|
Business Analyst (BA)
A business analyst (BA) is a person who processes, interprets and documents business processes, products, services and software through analysis of data. The role of a business analyst is to ensure business efficiency increases through their knowledge of both IT and business function. Some tasks of a business analyst include creating detailed business analysis, budgeting and forecasting, business strategising, planning and monitoring, variance analysis, pricing, reporting and defining business requirements for stakeholders. The business analyst role is applicable to four key areas/levels of business functions – operational, project, enterprise and competitive focuses. Each of these areas of business analysis have a significant impact on business performance, and assist in enhancing profitability and efficiency in all stages of the business process, and across all business functions. Role Business analysis has been defined as "a disciplined approach for introducing chang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Financial Analysis
Financial analysis (also known as financial statement analysis, accounting analysis, or analysis of finance) refers to an assessment of the viability, stability, and profitability of a business, sub-business, project or investment. It is performed by professionals who prepare reports using ratios and other techniques, that make use of information taken from financial statements and other reports. These reports are usually presented to top management as one of their bases in making business decisions. Financial analysis may determine if a business will: *Continue or discontinue its main operation or part of its business; *Make or purchase certain materials in the manufacture of its product; *Acquire or rent/lease certain machineries and equipment in the production of its goods; *Issue shares or negotiate for a bank loan to increase its working capital; *Make decisions regarding investing or lending capital; *Make other decisions that allow management to make an informed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cost Reduction
Cost reduction is the process used by organisations aiming to reduce their costs and increase their profits, or to accommodate reduced income. Depending on a company’s services or products, the strategies can vary. Every decision in the product development process affects cost: design is typically considered to account for 70–80% of the final cost of a project such as an engineering project or the construction of a building. In the public sector, cost reduction programs can be used where income is reduced or to reduce debt levels. Importance Companies typically launch a new product without focusing too much on cost. Cost becomes more important when competition increases and PRICE becomes a differentiator in the market. The importance of cost reduction in relation to other strategic business goals is often debated. Examples of cost reduction strategies and programmes Commercial businesses Consultants Deloitte reported in 2006 that over three-quarters of the FTSE 100 listed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Business Value
In management, business value is an informal term that includes all forms of Value (economics), value that determine the health and well-being of the firm in the long run. Business value expands concept of value of the firm beyond economic value (also known as economic profit, economic value added, and shareholder value) to include other forms of value such as employee value, customer value, supplier value, channel partner value, alliance partner value, managerial value, and societal value. Many of these forms of value are not directly measured in monetary terms. According to the Project Management Institute, business value is the "net quantifiable benefit derived from a business endeavor that may be tangible, intangible, or both." Business value often embraces intangible assets not necessarily attributable to any Stakeholder (corporate), stakeholder group. Examples include intellectual capital and a firm's business model. The balanced scorecard methodology is one of the most popula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
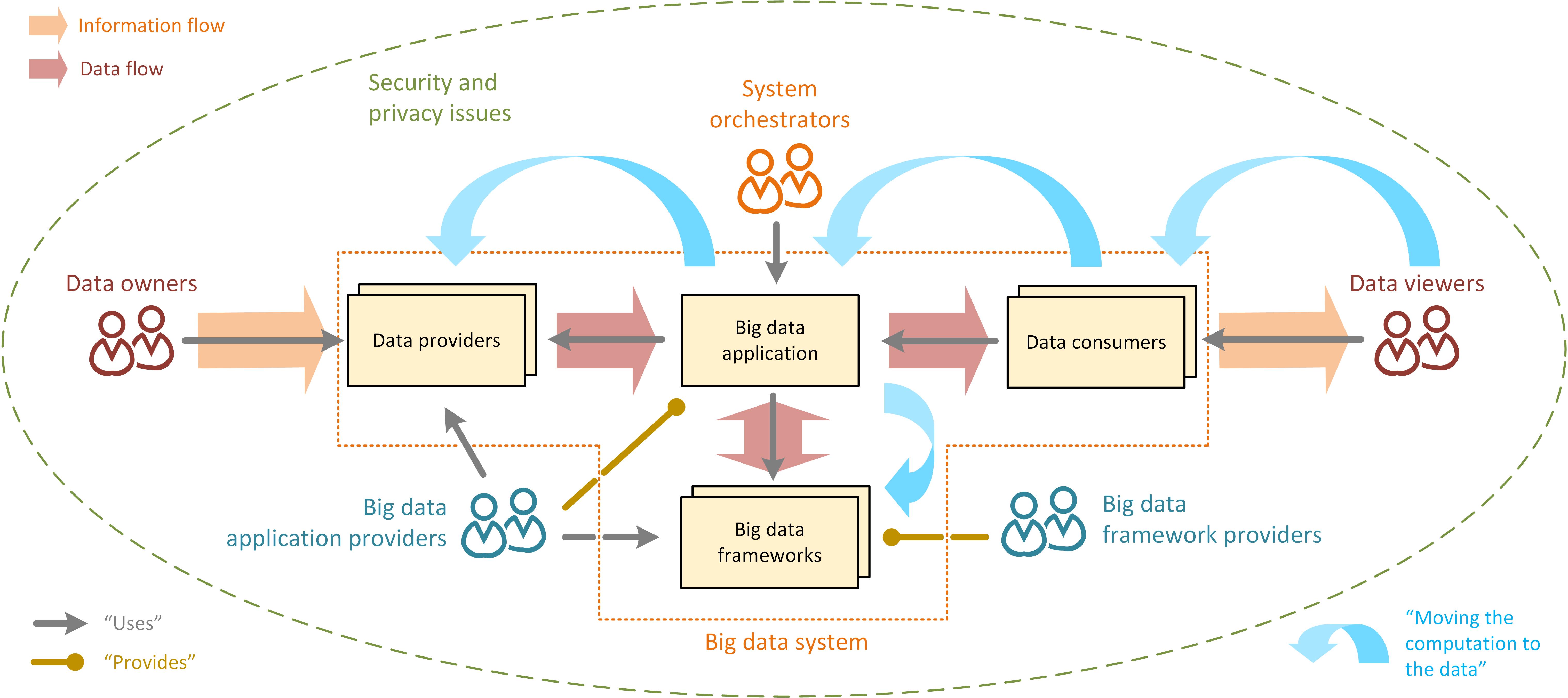
Big Data
Big data primarily refers to data sets that are too large or complex to be dealt with by traditional data processing, data-processing application software, software. Data with many entries (rows) offer greater statistical power, while data with higher complexity (more attributes or columns) may lead to a higher false discovery rate. Big data analysis challenges include Automatic identification and data capture, capturing data, Computer data storage, data storage, data analysis, search, Data sharing, sharing, Data transmission, transfer, Data visualization, visualization, Query language, querying, updating, information privacy, and data source. Big data was originally associated with three key concepts: ''volume'', ''variety'', and ''velocity''. The analysis of big data presents challenges in sampling, and thus previously allowing for only observations and sampling. Thus a fourth concept, ''veracity,'' refers to the quality or insightfulness of the data. Without sufficient investm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Technology
Technology is the application of Conceptual model, conceptual knowledge to achieve practical goals, especially in a reproducible way. The word ''technology'' can also mean the products resulting from such efforts, including both tangible tools such as Kitchen utensil, utensils or machines, and intangible ones such as software. Technology plays a critical role in science, engineering, and everyday life. Technological advancements have led to significant changes in society. The earliest known technology is the stone tool, used during prehistory, followed by the control of fire—which in turn contributed to the Brain size, growth of the human brain and the development of language during the Pleistocene, Ice Age, according to the cooking hypothesis. The invention of the wheel in the Bronze Age allowed greater travel and the creation of more complex machines. More recent technological inventions, including the printing press, telephone, and the Internet, have lowered barriers to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
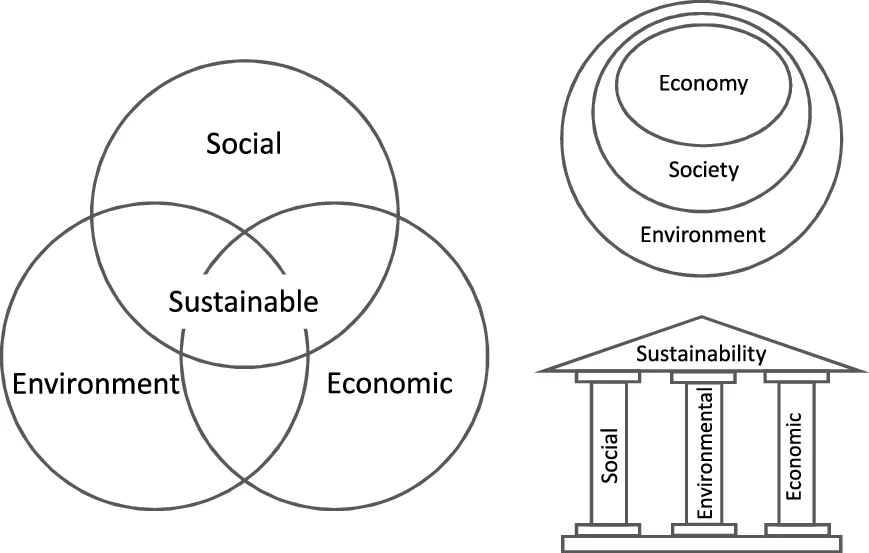
Sustainability
Sustainability is a social goal for people to co-exist on Earth over a long period of time. Definitions of this term are disputed and have varied with literature, context, and time. Sustainability usually has three dimensions (or pillars): environmental, economic, and social. Many definitions emphasize the environmental dimension. This can include addressing key environmental problems, including climate change and biodiversity loss. The idea of sustainability can guide decisions at the global, national, organizational, and individual levels. A related concept is that of sustainable development, and the terms are often used to mean the same thing. UNESCO distinguishes the two like this: "''Sustainability'' is often thought of as a long-term goal (i.e. a more sustainable world), while ''sustainable development'' refers to the many processes and pathways to achieve it." Details around the economic dimension of sustainability are controversial. Scholars have discussed this under ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strategy
Strategy (from Greek στρατηγία ''stratēgia'', "troop leadership; office of general, command, generalship") is a general plan to achieve one or more long-term or overall goals under conditions of uncertainty. In the sense of the " art of the general", which included several subsets of skills including military tactics, siegecraft, logistics etc., the term came into use in the 6th century C.E. in Eastern Roman terminology, and was translated into Western vernacular languages only in the 18th century. From then until the 20th century, the word "strategy" came to denote "a comprehensive way to try to pursue political ends, including the threat or actual use of force, in a dialectic of wills" in a military conflict, in which both adversaries interact. Strategy is important because the resources available to achieve goals are usually limited. Strategy generally involves setting goals and priorities, determining actions to achieve the goals, and mobilizing resources t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tactic (method)
A tactic is a conceptual action or short series of actions with the aim of achieving a short-term goal. This action can be implemented as one or more specific tasks. The term is commonly used in business, by protest groups, in military, espionage, and law enforcement contexts, as well as in chess, sports or other Competition, competitive activities. Etymology The word originates from the Ancient Greek adjective (''taktikos''), meaning ''that which pertains to ordinance''. The related Ancient Greek noun is (''tagma''), meaning ''ordinance, command''. Both words root in the verb (''tasso''), meaning ''draw up in order, station, appoint'' Distinction from strategy A strategy is a set of guidelines used to achieve an overall objective, whereas tactics are the specific actions aimed at adhering to those guidelines. Military usage In military usage, a Military tactics, military tactic is used by a military unit of no larger than a Division (military), division to implement a spec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Behavior
Behavior (American English) or behaviour (British English) is the range of actions of Individual, individuals, organisms, systems or Artificial intelligence, artificial entities in some environment. These systems can include other systems or organisms as well as the inanimate physical environment. It is the computed response of the system or organism to various stimuli or inputs, whether internal or external, conscious or subconscious, overt or covert, and voluntary action, voluntary or Volition (psychology), involuntary. While some behavior is produced in response to an organism's environment (extrinsic motivation), behavior can also be the product of intrinsic motivation, also referred to as "agency" or "free will". Taking a behavior informatics perspective, a behavior consists of actor, operation, interactions, and their properties. This can be represented as a behavior Euclidean vector, vector. Models Biology Definition Behavior may be defined as "the internally coordin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Consumer Behaviour
Consumer behaviour is the study of individuals, groups, or organisations and all activities associated with the Purchasing, purchase, Utility, use and disposal of goods and services. It encompasses how the consumer's emotions, Attitude (psychology), attitudes, and Preference (economics), preferences affect Buyer decision process, buying behaviour, and how external cues—such as visual prompts, auditory signals, or tactile (haptic) feedback—can shape those responses. Consumer behaviour emerged in the 1940–1950s as a distinct sub-discipline of marketing, but has become an Interdisciplinarity, interdisciplinary social science that blends elements from psychology, sociology, Social Anthropology, social anthropology, anthropology, ethnography, ethnology, marketing, and economics (especially behavioural economics). The study of consumer behaviour formally investigates individual qualities such as demographics, personality lifestyles, and behavioural variables (like usage rate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cost Reduction
Cost reduction is the process used by organisations aiming to reduce their costs and increase their profits, or to accommodate reduced income. Depending on a company’s services or products, the strategies can vary. Every decision in the product development process affects cost: design is typically considered to account for 70–80% of the final cost of a project such as an engineering project or the construction of a building. In the public sector, cost reduction programs can be used where income is reduced or to reduce debt levels. Importance Companies typically launch a new product without focusing too much on cost. Cost becomes more important when competition increases and PRICE becomes a differentiator in the market. The importance of cost reduction in relation to other strategic business goals is often debated. Examples of cost reduction strategies and programmes Commercial businesses Consultants Deloitte reported in 2006 that over three-quarters of the FTSE 100 listed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |