|
Busemann Biplane
The Busemann biplane is a theoretical aircraft configuration invented by Adolf Busemann, which avoids the formation of N-type shock waves and thus does not create a sonic boom or the associated wave drag. However in its original form it does not generate lift either. A Busemann biplane concept, which provides adequate lift, and which can reduce the wave intensity and drag but not eliminate them, has been studied for a "boomless" supersonic transport. Origins Busemann's original biplane consists of two triangular cross-section plates a certain distance apart, with the flat sides parallel to the fluid flow. The spacing between the plates is sufficiently large that the flow does not choke and supersonic flow is maintained between them. Supersonic flow around a conventional wing generates compressive sonic shock waves at the leading and trailing edges, with an expansion wave in between them. These shock waves correspond to pressure changes which impede airflow, known as wave drag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aircraft
An aircraft ( aircraft) is a vehicle that is able to flight, fly by gaining support from the Atmosphere of Earth, air. It counters the force of gravity by using either Buoyancy, static lift or the Lift (force), dynamic lift of an airfoil, or, in a few cases, direct Powered lift, downward thrust from its engines. Common examples of aircraft include airplanes, rotorcraft (including helicopters), airships (including blimps), Glider (aircraft), gliders, Powered paragliding, paramotors, and hot air balloons. Part 1 (Definitions and Abbreviations) of Subchapter A of Chapter I of Title 14 of the U. S. Code of Federal Regulations states that aircraft "means a device that is used or intended to be used for flight in the air." The human activity that surrounds aircraft is called ''aviation''. The science of aviation, including designing and building aircraft, is called ''aeronautics.'' Aircrew, Crewed aircraft are flown by an onboard Aircraft pilot, pilot, whereas unmanned aerial vehicles ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adolf Busemann
Adolf Busemann (20 April 1901 – 3 November 1986) was a German aerospace engineer and influential Nazi-era pioneer in aerodynamics, specialising in supersonic airflows. He introduced the concept of swept wings and, after emigrating in 1947 to the United States under Operation Paperclip, invented the shockwave-free supersonic Busemann biplane. Education and early life Born in Lübeck, Germany, Busemann attended the Technical University of Braunschweig, receiving his Ph.D. in engineering in 1924. Career and research The next year he was given the position of aeronautical research scientist at the Max-Planck Institute where he joined the famed team led by Ludwig Prandtl, including Theodore von Kármán, Max Munk and Jakob Ackeret. In 1930 he was promoted to professor at University of Göttingen. He held various positions within the German scientific community during this period, and during the war he was the director of the Braunschweig Laboratory, a famous research establishm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sonic Boom
A sonic boom is a sound associated with shock waves created when an object travels through the air faster than the speed of sound. Sonic booms generate enormous amounts of sound energy, sounding similar to an explosion or a thunderclap to the human ear. The crack of a supersonic bullet passing overhead or the crack of a bullwhip are examples of a small sonic boom. Sonic booms due to large supersonic aircraft can be particularly loud and startling, tend to awaken people, and may cause minor damage to some structures. This led to the prohibition of routine supersonic flight overland. Although sonic booms cannot be completely prevented, research suggests that with careful shaping of the vehicle, the nuisance due to sonic booms may be reduced to the point that overland supersonic flight may become a feasible option. A sonic boom does not occur only at the moment an object crosses the sound barrier and neither is it heard in all directions emanating from the supersonic objec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shock Wave
In physics, a shock wave (also spelled shockwave), or shock, is a type of propagating disturbance that moves faster than the local speed of sound in the medium. Like an ordinary wave, a shock wave carries energy and can propagate through a medium, but is characterized by an abrupt, nearly discontinuous, change in pressure, temperature, and density of the medium. For the purpose of comparison, in supersonic speed, supersonic flows, additional increased expansion may be achieved through an expansion fan, also known as a Prandtl–Meyer expansion fan. The accompanying expansion wave may approach and eventually collide and recombine with the shock wave, creating a process of destructive interference. The sonic boom associated with the passage of a supersonic aircraft is a type of sound wave produced by Wave interference, constructive interference. Unlike solitons (another kind of nonlinear wave), the energy and speed of a shock wave alone dissipates relatively quickly with distan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sonic Boom
A sonic boom is a sound associated with shock waves created when an object travels through the air faster than the speed of sound. Sonic booms generate enormous amounts of sound energy, sounding similar to an explosion or a thunderclap to the human ear. The crack of a supersonic bullet passing overhead or the crack of a bullwhip are examples of a small sonic boom. Sonic booms due to large supersonic aircraft can be particularly loud and startling, tend to awaken people, and may cause minor damage to some structures. This led to the prohibition of routine supersonic flight overland. Although sonic booms cannot be completely prevented, research suggests that with careful shaping of the vehicle, the nuisance due to sonic booms may be reduced to the point that overland supersonic flight may become a feasible option. A sonic boom does not occur only at the moment an object crosses the sound barrier and neither is it heard in all directions emanating from the supersonic objec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wave Drag
In aeronautics, wave drag is a component of the aerodynamic drag In fluid dynamics, drag, sometimes referred to as fluid resistance, is a force acting opposite to the direction of motion of any object moving with respect to a surrounding fluid. This can exist between two fluid layers, two solid surfaces, or b ... on aircraft wings and fuselage, propeller blade tips and Shell (projectile), projectiles moving at transonic and supersonic speeds, due to the presence of shock waves. Wave drag is independent of viscous effects,Clancy, L.J. (1975), ''Aerodynamics'', Section 11.7 and tends to present itself as a sudden and dramatic increase in drag as the vehicle increases speed to the critical Mach number. It is the sudden and dramatic rise of wave drag that leads to the concept of a sound barrier. Overview Wave drag is a component of pressure drag due to compressibility effects. It is caused by the formation of shock waves around a body. Shock waves create a considerable amount ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lift (force)
When a fluid flows around an object, the fluid exerts a force on the object. Lift is the Euclidean_vector#Decomposition_or_resolution, component of this force that is perpendicular to the oncoming flow direction. It contrasts with the drag (physics), drag force, which is the component of the force parallel to the flow direction. Lift conventionally acts in an upward direction in order to counter the force of gravity, but it is defined to act perpendicular to the flow and therefore can act in any direction. If the surrounding fluid is air, the force is called an aerodynamic force. In water or any other liquid, it is called a Fluid dynamics, hydrodynamic force. Dynamic lift is distinguished from other kinds of lift in fluids. Aerostatics, Aerostatic lift or buoyancy, in which an internal fluid is lighter than the surrounding fluid, does not require movement and is used by balloons, blimps, dirigibles, boats, and submarines. Planing (boat), Planing lift, in which only the lower po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Choked Flow
Choked flow is a compressible flow effect. The parameter that becomes "choked" or "limited" is the fluid velocity. Choked flow is a Fluid dynamics, fluid dynamic condition associated with the Venturi effect. When a flowing fluid at a given pressure and temperature passes through a constriction (such as the throat of a convergent-divergent nozzle or a valve in a pipe (material), pipe) into a lower pressure environment the fluid velocity increases. At initially subsonic upstream conditions, the conservation of energy principle requires the fluid velocity to increase as it flows through the smaller cross-sectional area of the constriction. At the same time, the Venturi effect causes the static pressure, and therefore the density, to decrease at the constriction. Choked flow is a limiting condition where the mass flow cannot increase with a further decrease in the downstream pressure environment for a fixed upstream pressure and temperature. For homogeneous fluids, the physical point ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
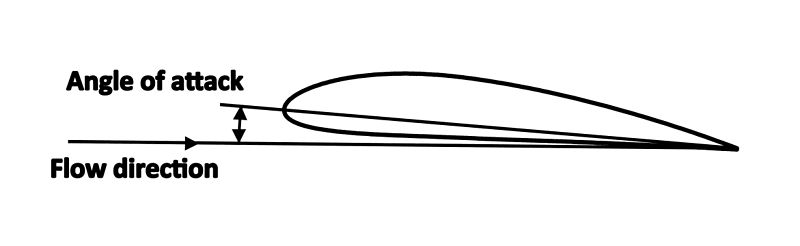
Angle Of Attack
In fluid dynamics, angle of attack (AOA, α, or \alpha) is the angle between a Airfoil#Airfoil terminology, reference line on a body (often the chord (aircraft), chord line of an airfoil) and the vector (geometry), vector representing the relative motion between the body and the fluid through which it is moving. Angle of attack is the angle between the body's reference line and the oncoming flow. This article focuses on the most common application, the angle of attack of a wing or airfoil moving through air. In aerodynamics, angle of attack specifies the angle between the chord line of the wing of a fixed-wing aircraft and the vector representing the relative motion between the aircraft and the atmosphere. Since a wing can have twist, a chord line of the whole wing may not be definable, so an alternate reference line is simply defined. Often, the chord line of the Wing root, root of the wing is chosen as the reference line. Another choice is to use a horizontal line on the fuse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Newton's Laws Of Motion
Newton's laws of motion are three physical laws that describe the relationship between the motion of an object and the forces acting on it. These laws, which provide the basis for Newtonian mechanics, can be paraphrased as follows: # A body remains at rest, or in motion at a constant speed in a straight line, unless it is acted upon by a force. # At any instant of time, the net force on a body is equal to the body's acceleration multiplied by its mass or, equivalently, the rate at which the body's momentum is changing with time. # If two bodies exert forces on each other, these forces have the same magnitude but opposite directions. The three laws of motion were first stated by Isaac Newton in his ''Philosophiæ Naturalis Principia Mathematica'' (''Mathematical Principles of Natural Philosophy''), originally published in 1687. Newton used them to investigate and explain the motion of many physical objects and systems. In the time since Newton, new insights, especially around t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pratt & Whitney J58
The Pratt & Whitney J58 (company designation JT11D-20) is an American jet engine that powered the Lockheed A-12, and subsequently the Lockheed YF-12, YF-12 and the Lockheed SR-71 Blackbird, SR-71 aircraft. It was an afterburning turbojet engine with a unique compressor bleed to the afterburner that gave increased thrust at high speeds. Because of the wide speed range of the aircraft, the engine needed two modes of operation to take it from stationary on the ground to at altitude. It was a conventional afterburning turbojet for take-off and acceleration to Mach 2 and then used bleed air, permanent compressor bleed to the afterburner above Mach 2. The way the engine worked at cruise led it to be described as "acting like a turboramjet". It has also been described as a turboramjet based on incorrect statements describing the turbomachinery as being completely bypassed. The engine performance that met the mission requirements for the CIA and USAF over many years was later enhanced ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |