|
Burns Night
A Burns supper is a celebration of the life and poetry of the poet Robert Burns (25 January 175921 July 1796), the author of many Scots poems. The suppers are usually held on or near the poet's birthday, 25 January, known as Burns Night (; ) also called Robert Burns Day or Rabbie Burns Day (or Robbie Burns Day in Canada). Sometimes, celebrations are also held at other times of the year. Burns suppers are held all around the world. History The first supper was held ''in memoriam'' at Burns Cottage in Ayrshire by Burns's friends, on 21 July 1801, the fifth anniversary of his death. The first still extant Burns Club was founded in Greenock in 1801 by merchants who were born in Ayrshire, some of whom had known Burns. They held the first Burns supper on what they thought was his birthday, 29 January 1802, but in 1803, they discovered the Ayr parish records that noted his date of birth was actually 25 January 1759. Since then, suppers have been held on or about 25 January. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
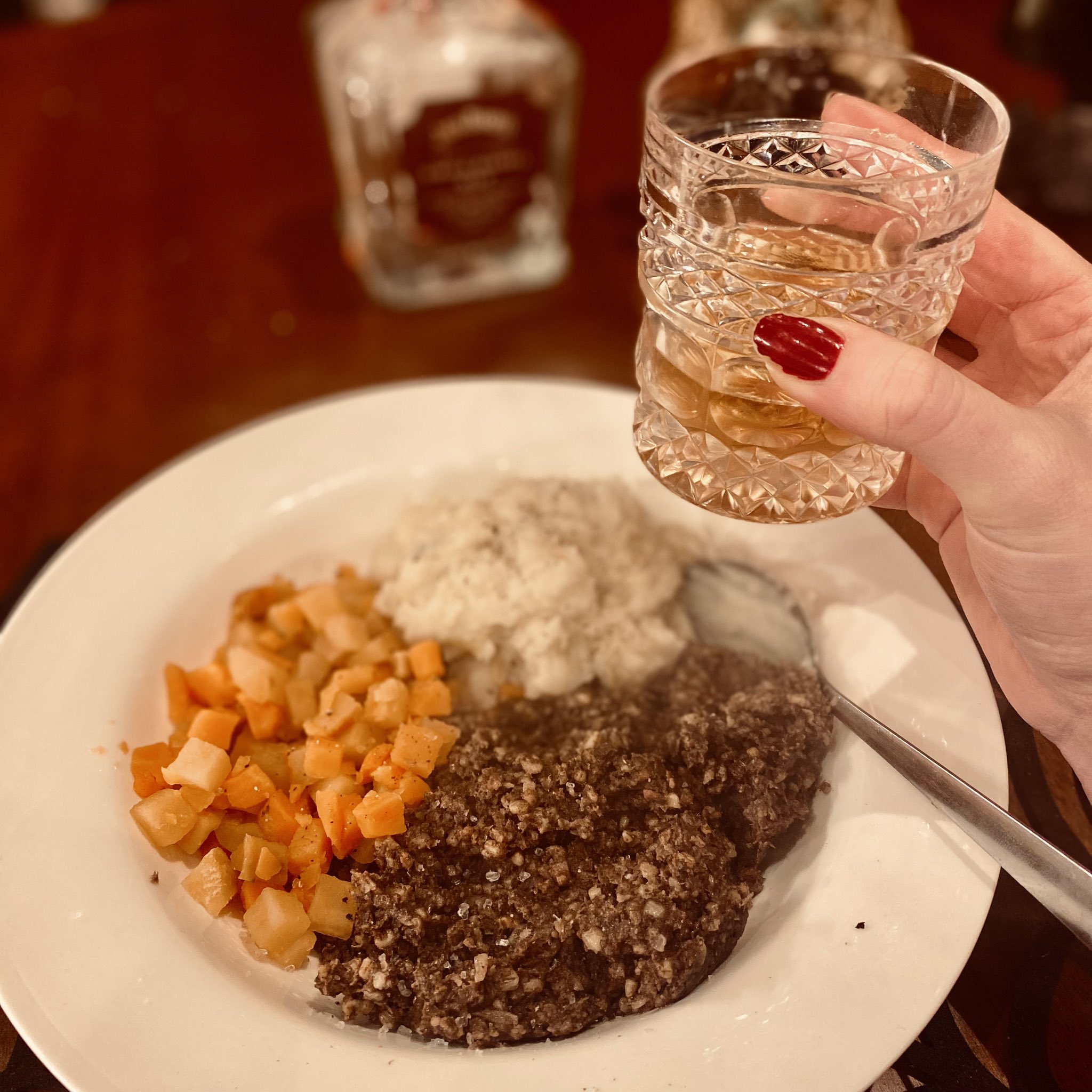
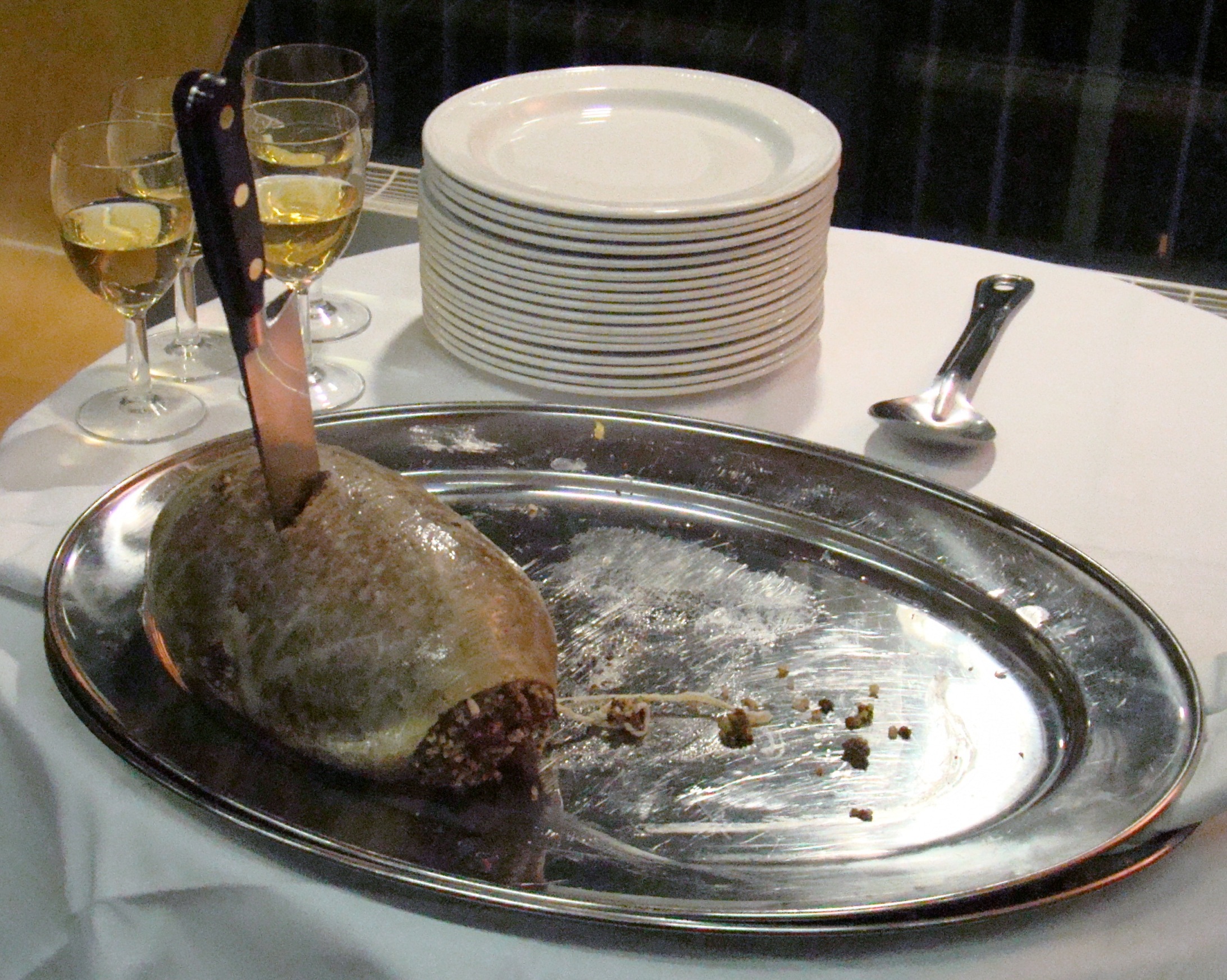
Haggis
Haggis ( ) is a savoury pudding containing sheep's offal, pluck (heart, liver, and lungs), Mincing, minced with chopped onion, oatmeal, suet, spices, and salt, mixed with Stock (food), stock, and cooked while traditionally encased in the animal's stomach though now an artificial sausage casing, casing is often used instead. According to the 2001 English edition of the ''Larousse Gastronomique'': "Although its description is not immediately appealing, haggis has an excellent nutty texture and delicious savoury flavour". It is believed that food similar to haggis — perishable offal quickly cooked inside an animal's stomach, all conveniently available after a hunt — was eaten from ancient times. Although the name "hagws" or "hagese" was first recorded in England c. 1430, the dish is considered traditionally of Scottish origin. It is even the national dish as a result of Scots poet Robert Burns' poem "Address to a Haggis" of 1786. Haggis is traditionally served with "rutabaga, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint Andrew's Society
Saint Andrew's Society refers to one of many independent organizations celebrating Scottish heritage which can be found all over the world. Some Saint Andrew's Societies limit membership to people born in Scotland or their descendants. Some still only accept male members. They are generally not-for-profit or charitable organizations. These societies organize social activities for their members as well as promoting the preservation of Scottish heritage. USA List USA (Alabama) St. Andrews Society of Mid South- Birmingham, Alabama, USA St. Andrews Society of S. E. Alabama- Enterprise, Alabama, USA St. Andrews Society of Montgomery- Montgomery, Alabama, USASt. Andrew’s Society of the Middle South- Middle South, Alabama, USA St. Andrews Society of Tuscaloosa- Tuscaloosa, Alabama, USA USA (California) Saint Andrew's Society of San Francisco- San Francisco, California, USA St. Andrew's Society of Los Angeles- Beverly Hills, California, USA St. Andrew's Society of Southern Ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scotch Broth
Scotch broth is a soup originating in Scotland. The principal ingredients are usually barley, stewing or braising cuts of Lamb and mutton, lamb, mutton or beef, root vegetables (such as carrots, Rutabaga, swedes, or sometimes turnips), and dried pulse (legume), pulses (most often split peas and red lentils). Cabbage and leeks are often added shortly before serving to preserve their texture, colour and flavours. The proportions and ingredients vary according to the recipe or availability. Scotch broth has been sold ready-prepared in tins for many years. History In the early 19th-century cookery book ''A New System of Domestic Cookery'' by Maria Rundell, "Scotch Mutton Broth" is made with mutton neck, skimmed and simmered around an hour before good-quality cuts of bone-in mutton are trimmed of their fat and added to the soup. After several hours, soup vegetables are added—turnips, carrots and onion—and simmered until just tender; finally, pre-soaked Scotch barley is added. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cullen Skink
Cullen skink is a thick Scottish soup made of smoked haddock, potatoes, and onions. An authentic Cullen skink will use finnan haddie, but it may be prepared with any other undyed smoked haddock. Sometimes ocean perch or salmon are used in the soup. This soup is a local speciality from the town of Cullen in Moray on the northeast coast of Scotland. It is often served as a starter at formal Scottish dinners but is also widely served as an everyday dish across the northeast of Scotland. Local recipes for Cullen skink have several slight variations, such as the use of milk instead of water or the addition of single cream. Other variations include mashing the potatoes to make the soup thicker. Cullen skink is traditionally served with bread or oatcakes crumbled through it for added texture. It has been described as "smokier and more assertive than American chowder, heartier than classical French bisque". Cullen skink appears in many traditional Scottish cookery books and rest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dunbar Douglas, 4th Earl Of Selkirk
Dunbar () is a town on the North Sea coast in East Lothian in the south-east of Scotland, approximately east of Edinburgh and from the English border north of Berwick-upon-Tweed. Dunbar is a former royal burgh, and gave its name to an ecclesiastical and civil parish. The parish extends around east to west and is deep at its greatest extent, or , and contains the villages of West Barns, Belhaven, and East Barns (abandoned) and several hamlets and farms. Dunbar has a harbour dating from 1574 and is home to the Dunbar Lifeboat Station, the second-oldest RNLI station in Scotland. The Dunbar Primary School and Dunbar Grammar School opened in the 1950s and 1960s. Dunbar is the birthplace of the explorer, naturalist, and influential conservationist John Muir. The house in which Muir was born is located on the High Street, and has been converted into a museum. There is also a commemorative statue beside the town clock, and John Muir Country Park is located to the north-west o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Covenanters
Covenanters were members of a 17th-century Scottish religious and political movement, who supported a Presbyterian Church of Scotland and the primacy of its leaders in religious affairs. It originated in disputes with James VI and his son Charles I over church organisation and doctrine, but expanded into political conflict over the limits of royal authority. In 1638, thousands of Scots signed the National Covenant, pledging to resist changes in religious practice imposed by Charles. This led to the 1639 and 1640 Bishops' Wars, which ended with the Covenanters in control of the Scottish government. In response to the Irish Rebellion of 1641, Covenanter troops were sent to Ireland, and the 1643 Solemn League and Covenant brought them into the First English Civil War on the side of Parliament. As the Wars of the Three Kingdoms progressed, many Covenanters came to view English religious Independents like Oliver Cromwell as a greater threat than the Royalists, particu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galloway
Galloway ( ; ; ) is a region in southwestern Scotland comprising the counties of Scotland, historic counties of Wigtownshire and Kirkcudbrightshire. It is administered as part of the council areas of Scotland, council area of Dumfries and Galloway. Galloway is bounded by sea to the west and south, the Galloway Hills to the north, and the River Nith to the east; the border between Kirkcudbrightshire and Wigtownshire is marked by the River Cree. The definition has, however, fluctuated greatly in size over history. A native or inhabitant of Galloway is called a Gallovidian. The region takes its name from the ''Gall-Gàidheil'', or "stranger Gaels", Norse–Gaels, a people of mixed Gaelic and Norse descent who seem to have settled here in the 10th century. Galloway remained a Gàidhealtachd area for much longer than other regions of the Scottish Lowlands and a Galwegian Gaelic, distinct local dialect of the Scottish Gaelic language survived into at least the 18th century. A hardy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Modern Scots
Modern Scots comprises the varieties of Scots traditionally spoken in Lowland Scotland and parts of Ulster, from 1700. Throughout its history, Modern Scots has been undergoing a process of language attrition, whereby successive generations of speakers have adopted more and more features from English, largely from the colloquial register. This process of language contact or dialectisation under English has accelerated rapidly since widespread access to mass media in English, and increased population mobility became available after the Second World War. It has recently taken on the nature of wholesale language shift towards Scottish English, sometimes also termed language Language change, change, Language convergence, convergence or merger. By the end of the twentieth century, Scots was at an advanced stage of language death over much of Lowland Scotland. Residual features of Scots are often simply regarded today as slang, especially by people from outwith Scotland, but even ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grace (prayer)
A grace is a short prayer or thankful phrase said before or after eating. The term most commonly refers to Christianity, Christian traditions. Some traditions hold that grace and thanksgiving imparts a blessing which sanctifies the meal. In English language, English, reciting such a prayer is sometimes referred to as "saying grace". The term comes from the Ecclesiastical Latin phrase ''gratiarum actio'', "act of thanks." Christian theology, Theologically, the act of saying grace is derived from the Bible, in which Jesus and Saint Paul pray before meals (cf. , ). The practice reflects the belief that humans should thank God who is believed to be the origin of everything. Christianity Pope Francis has suggested that "all believers ... return to [the] beautiful and meaningful custom" of stopping to "give thanks to God before and after meals". Typical Christian grace prayers Typical Christian mealtime grace prayers include: * Latin Catholic (before eating) – "Bless us, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
VisitScotland
VisitScotland, formerly the Scottish Tourist Board (), is a national tourism organisation for Scotland. It is an executive non-departmental public body of the Scottish Government, with offices in Edinburgh, Glasgow, Aberdeen, Inverness, and other parts of Scotland. Among the organisation's tasks is the attraction of visitors to Scotland through advertising Advertising is the practice and techniques employed to bring attention to a Product (business), product or Service (economics), service. Advertising aims to present a product or service in terms of utility, advantages, and qualities of int ... and promotional campaigns. VisitScotland also manages a number of quality grading schemes for tourist accommodation and attractions. The organisation also operates the VisitScotland.com website which provides bookings and information service for visitors to Scotland. From 2001 this website was operated as a public-private partnership venture, though this venture (and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scottish Music
Scotland is internationally known for its traditional music, often known as Scottish folk music, which remained vibrant throughout the 20th century and into the 21st when many traditional forms worldwide lost popularity to pop music. Traditional Scottish music comprises a variety of different styles such as ballads, reels, jigs, and airs. Traditional Scottish music is closely associated with the bagpipes which is credited as having a prominent role in traditional music originating from the country. The bagpipes are considered an "iconic Scottish instrument" with a history dating back to the 15th century. Other notable Scottish instruments include the tin whistle, the accordion and the fiddle. The origins of Scottish music are said to have originated over 2,300 years ago following the discovery of Western Europe's first known stringed instrument which was a "lyre-like artifact", which was discovered on the Isle of Skye. The earliest known traces of published Scottish music dates ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |