|
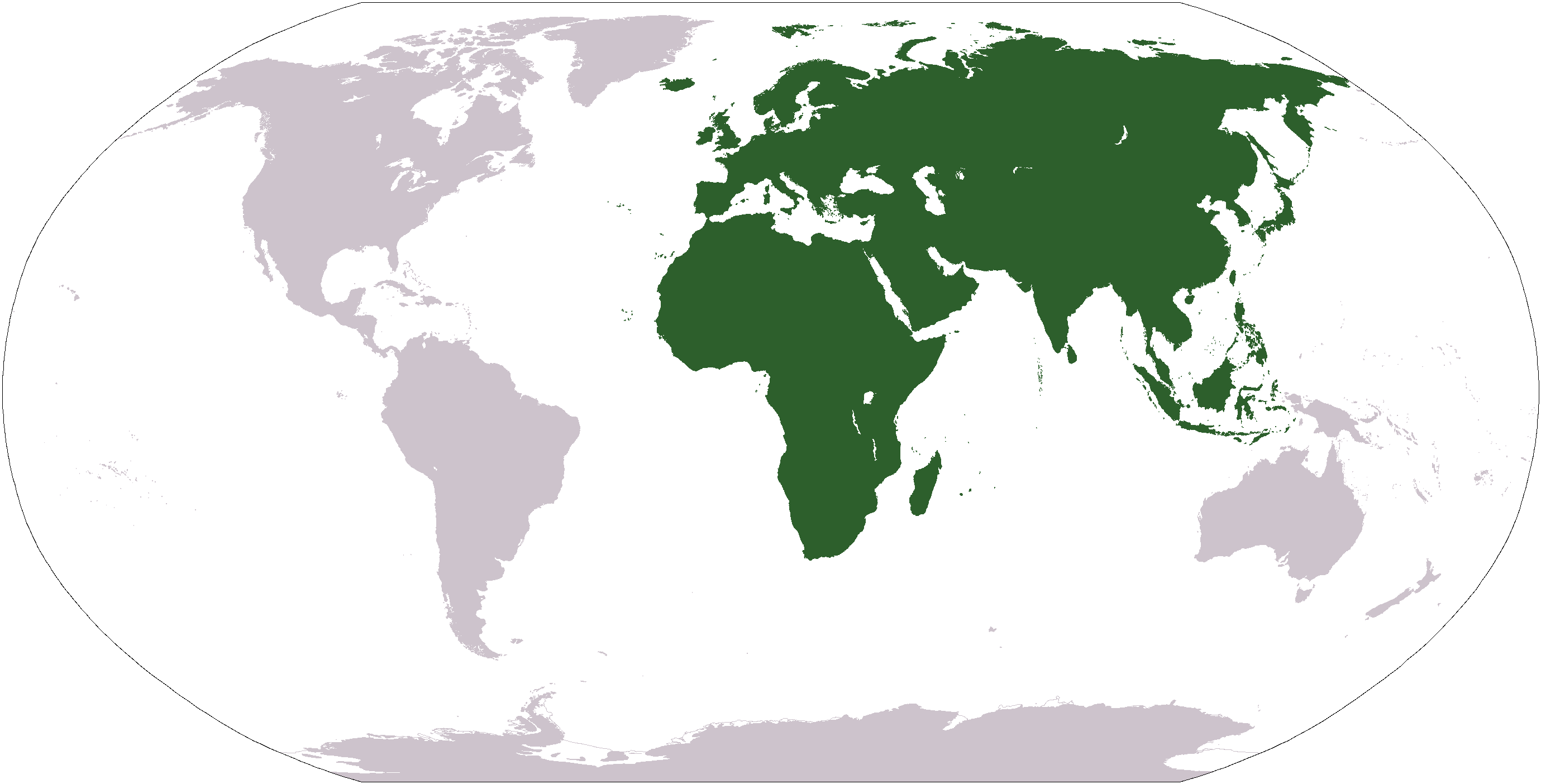
Bustards
Bustards, including floricans and korhaans, are large, terrestrial birds living mainly in dry grassland areas and on the steppes of the Old World. They range in length from . They make up the family Otididae (, formerly known as Otidae). Bustards are omnivorous and opportunistic, eating leaves, buds, seeds, fruit, small vertebrates, and invertebrates.del Hoyo, J. Elliott, A. & Sargatal, J. (editors). (1996) ''Handbook of the Birds of the World. Volume 3: Hoatzin to Auks''. Lynx Edicions. There are 26 species currently recognised. Description Bustards are all fairly large with the two largest species, the kori bustard (''Ardeotis kori'') and the great bustard (''Otis tarda''), being frequently cited as the world's heaviest flying birds. In both the largest species, large males exceed a weight of , weigh around on average and can attain a total length of . The smallest species is the little brown bustard (''Eupodotis humilis''), which is around long and weighs around ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kori Bustard
The kori bustard (''Ardeotis kori'') is the largest flying bird native to Africa. It is a member of the bustard family, which all belong to the order Otidiformes and are restricted in distribution to the Old World. It is one of the four species (ranging from Africa to India to Australia) in the large-bodied genus '' Ardeotis''. In fact, the male kori bustard may be the heaviest living animal capable of flight. This species, like most bustards, is a ground-dwelling bird and an opportunistic omnivore. Male kori bustards, which can be more than twice as heavy as the female, attempt to breed with as many females as possible and then take no part in the raising of the young. The nest is a shallow hollow in the earth, often disguised by nearby obstructive objects such as trees. Taxonomy English naturalist William John Burchell described the kori bustard in 1822. The specific epithet ''kori'' is derived from the Tswana name for this bird – ''Kgori''. Two subspecies are currently re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Bustard
The great bustard (''Otis tarda'') is a bird in the bustard family, the only member of the genus ''Otis''. It breeds in open grasslands and farmland from northern Morocco, South and Central Europe, to temperate Central and East Asia. European populations are mainly resident, but Asian populations migrate farther south in winter. It has been listed as Vulnerable on the IUCN Red List since 1996. Portugal and Spain now have about 60% of the world's population. It became extinct in Great Britain when the last bird was shot in 1832. Recent attempts to reintroduce it into England have met with some success and there is a population of 40 birds on Salisbury Plain, a British Army training area. Here the lack of public access allows them the freedom needed as a large ground-nesting bird. Taxonomy and etymology The genus ''Otis'' was introduced in 1758 by the Swedish naturalist Carl Linnaeus in the tenth edition of his ''Systema Naturae''. Linnaeus placed four species in the genus bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sypheotides
The lesser florican (''Sypheotides indicus''), also known as the likh or ''kharmore'', is the smallest in the bustard family and the only member of the genus ''Sypheotides''. It is endemic to the Indian Subcontinent where it is found in tall grasslands and is best known for the leaping breeding displays made by the males during the monsoon season. The male has a contrasting black and white breeding plumage and distinctive elongated head feathers that extend behind the neck. These bustards are found mainly in northwestern and central India during the summer but are found more widely distributed across India in winter. The species is highly endangered and has been extirpated in some parts of its range such as Pakistan. It is threatened both by hunting and habitat degradation. The only similar species is the Bengal florican (''Houbarobsis bengalensis'') which is larger and lacks the white throat, collar and elongated plumes. Description A male in breeding plumage has a black head, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bird
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the laying of hard-shelled eggs, a high metabolic rate, a four-chambered heart, and a strong yet lightweight skeleton. Birds live worldwide and range in size from the bee hummingbird to the ostrich. There are about ten thousand living species, more than half of which are passerine, or "perching" birds. Birds have whose development varies according to species; the only known groups without wings are the extinct moa and elephant birds. Wings, which are modified forelimbs, gave birds the ability to fly, although further evolution has led to the loss of flight in some birds, including ratites, penguins, and diverse endemic island species. The digestive and respiratory systems of birds are also uniquely adapted for flight. Some bird species of aquatic environments, particularly seabirds and some waterbirds, have further evolved for swimm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chlamydotis
'' Chlamydotis '' is a genus of large birds in the bustard family. The genus name is from Ancient Greek ''khlamus'', a horseman's cloak with weights sewn into the corners, and ''otis'', bustard. Members of this genus show very little sexual dimorphism in their plumage. The clade consists of two extant species, formerly considered to be conspecific forms a sister group within the clade that includes the genus ''Otis''. The genus was established by the French naturalist René Primevère Lesson in 1839 and included only one species which was formerly described in the genus ''Otis''. The genus name of ''Houbara'' was used by Charles Lucien Bonaparte but this was dropped, being a ''nomen nudum'', as not following the requirements for zoological names. MacQueen's was split on the basis of distinctive display, differences in feather colours and on the basis of well established genetic differences. The two species are thought to have separated during a period of extreme aridity around ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ardeotis
''Ardeotis'' is a genus of birds in the family Otididae. The genus was described in 1853 by the French naturalist Emmanuel Le Maout to accommodate the Arabian bustard The Arabian bustard (''Ardeotis arabs'') is a species of bustard which is found across the Sahel region of Africa and south western Arabia. It is part of the large-bodied genus, ''Ardeotis'', and, though little known, appears to be a fairly typi .... It contains the following species: References Bird genera Taxonomy articles created by Polbot {{bird-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old World
The "Old World" is a term for Afro-Eurasia that originated in Europe , after Europeans became aware of the existence of the Americas. It is used to contrast the continents of Africa, Europe, and Asia, which were previously thought of by their inhabitants as comprising the entire world, with the "New World", a term for the newly encountered lands of the Western Hemisphere, particularly the Americas. Etymology In the context of archaeology and world history, the term "Old World" includes those parts of the world which were in (indirect) cultural contact from the Bronze Age onwards, resulting in the parallel development of the early civilizations, mostly in the temperate zone between roughly the 45th and 25th parallels north, in the area of the Mediterranean, including North Africa. It also included Mesopotamia, the Persian plateau, the Indian subcontinent, China, and parts of Sub-Saharan Africa. These regions were connected via the Silk Road trade route, and they hav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Family (biology)
Family ( la, familia, plural ') is one of the eight major hierarchical taxonomic ranks in Linnaean taxonomy. It is classified between order and genus. A family may be divided into subfamilies, which are intermediate ranks between the ranks of family and genus. The official family names are Latin in origin; however, popular names are often used: for example, walnut trees and hickory trees belong to the family Juglandaceae, but that family is commonly referred to as the "walnut family". What belongs to a family—or if a described family should be recognized at all—are proposed and determined by practicing taxonomists. There are no hard rules for describing or recognizing a family, but in plants, they can be characterized on the basis of both vegetative and reproductive features of plant species. Taxonomists often take different positions about descriptions, and there may be no broad consensus across the scientific community for some time. The publishing of new data and opi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Omnivorous
An omnivore () is an animal that has the ability to eat and survive on both plant and animal matter. Obtaining energy and nutrients from plant and animal matter, omnivores digest carbohydrates, protein, fat, and fiber, and metabolize the nutrients and energy of the sources absorbed. Often, they have the ability to incorporate food sources such as algae, fungi, and bacteria into their diet. Omnivores come from diverse backgrounds that often independently evolved sophisticated consumption capabilities. For instance, dogs evolved from primarily carnivorous organisms ( Carnivora) while pigs evolved from primarily herbivorous organisms ( Artiodactyla). Despite this, physical characteristics such as tooth morphology may be reliable indicators of diet in mammals, with such morphological adaptation having been observed in bears. The variety of different animals that are classified as omnivores can be placed into further sub-categories depending on their feeding behaviors. Frugivor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vertebrate
Vertebrates () comprise all animal taxon, taxa within the subphylum Vertebrata () (chordates with vertebral column, backbones), including all mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and fish. Vertebrates represent the overwhelming majority of the phylum Chordata, with currently about 69,963 species described. Vertebrates comprise such groups as the following: * Agnatha, jawless fish, which include hagfish and lampreys * Gnathostomata, jawed vertebrates, which include: ** Chondrichthyes, cartilaginous fish (sharks, Batoidea, rays, and Chimaeriformes, ratfish) ** Euteleostomi, bony vertebrates, which include: *** Actinopterygii, ray-fins (the majority of living Osteichthyes, bony fish) *** lobe-fins, which include: **** coelacanths and lungfish **** tetrapods (limbed vertebrates) Extant taxon, Extant vertebrates range in size from the frog species ''Paedophryne amauensis'', at as little as , to the blue whale, at up to . Vertebrates make up less than five percent of all described a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miocene
The Miocene ( ) is the first geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and means "less recent" because it has 18% fewer modern marine invertebrates than the Pliocene has. The Miocene is preceded by the Oligocene and is followed by the Pliocene. As Earth went from the Oligocene through the Miocene and into the Pliocene, the climate slowly cooled towards a series of ice ages. The Miocene boundaries are not marked by a single distinct global event but consist rather of regionally defined boundaries between the warmer Oligocene and the cooler Pliocene Epoch. During the Early Miocene, the Arabian Peninsula collided with Eurasia, severing the connection between the Mediterranean and Indian Ocean, and allowing a faunal interchange to occur between Eurasia and Africa, including the dispersal of proboscideans into Eurasia. During the la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)