that belongs to Bač"). The name of " Bač" (Bács) town is of uncertain origin and its existence was recorded among Vlachs, Slavs and Hungarians in the Middle Ages. The origin of the name could be Paleo-Balkanic, Romanian, Slavic, or Old Turkic. According to Hungarian historians, the denominator of the lands ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Romania In The Early Middle Ages
The Early Middle Ages in Romania started with the withdrawal of the Roman troops and administration from Dacia province in the 270s. In the next millennium a series of peoples, most of whom only controlled two or three of the nearly ten historical regions that now form Romania, arrived. During this period, society and culture underwent fundamental changes. Town life came to an end in Dacia with the Roman withdrawal, and in Scythia Minorthe other Roman province in the territory of present-day Romania400 years later. Fine vessels made on fast potter's wheels disappeared and hand-made pottery became dominant from the 450s. Burial rites changed more than once from cremation to inhumation and ''vice versa'' until inhumation became dominant by the end of the 10th century. The East Germanic Goths and Gepids, who lived in sedentary communities, were the first new arrivals. The Goths dominated Moldavia and Wallachia from the 290s, and parts of Transylvania from the 330s. Their powe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
8th-century Rulers In Europe
The 8th century is the period from 701 ( DCCI) through 800 ( DCCC) in accordance with the Julian Calendar. The coast of North Africa and the Iberian Peninsula quickly came under Islamic Arab domination. The westward expansion of the Umayyad Empire was famously halted at the siege of Constantinople by the Byzantine Empire and the Battle of Tours by the Franks. The tide of Arab conquest came to an end in the middle of the 8th century.Roberts, J., '' History of the World'', Penguin, 1994. In Europe, late in the century, the Vikings, seafaring peoples from Scandinavia, begin raiding the coasts of Europe and the Mediterranean, and go on to found several important kingdoms. In Asia, the Pala Empire is founded in Bengal. The Tang dynasty reaches its pinnacle under Chinese Emperor Xuanzong. The Nara period begins in Japan. Events * Estimated century in which the poem Beowulf is composed. * Classical Maya civilization begins to decline. * The Kombumerri burial grounds are fou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rulers Of Vojvodina
This is a list of local rulers of Vojvodina. The list also include local rulers of Banat, Bačka and Srem, including parts of mentioned regions, which are not part of present-day Vojvodina, as well as other rulers of larger political units that had specific local ties to territory of present-day Vojvodina. Ancient times Roman emperors * Maximinus, Roman emperor (235–238), ruled from residence in Sirmium * Decius Traian, Roman emperor (249–251), born in village Budalia near Sirmium *Ingenuus, Roman emperor (260), proclaimed himself emperor in Sirmium *Regalianus, Roman emperor (260), proclaimed himself emperor in Sirmium *Claudius II, Roman emperor (268–270), spent most of his life in Sirmium *Aurelian, Roman emperor (270–275), born in Sirmium * Probus, Roman emperor (276–282), born in Sirmium *Maximianus Herculius, Roman emperor (285–310), born near Sirmium *Galerius, Roman emperor (305–311), ruled as Caesar during the Tetrarchy from residence in Sirmium (293–296 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Vojvodina
Vojvodina ( Serbian: Војводина or ''Vojvodina''; hu, Vajdaság; sk, Vojvodina; ro, Voivodina; hr, Vojvodina; Rusyn: Войводина) is an autonomous province that comprises northern Serbia. It consists of the southern part of the Pannonian Plain, mostly located north from the Danube and Sava rivers (part of the Mačva region that belongs to Vojvodina is located south of Sava). Name The name ''"Vojvodina"'' (Војводина) in the Serbian language simply means "voivodship" or " duchy". Its original historical name from 1848 was " Serbian Voivodship" (Serbian Vojvodina). The Serbian language uses two more varieties of the word ''Vojvodina''. These varieties are ''Vojvodovina'' (Војводовина), and ''Vojvodstvo'' (Војводство), the latter being an equivalent to the Polish word for province, ''województwo'' (voivodship). As for the names of the three historical and geographical regions of which Vojvodina is composed, Syrmia was named after th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caganate
Khagan or Qaghan (Mongolian:; or ''Khagan''; otk, 𐰴𐰍𐰣 ), or , tr, Kağan or ; ug, قاغان, Qaghan, Mongolian Script: ; or ; fa, خاقان ''Khāqān'', alternatively spelled Kağan, Kagan, Khaghan, Kaghan, Khakan, Khakhan, Khaqan, Xagahn, Qaghan, Chagan, Қан, or Kha'an is a title of imperial rank in the Turkic, Mongolic and some other languages, equal to the status of emperor and someone who rules a khaganate (empire). The female equivalent is Khatun. It may also be translated as " Khan of Khans", equivalent to King of Kings. In Bulgarian, the title became known as ''Khan'', while in modern Turkic, the title became ''Khaan'' with the ''g'' sound becoming almost silent or non-existent; the ''ğ'' in modern Turkish ''Kağan'' is also silent. Since the division of the Mongol Empire, monarchs of the Yuan dynasty and the Northern Yuan held the title of ''Khagan''. ''Kağan, Hakan'' and ''Kaan'', Turkish equivalents of the title are common Turkish names ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charlemagne
Charlemagne ( , ) or Charles the Great ( la, Carolus Magnus; german: Karl der Große; 2 April 747 – 28 January 814), a member of the Carolingian dynasty, was King of the Franks from 768, King of the Lombards from 774, and the first Emperor of the Romans from 800. Charlemagne succeeded in uniting the majority of western and central Europe and was the first recognized emperor to rule from western Europe after the fall of the Western Roman Empire around three centuries earlier. The expanded Frankish state that Charlemagne founded was the Carolingian Empire. He was canonized by Antipope Paschal III—an act later treated as invalid—and he is now regarded by some as beatified (which is a step on the path to sainthood) in the Catholic Church. Charlemagne was the eldest son of Pepin the Short and Bertrada of Laon. He was born before their canonical marriage. He became king of the Franks in 768 following his father's death, and was initially co-ruler with his brother ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Franks
The Franks ( la, Franci or ) were a group of Germanic peoples whose name was first mentioned in 3rd-century Roman sources, and associated with tribes between the Lower Rhine and the Ems River, on the edge of the Roman Empire.H. Schutz: Tools, Weapons and Ornaments: Germanic Material Culture in Pre-Carolingian Central Europe, 400-750. BRILL, 2001, p.42. Later the term was associated with Romanization (cultural), Romanized Germanic dynasties within the collapsing Western Roman Empire, who eventually commanded the whole region between the rivers Loire and Rhine. They imposed power over many other post-Roman kingdoms and Germanic peoples. Beginning with Charlemagne in 800, Frankish rulers were given recognition by the Catholic Church as successors to the old rulers of the Western Roman Empire. Although the Frankish name does not appear until the 3rd century, at least some of the original Frankish tribes had long been known to the Romans under their own names, both as allies providi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pepin Of Italy
Pepin or Pippin (or ''Pepin Carloman'', ''Pepinno'', April 777 – 8 July 810), born Carloman, was the son of Charlemagne and King of the Lombards (781–810) under the authority of his father. Pepin was the second son of Charlemagne by his then-wife Hildegard. He was born Carloman, but was rechristened with the royal name Pepin (also the name of his older half-brother Pepin the Hunchback, and his grandfather Pepin the Short) when he was a young child. He was made "king of Italy" after his father's conquest of the Lombards, in 781, and crowned by Pope Hadrian I with the Iron Crown of Lombardy. He was active as ruler of Lombardy and worked to expand the Frankish empire. In 791, he marched a Lombard army into the Drava valley and ravaged Pannonia, while his father marched along the Danube into Avar territory. Charlemagne left the campaigning to deal with a Saxon revolt in 792. Pepin and Duke Eric of Friuli continued, however, to assault the Avars' ring-shaped strongholds. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treasure Of Groß Sankt Nikolaus
Treasure (from la, thesaurus from Greek language ''thēsauros'', "treasure store") is a concentration of wealth — often originating from ancient history — that is considered lost and/or forgotten until rediscovered. Some jurisdictions legally define what constitutes treasure, such as in the British Treasure Act 1996. The phrase "blood and treasure" has been used to refer to the human and monetary costs associated with massive endeavours such as war that expend both. Searching for hidden treasure is a common theme in legend; treasure hunters do exist, and can seek lost wealth for a living. Burial Buried treasure is an important part of the popular mythos surrounding pirates. According to popular conception, pirates often buried their stolen fortunes in remote places, intending to return for them later (often with the use of treasure maps). There are three well-known stories that helped popularize the myth of buried pirate treasure: "The Gold-Bug" by Edgar Allan Poe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |