|
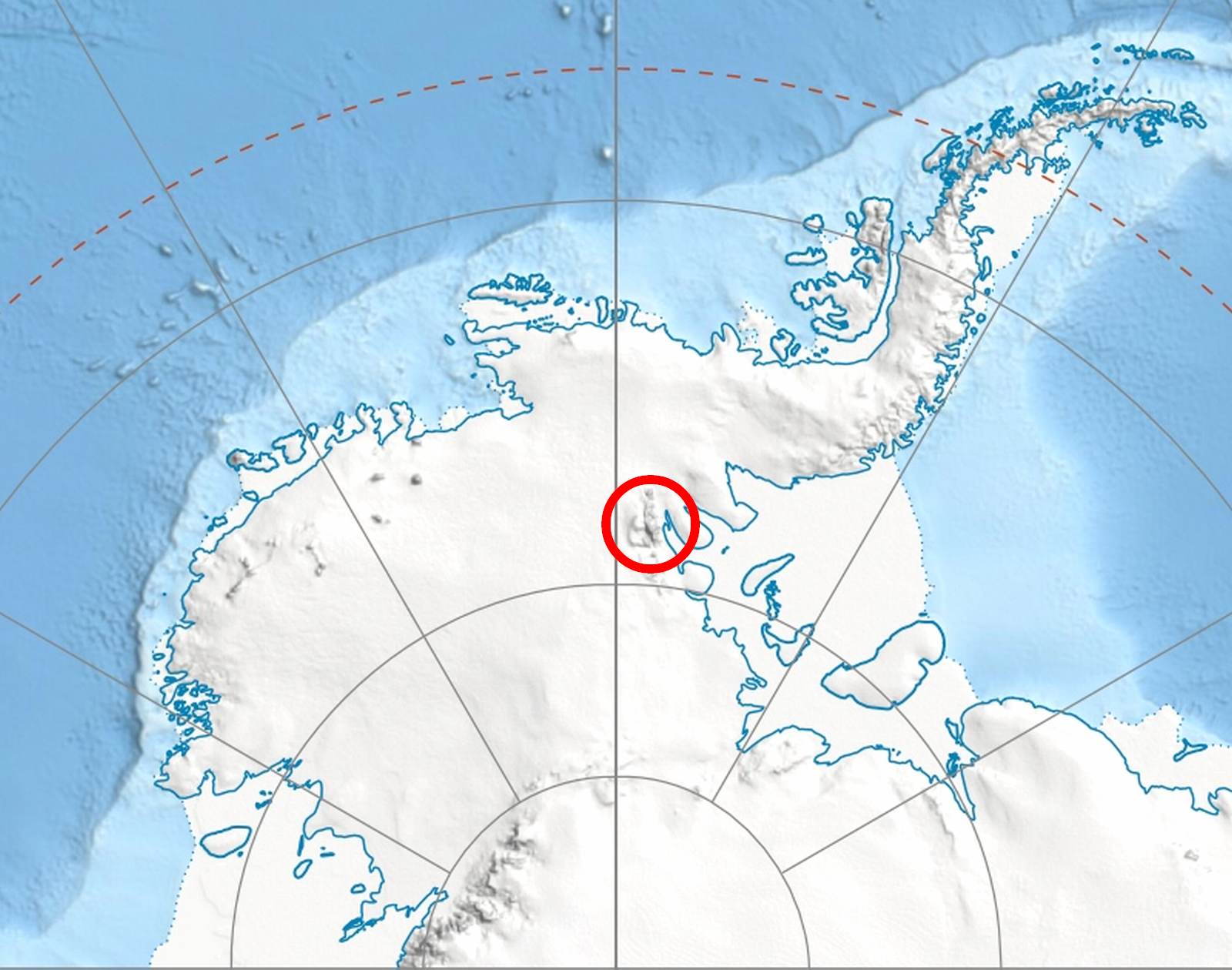
Burdenis Glacier
Burdenis Glacier ( bg, ледник Бурденис, lednik Burdenis, ) is the 6 km long and 1.7 km wide glacier on the east side of the main crest of north-central Sentinel Range in Ellsworth Mountains, Antarctica. It is situated north of Delyo Glacier and south of Gerila Glacier. The glacier drains the north slopes of Mount Viets and the southeast slopes of the southern summit of Long Gables Peak, flows northeastwards and together with Delyo Glacier and Gerila Glacier joins upper Ellen Glacier north of Bruguière Peak. The glacier is named after the ancient Roman settlement of Burdenis in Southern Bulgaria. Location Burdenis Glacier is centred at . US mapping in 1961 and 1988. See also * List of glaciers in the Antarctic * Glaciology Maps * Vinson Massif. Scale 1:250 000 topographic map. Reston, Virginia: US Geological Survey, 1988. Antarctic Digital Database (ADD).Scale 1:250000 topographic map of Antarctica. Scientific Committee on Antarctic Research ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean, it contains the geographic South Pole. Antarctica is the fifth-largest continent, being about 40% larger than Europe, and has an area of . Most of Antarctica is covered by the Antarctic ice sheet, with an average thickness of . Antarctica is, on average, the coldest, driest, and windiest of the continents, and it has the highest average elevation. It is mainly a polar desert, with annual precipitation of over along the coast and far less inland. About 70% of the world's freshwater reserves are frozen in Antarctica, which, if melted, would raise global sea levels by almost . Antarctica holds the record for the lowest measured temperature on Earth, . The coastal regions can reach temperatures over in summer. Native species of animals include mites, nematodes, penguins, seals and tardigrades. Where ve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bruguière Peak
Bruguière Peak ( bg, връх Брюгиер, vrah Bruguière, ) is the sharp rocky peak rising to Reference Elevation Model of Antarctica. Polar Geospatial Center. University of Minnesota, 2019 near the end of the side ridge that trends northeastwards from on the main crest of north-central in , |
Antarctic Place-names Commission
The Antarctic Place-names Commission was established by the Bulgarian Antarctic Institute in 1994, and since 2001 has been a body affiliated with the Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Bulgaria. The Commission approves Bulgarian place names in Antarctica, which are formally given by the President of the Republic according to the Bulgarian Constitution (Art. 98) and the established international practice. Bulgarian names in Antarctica Geographical names in Antarctica reflect the history and practice of Antarctic exploration. The nations involved in Antarctic research give new names to nameless geographical features for the purposes of orientation, logistics, and international scientific cooperation. As of 2021, there are some 20,091 named Antarctic geographical features, including 1,601 features with names given by Bulgaria.Bulgarian Antarctic Gaze ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Composite Gazetteer Of Antarctica
The Composite Gazetteer of Antarctica (CGA) of the Scientific Committee on Antarctic Research (SCAR) is the authoritative international gazetteer containing all Antarctic toponyms published in national gazetteers, plus basic information about those names and the relevant geographical features. The Gazetteer includes also parts of the International Hydrographic Organization (IHO) General Bathymetric Chart of the Oceans (GEBCO) gazetteer for under-sea features situated south of 60° south latitude. , the overall content of the CGA amounts to 37,893 geographic names for 19,803 features including some 500 features with two or more entirely different names, contributed by the following sources: {, class="wikitable sortable" ! Country ! Names , - , United States , 13,192 , - , United Kingdom , 5,040 , - , Russia , 4,808 , - , New Zealand , 2,597 , - , Australia , 2,551 , - , Argentina , 2,545 , - , Chile , 1,866 , - , Norway , 1,706 , - , Bulgaria , 1,450 , - ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scientific Committee On Antarctic Research
The Scientific Committee on Antarctic Research (SCAR) is an interdisciplinary body of the International Science Council (ISC). SCAR coordinates international scientific research efforts in Antarctica, including the Southern Ocean. SCAR's scientific work is administered through several discipline-themed ''science groups''. The organisation has observer status at, and provides independent advice to Antarctic Treaty Consultative Meetings, and also provides information to other international bodies such as the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) and the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC). History At the International Council of Scientific Unions (ICSU)’s Antarctic meeting held in Stockholm from 9–11 September 1957, it was agreed that a committee should be created to oversee scientific research in Antarctica. At the time there were 12 nations actively conducting Antarctic research and they were each invited to nominate one delegate to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glaciology
Glaciology (; ) is the scientific study of glaciers, or more generally ice and natural phenomena that involve ice. Glaciology is an interdisciplinary Earth science that integrates geophysics, geology, physical geography, geomorphology, climatology, meteorology, hydrology, biology, and ecology. The impact of glaciers on people includes the fields of human geography and anthropology. The discoveries of water ice on the Moon, Mars, Europa and Pluto add an extraterrestrial component to the field, which is referred to as "astroglaciology". Overview A glacier is an extended mass of ice formed from snow falling and accumulating over a long period of time; glaciers move very slowly, either descending from high mountains, as in valley glaciers, or moving outward from centers of accumulation, as in continental glaciers. Areas of study within glaciology include glacial history and the reconstruction of past glaciation. A glaciologist is a person who studies glaciers. A glaci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Glaciers In The Antarctic
There are many glaciers in the Antarctic. This set of lists does not include ice sheets, ice caps or ice fields, such as the Antarctic ice sheet, but includes glacial features that are defined by their flow, rather than general bodies of ice. The lists include outlet glaciers, valley glaciers, cirque glaciers, tidewater glaciers and ice streams. Ice streams are a type of glacier and many of them have "glacier" in their name, e.g. Pine Island Glacier. Ice shelves are listed separately in the List of Antarctic ice shelves. For the purposes of these lists, the Antarctic is defined as any latitude further south than 60° (the continental limit according to the Antarctic Treaty System). List by letters * List of glaciers in the Antarctic: A–H * List of glaciers in the Antarctic: I–Z See also * List of Antarctic and subantarctic islands * List of Antarctic ice rises * List of Antarctic ice shelves This is a list of Antarctic ice shelves. Ice shelves ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Rome
In modern historiography, ancient Rome refers to Roman civilisation from the founding of the city of Rome in the 8th century BC to the collapse of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD. It encompasses the Roman Kingdom (753–509 BC), Roman Republic (509–27 BC) and Roman Empire (27 BC–476 AD) until the fall of the western empire. Ancient Rome began as an Italic settlement, traditionally dated to 753 BC, beside the River Tiber in the Italian Peninsula. The settlement grew into the city and polity of Rome, and came to control its neighbours through a combination of treaties and military strength. It eventually dominated the Italian Peninsula, assimilated the Greek culture of southern Italy (Magna Grecia) and the Etruscan culture and acquired an Empire that took in much of Europe and the lands and peoples surrounding the Mediterranean Sea. It was among the largest empires in the ancient world, with an estimated 50 to 90 million inhabitants, roughly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ellen Glacier
The Ellen Glacier is a glacier in the central Sentinel Range of the Ellsworth Mountains of Antarctica. It drains the eastern slopes of Mount Anderson and Long Gables and flows generally southeast for to Barnes Ridge, where it leaves the range and enters the south flowing Rutford Ice Stream. It was first mapped by the United States Geological Survey from surveys and U.S. Navy air photos, 1957–59, and was named by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names for Lieutenant Colonel Cicero J. Ellen of the U.S. Air Force, who was in command of many of the air operations when the South Pole Station was established by air drop in the 1956–57 season. Tributary glaciers * Pulpudeva Glacier * Crosswell Glacier * Patton Glacier * Rumyana Glacier * Delyo Glacier * Burdenis Glacier * Gerila Glacier * Fonfon Glacier * Arapya Glacier See also * List of glaciers in the Antarctic * Glaciology Glaciology (; ) is the scientific study of glaciers, or more generally ice and natural ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ellsworth Land
Ellsworth Land is a portion of the Antarctic continent bounded on the west by Marie Byrd Land, on the north by Bellingshausen Sea, on the northeast by the base of Antarctic Peninsula, and on the east by the western margin of the Filchner–Ronne Ice Shelf. It extends between 103°24'W and 79°45'W. The area west of 90°W is unclaimed, the area between 84°W and 90°W is claimed by Chile only, and the remainder by Chile and the United Kingdom as a part of the British Antarctic Territory. Eights Coast stretches between 103°24'W and 89°35'W, and Bryan Coast between 89°35'W and 79°45'W. It is largely a high ice plateau, but includes the Ellsworth Mountains and a number of scattered mountain groups: Hudson, Jones, Behrendt, Hauberg, Merrick, Sweeney and Scaife Mountains. This land lies near the center of the area traversed by American explorer Lincoln Ellsworth on an airplane flight during November–December 1935. It was named for him by the Advisory Committee on Antarc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Long Gables
The Long Gables () are prominent twin peaks, with heights of , joined by a col, with the lower rock exposures being in the form of steep buttresses. The peaks rise from the main ridge of the Sentinel Range, Ellsworth Mountains, Antarctica between Mount Anderson and Mount Viets. They surmount Burdenis Glacier to the southeast, Gerila Glacier to the east and Fonfon Glacier to the northeast. The peaks were discovered by the Marie Byrd Land Traverse party of 1957–58 under Charles R. Bentley, and were named for Jack B. Long. Jack Long was a member of the Marie Byrd Land Traverse party and a participant in many oversnow traverses and other Antarctic research activities in the following decade. The south summit of Long Gables (Peak 4111) was climbed for the first time on January 13, 1996, by the French alpinists Erik Decamp and Catherine Destivelle.Decamp, Erik"Misadventures Below Zero" in Christian Beckwith (ed.), ''The American Alpine Journal'', The Mountaineers Books, 1997, pp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Viets
Mount Viets () is a sharp pyramidal mountain over 3,600 m, standing north of Mount Giovinetto in the main ridge of the Sentinel Range, Ellsworth Mountains. It surmounts Delyo Glacier to the east and Burdenis Glacier to the northeast. The mountain was discovered by the Marie Byrd Land Traverse party of 1957–58 under Charles R. Bentley. It was named for Ronald L. Viets, a geophysicist at Little America V Station in 1957. It was climbed for the first time on January 11, 1996, by the French alpinists Erik Decamp and Catherine Destivelle Catherine Destivelle (born 24 July 1960) is a French rock climber and mountaineer who is considered one of the greatest and most important female climbers in the history of the sport. She came to prominence in the mid-1980s for sport climbing by ....Decamp, Erik"Misadventures Below Zero" in Christian Beckwith (ed.), ''The American Alpine Journal'', The Mountaineers Books, 1997, pp. 98–107. Maps Vinson Massif. Scale 1:250 000 topographic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |