|
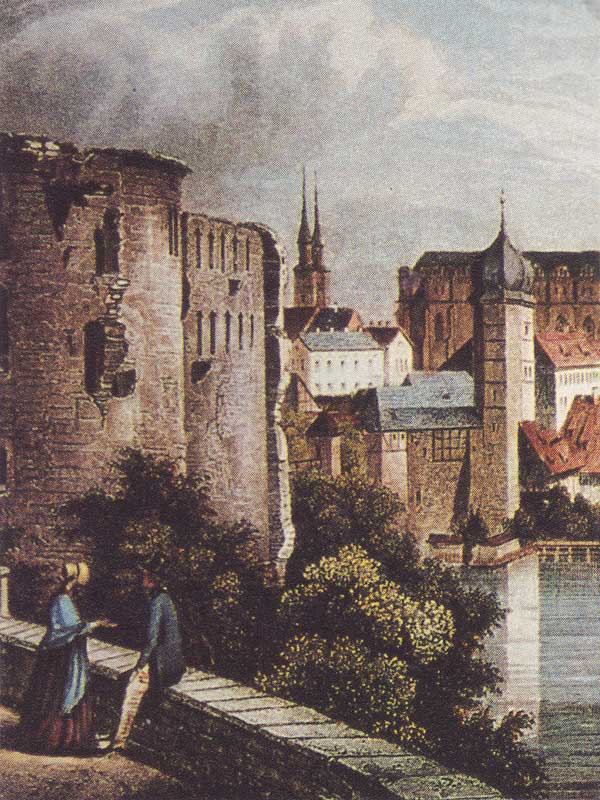
Burg Giebichenstein
Giebichenstein Castle () is a castle in Giebichenstein district of Halle (Saale) in Saxony-Anhalt, Germany. It is part of the Romanesque Road (''Strasse der Romanik''). Being a Burgward in the 9th century, the castle became a royal residence of Otto I, Holy Roman Emperor, who gave it to the Archbishopric of Magdeburg which he had established in 968. Giebichenstein Castle served as the place of death or lying in state for three bishops: Bishop Adalbert in 981, Bishop Tagino in 1012, and later that same year, Bishop Walthard. In addition, Giebichenstein was used by King (later Emperor) Henry II as a state prison for members of the high nobility. Among the imprisoned were such notable figures as Henry of Schweinfurt (in 1004), Ezzo of Este (1014–1018), Ernest of Swabia (1027–1029), and Godfrey the Bearded. According to legend, the Thuringian Landgrave Louis the Springer, founder of the Ludovingian dynasty, was also imprisoned at Giebichenstein, although there is no histori ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
20150902-BurgGiebichenstein
Fifteen or 15 may refer to: *15 (number) *one of the years 15 BC, AD 15, 1915, 2015 Music *Fifteen (band), a punk rock band Albums * ''15'' (Buckcherry album), 2005 * ''15'' (Ani Lorak album), 2007 * ''15'' (Phatfish album), 2008 * ''15'' (Tuki album), 2025 * ''15'' (mixtape), a 2018 mixtape by Bhad Bhabie * ''Fifteen'' (Green River Ordinance album), 2016 * ''Fifteen'' (The Wailin' Jennys album), 2017 * ''Fifteen'', a 2012 album by Colin James Songs * "Fifteen" (song), a 2008 song by Taylor Swift *"Fifteen", a song by Harry Belafonte from the album ''Love Is a Gentle Thing'' *"15", a song by Rilo Kiley from the album ''Under the Blacklight'' *"15", a song by Marilyn Manson from the album ''The High End of Low'' Other media * ''15'' (film), a 2003 Singaporean film * ''Fifteen'' (TV series), international release name of ''Hillside'', a Canadian-American teen drama * "Fifteen" (''Runaways''), an episode of ''Runaways'' *Fifteen (novel), a 1956 juvenile fiction ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry IV, Holy Roman Emperor
Henry IV (; 11 November 1050 – 7 August 1106) was Holy Roman Emperor from 1084 to 1105, King of Germany from 1054 to 1105, King of Italy and List of kings of Burgundy, Burgundy from 1056 to 1105, and Duke of Bavaria from 1052 to 1054. He was the son of Henry III, Holy Roman Emperor—the second monarch of the Salian dynasty—and Agnes of Poitou. After his father's death on 5 October 1056, Henry was placed under his mother's guardianship. She made grants to German aristocrats to secure their support. Unlike her late husband, she could not control the election of the popes, thus the idea of the Libertas ecclesiae, "liberty of the Church" strengthened during her rule. Taking advantage of her weakness, Archbishop Anno II of Cologne kidnapped Henry in April 1062. He administered Germany until Henry came of age in 1065. Henry endeavoured to recover the royal estates that had been lost during his minority. He employed low-ranking officials to carry out his new policies, causing disco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flanking Tower
A flanking tower is a fortified tower that is sited on the outside of a defensive wall or other fortified structure and thus forms a flank. From the defensive platform and embrasures the section of wall between them (the curtain wall) could be swept from the side by ranged weapons. In High and Late Medieval castles and town walls, flanking towers often had a semi-circular floor plan or a combination of a rectangular inner and semi-circular outer plans. There were also circular and rectangular towers. Corner flanking towers are found, for example, in the fortifications of the Alhambra and at the manor house of Hugenpoet Palace; Wellheim Castle has a square flanking tower. Semi-circular flanking towers were common in Sasanian architecture. In church architecture, a flanking tower is a semi-circular or polygonal (for example, octagonal) tower on the outer wall of the church. The church of Great St. Martin Church in Cologne Cologne ( ; ; ) is the largest city of the St ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schkopau
Schkopau () is a municipality in the Saalekreis district, in Saxony-Anhalt, Germany. Geography It is situated at the confluence of the Saale River with its White Elster and Luppe tributaries, approx. north of Merseburg, and south of Halle. Schkopau station is a stop on the Thuringian Railway line from Halle to Eisenach. Another connection is provided by an interurban tramway line from Halle to Bad Dürrenberg. Beside the resident chemical industry, the municipality is the site of the Schkopau Power Station, a brown coal power plant run by the E.ON electric utility. The municipal area comprises the localities of Burgliebenau, Döllnitz, Ermlitz, Hohenweiden, Knapendorf, Korbetha, Lochau, Luppenau, Raßnitz, Röglitz, Schkopau, and Wallendorf. History A ''Scapowe'' Castle was first mentioned in an 1177 deed. Already in the ninth century, a Carolingian fortress had been erected on the Saale River, then the eastern border of East Francia with the lands of the Polabian Slavs. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bad Lauchstädt
Bad Lauchstädt (; until 1925 ''Lauchstädt''), officially the Goethe Town of Bad Lauchstädt (), is a town in the district Saalekreis, Saxony-Anhalt, Germany, 13 km southwest of Halle. Population 8,781 (2020). Lauchstädt was a popular watering-place in the 18th century, the dukes of Saxe-Merseburg often making it their summer residence. From 1789 to 1811 the Weimar court theatrical company gave performances here of the plays of Friedrich Schiller and Johann Wolfgang von Goethe, an attraction which greatly contributed to the well-being of the town. Further reading noted there: * Maak, ''Das Goethetheater in Lauchstädt'' (Lauchstädt, 1905); * Nasemann, ''Bad Lauchstädt'' (Halle, 1885). During the 19th century, its industries included malting, vinegar-making and brewing. In January 2008, Bad Lauchstädt incorporated the former municipalities Schafstädt, Delitz am Berge and Klobikau. On 1 January 2010 Milzau was also incorporated, [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moritzburg (Halle)
The Moritzburg is a fortified castle in Halle (Saale), Germany. The cornerstone of what would later become the residence of the Archbishops of Magdeburg was laid in 1484; the castle was built in the style of the Early Renaissance. Since the end of the 19th century, it has housed an arts museum which is recognised as being of national importance. History Origins The history of the Moritzburg is closely connected to that of Halle. In 968, when the Archbishopric of Magdeburg was established by Otto I, Holy Roman Emperor, he granted the archbishop his Giebichenstein Castle near Halle. Already in the 13th century, powerful aristocrats could buy privileges, reduce the influence of the sovereign, the Archbishop of Magdeburg, on the town. Thus, Halle had practically reached a state of political autonomy in 1263. The same happened with Magdeburg and when the archbishops finally left Magdeburg, after a series of conflicts with the ever more powerful city council, Giebichenstein Cas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magdeburg
Magdeburg (; ) is the Capital city, capital of the Germany, German States of Germany, state Saxony-Anhalt. The city is on the Elbe river. Otto I, Holy Roman Emperor, Otto I, the first Holy Roman Emperor and founder of the Archbishopric of Magdeburg, was buried in the city's Magdeburg Cathedral, cathedral after his death. Magdeburg's version of German town law, known as Magdeburg rights, spread throughout Central Europe, Central and Eastern Europe. In the Late Middle Ages, Magdeburg was one of the largest and most prosperous German cities and a notable member of the Hanseatic League. One of the most notable people from the city was Otto von Guericke, famous for his experiments with the Magdeburg hemispheres. Magdeburg has experienced three major devastations in its history. In 1207 the first catastrophe struck the city, with a fire burning down large parts of the city, including the Magdeburg Cathedral#Previous building, Ottonian cathedral. The Catholic League (German), Catholi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autonomy
In developmental psychology and moral, political, and bioethical philosophy, autonomy is the capacity to make an informed, uncoerced decision. Autonomous organizations or institutions are independent or self-governing. Autonomy can also be defined from a human resources perspective, where it denotes a (relatively high) level of discretion granted to an employee in his or her work. In such cases, autonomy is known to generally increase job satisfaction. Self-actualized individuals are thought to operate autonomously of external expectations. In a medical context, respect for a patient's personal autonomy is considered one of many fundamental ethical principles in medicine. Sociology In the sociology of knowledge, a controversy over the boundaries of autonomy inhibited analysis of any concept beyond relative autonomy, until a typology of autonomy was created and developed within science and technology studies. According to it, the institution of science's existing autonom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albert I Of Käfernburg
Albert I of Käfernburg (; – 15 October 1232) was Archbishop of Magdeburg from 1205 until his death. He was the son of Count Gunther II of Käfernburg (d. about 1197), a member of the Thuringian nobility and relative of the comital House of Schwarzburg, who held large estates in the area around Arnstadt. His mother was Gunther's first wife Agnes, a daughter of Count Simon I of Saarbrücken. Albert began his studies at the cathedral school in Hildesheim, completing them later at Paris and Bologna. At an early age he was made a prebendary of Magdeburg Cathedral, and in 1200 was appointed Provost of the collegiate church of St Mary in Mainz by Pope Innocent III. Albert played a prominent part in the great struggle for the Imperial crown, which marked the close of the twelfth and the beginning of the thirteenth centuries. Even before his consecration, he had inclined to the side of the Hohenstaufen candidate Philip of Swabia, who sought the crown in spite of his minor nephew ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
House Of Welf
The House of Welf (also Guelf or Guelph) is a European dynasty that has included many German and British monarchs from the 11th to 20th century and Emperor Ivan VI of Russia in the 18th century. The originally Franconian family from the Meuse-Moselle area was closely related to the imperial family of the Carolingians. Origins The (Younger) House of Welf is the older branch of the House of Este, a dynasty whose earliest known members lived in Veneto and Lombardy in the late 9th/early 10th century, sometimes called Welf-Este. The first member was Welf I, Duke of Bavaria, also known as Welf IV. He inherited the property of the Elder House of Welf when his maternal uncle Welf, Duke of Carinthia, Welf III, Duke of Carinthia and Verona, the last male Welf of the Elder House, died in 1055. Welf IV was the son of Welf III's sister Kunigunde of Altdorf and her husband Albert Azzo II, Margrave of Milan. In 1070, Welf IV became Duke of Bavaria. Welf II, Duke of Bavaria married Countess Ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Otto IV, Holy Roman Emperor
Otto IV (1175 – 19 May 1218) was the Holy Roman Emperor from 1209 until his death in 1218. Otto spent most of his early life in England and France. He was a follower of his uncle Richard the Lionheart, who made him Count of Poitou in 1196. With Richard's support, he was elected King of Germany by one faction in a disputed election in 1198, sparking German throne dispute, ten years of civil war. The death of his rival, Philip of Swabia, in 1208 left him sole king of Germany. In 1209, Otto Italienzug, marched to Italy to be crowned emperor by Pope Innocent III. In 1210, he sought to unite the Kingdom of Sicily with the Empire, breaking with Innocent, who excommunicated him. He allied with England against France and participated in the alliance's Battle of Bouvines, defeat at Bouvines in 1214. He was abandoned by most of his supporters in 1215 and lived the rest of his life in retirement on his estates near Braunschweig, Brunswick. He was the only German king of the House of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frederick II, Holy Roman Emperor
Frederick II (, , , ; 26 December 1194 – 13 December 1250) was King of Sicily from 1198, King of Germany from 1212, King of Italy and Holy Roman Emperor from 1220 and King of Jerusalem from 1225. He was the son of Emperor Henry VI, Holy Roman Emperor, Henry VI of the Hohenstaufen dynasty (the second son of Emperor Frederick Barbarossa) and Queen Constance I of Sicily of the Hauteville dynasty. Frederick was one of the most powerful figures of the Middle Ages and ruled a vast area, beginning with Sicily and stretching through Italy all the way north to Germany. Viewing himself as a direct successor to the Roman emperors of antiquity, he was Holy Roman Emperor, Emperor of the Romans from his papal coronation in 1220 until his death; he was also a claimant to the title of King of the Romans from 1212 and unopposed holder of that monarchy from 1215. As such, he was King of Germany, King of Italy, of Italy, and King of Burgundy, of Burgundy. At the age of three, he was crowned King ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |