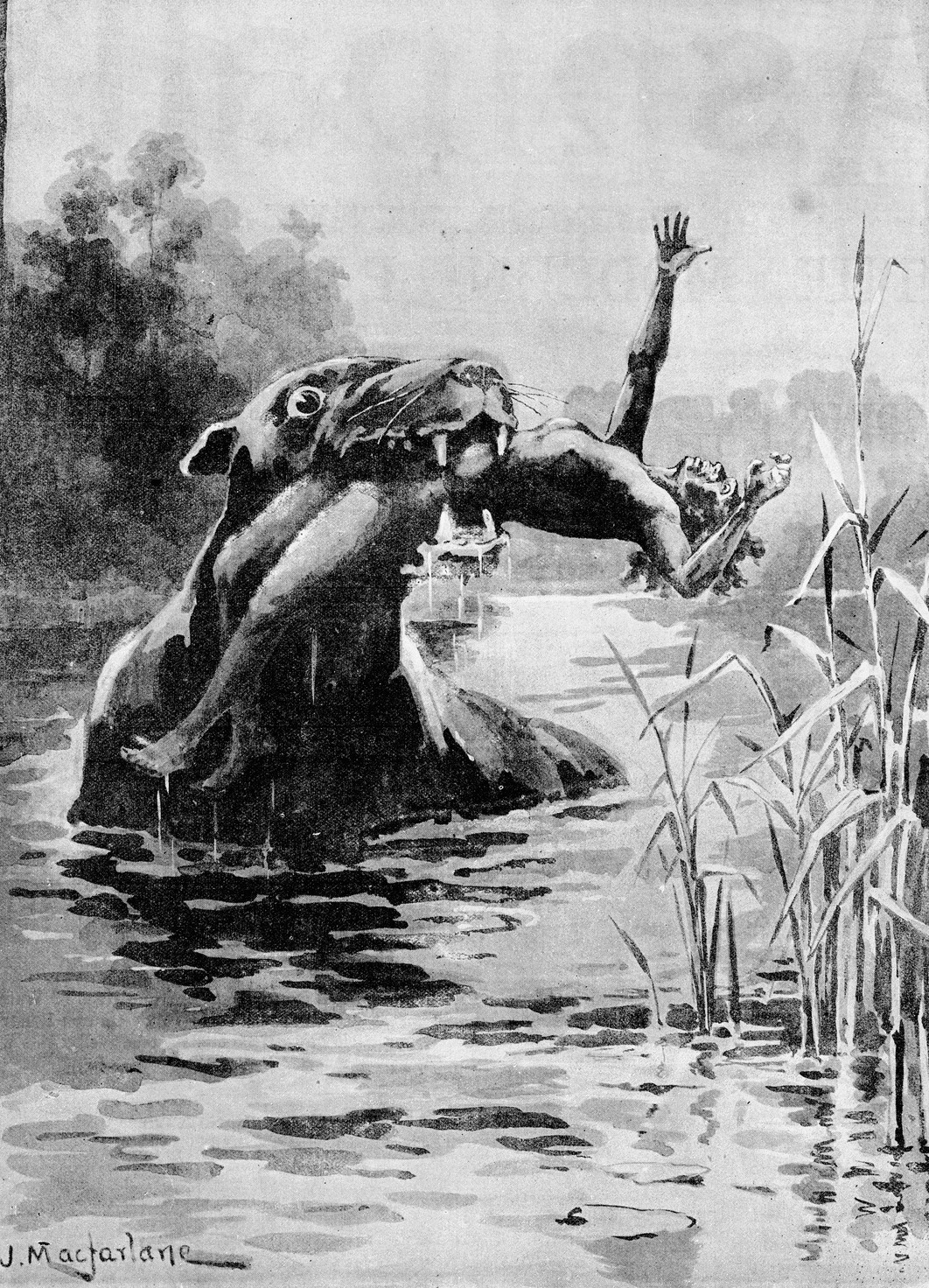|
Bunyip
The bunyip is a creature from the aboriginal mythology of southeastern Australia, said to lurk in swamps, billabongs, creeks, riverbeds, and waterholes. Name The origin of the word ''bunyip'' has been traced to the Wemba-Wemba or Wergaia language of the Aboriginal people of Victoria, in South-Eastern Australia. The word ''bunyip'' is usually translated by Aboriginal Australians today as "devil" or "evil spirit". This contemporary translation may not accurately represent the role of the bunyip in pre-contact Aboriginal mythology or its possible origins before written accounts were made. Some modern sources allude to a linguistic connection between the bunyip and Bunjil, "a mythic 'Great Man' who made the mountains, rivers, man, and all the animals". The word ''bahnyip'' first appeared in the ''Sydney Gazette'' in 1812. It was used by James Ives to describe "a large black animal like a seal, with a terrible voice which creates terror among the blacks". Distribution The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australian Aboriginal Mythology
Australian Aboriginal religion and mythology is the sacred spirituality represented in the stories performed by Aboriginal Australians within each of the language groups across Australia in their ceremonies. Aboriginal spirituality includes the Dreamtime (''the Dreaming''), songlines, and Aboriginal oral literature. Aboriginal spirituality often conveys descriptions of each group's local cultural landscape, adding meaning to the whole country's topography from oral history told by ancestors from some of the earliest recorded history. Most of these spiritualities belong to specific groups, but some span the whole continent in one form or another. Antiquity An Australian linguist, R. M. W. Dixon, recording Aboriginal myths in their original languages, encountered coincidences between some of the landscape details being told about within various myths, and scientific discoveries being made about the same landscapes. In the case of the Atherton Tableland, myths tell of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aboriginal Mythology
Australian Aboriginal religion and mythology is the sacred spirituality represented in the stories performed by Aboriginal Australians within each of the Aboriginal Australian languages, language groups across Australia in their Aboriginal ceremonies, ceremonies. Aboriginal spirituality includes The Dreaming, the Dreamtime (''the Dreaming''), songlines, and Aboriginal oral literature. Aboriginal spirituality often conveys descriptions of each group's local cultural landscape, adding meaning to the whole country's topography from oral tradition, oral history told by ancestors from some of the earliest recorded history. Most of these spiritualities belong to specific groups, but some span the whole continent in one form or another. Antiquity An Australian Linguistics, linguist, R. M. W. Dixon, recording Aboriginal myths in their original languages, encountered coincidences between some of the landscape details being told about within various myths, and Hard science, scientific ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nocturnal
Nocturnality is a ethology, behavior in some non-human animals characterized by being active during the night and sleeping during the day. The common adjective is "nocturnal", versus diurnality, diurnal meaning the opposite. Nocturnal creatures generally have highly developed senses of hearing (sense), hearing, olfaction, smell, and specially adapted eyesight. Some animals, such as ferrets, have eyes that can adapt to both low-level and bright day levels of illumination (see metaturnal). Others, such as bushbaby, bushbabies and (some) bats, can function only at night. Many nocturnal creatures including tarsier, tarsiers and some owl, owls have large eyes in comparison with their body size to compensate for the lower light levels at night. More specifically, they have been found to have a larger cornea relative to their eye size than diurnal creatures to increase their : in the low-light conditions. Nocturnality helps wasps, such as ''Apoica flavissima'', avoid hunting in intens ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ararat, Victoria
Ararat () is a town in the Central Highlands (Victoria), Central Highlands region in Victoria (Australia), Victoria, Australia, about west of Melbourne, on the Western Highway, Victoria, Western Highway on the eastern slopes of the Ararat Hills and Cemetery Creek valley between Victoria's Western District (Victoria), Western District and the Wimmera. The source of the Hopkins River is a few kilometres to the east below Telegraph Hill. Its urban population according to 2021 census is 8,500 and services the region of 11,880 residents across the Rural City's boundaries. It is also the home of the 2018/19 GMGA Golf Championship Final. It is the largest Human settlement, settlement in the Rural City of Ararat local government area and is the administrative centre. The discovery of gold in 1857 during the Victorian gold rush transformed it into a boomtown which continued to prosper until the turn of the 20th century, after which it has steadily declined in population. It was procl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Australasian
The ''Australasian Post'', commonly called the ''Aussie Post'', was Australia's longest-running weekly picture magazine. History and profile Its origins are traceable to Saturday, 3 January 1857, when the first issue of ''Bell's Life in Victoria and Sporting Chronicle'' (probably best known for Tom Wills's famous 1858 Australian rules football letter) was released. The weekly, which was produced by Charles Frederic Somerton in Melbourne, was one of several Bell's Life publications based on the format of '' Bell's Life in London'', a Sydney version having been published since 1845. On 1 October 1864, the weekly newspaper ''The Australasian'' was launched in Melbourne, Victoria by the proprietors of '' The Argus''. It supplanted three unprofitable ''Argus'' publications: ''The Weekly Argus'', ''The Examiner'', and ''The Yeoman'', and contained features of all three. A competitor, ''The Age'', gloated that as it was printed on coarse heavy paper, its weight exceeded the maximum f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australian Boobook
The Australian boobook (''Ninox boobook''), is a species of owl native to mainland Australia, southern New Guinea, the island of Timor, and the Sunda Islands. Described by John Latham (ornithologist), John Latham in 1801, it was generally considered to be the same species as the morepork of New Zealand until 1999. Its name is derived from its two-tone ''boo-book'' call. Eight subspecies of the Australian boobook are recognized, with three further subspecies being reclassified as separate species in 2019 due to their distinctive calls and genetics. The smallest owl on the Australian mainland, the Australian boobook is long, with predominantly dark-brown plumage with prominent pale spots. It has grey-green or yellow-green eyes. It is generally nocturnal, though sometimes it is active at dawn and dusk, retiring to roost in secluded spots in the foliage of trees. The Australian boobook feeds on insects and small vertebrates, hunting by pouncing on them from tree perches. Breeding ta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bulldog Breeds
Bulldogs are a Dog type, type of dog that were traditionally used for the blood sports of Baiting (blood sport), baiting and dog fighting, but today are kept for other purposes, including companion dogs, guard dogs and catch dogs. Bulldogs are typically stocky, powerful, square-built animals with large, strong, brachycephalic-type muzzles. "Bull" is a reference that originated in England that refers to the sport of bull-baiting, which was a national sport in England between the 13th and 18th century. It is believed that bulldogs were developed during the 16th century in the Elizabethan era from the larger mastiffs, as smaller, more compact dogs were better suited for baiting. List of bulldog breeds Extant breeds * Alano Español (Spanish Bulldog) * Alapaha Blue Blood Bulldog * American Bulldog * Bulldog * Campeiro Bulldog * Continental bulldog, Continental Bulldog * French Bulldog * Olde English Bulldogge * Ca de Bou, Perro de Presa Mallorquin * Serrano Bulldog Extinct breeds * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coat (animal)
Coat is the nature and quality of a mammal's fur. In the animal fancy, coat is an attribute that reflects the quality of a specimen's Selective breeding, breeding as well as the level of the animal's Animal husbandry, care, conditioning, and management. Coat is an integral aspect of the judging at competitions such as a Conformation show, conformation dog show, a cat show, a horse show (especially Horse showmanship, showmanship classes), or a American Rabbit Breeders Association#Rabbit shows, rabbit show. The pelage of a show animal may be divided into different types of hair, fur or wool with a texture ranging from downy to spiky. In addition, the animal may be single-coated or may have a number of coats, such as an Fur#Down hair, undercoat and a topcoat (also called an ''outer coat'' or, sometimes, ''overcoat''), which is made up of Fur#Guard hair, guard hair. The state of the coat is considered an indication of the animal's selective breeding, breeding and health. Animals mig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Murray River
The Murray River (in South Australia: River Murray; Ngarrindjeri language, Ngarrindjeri: ''Millewa'', Yorta Yorta language, Yorta Yorta: ''Dhungala'' or ''Tongala'') is a river in Southeastern Australia. It is List of rivers of Australia, Australia's longest river at extent. Its Tributary, tributaries include five of the next six longest rivers of Australia (the Murrumbidgee River, Murrumbidgee, Darling River, Darling, Lachlan River, Lachlan, Warrego River, Warrego and Paroo Rivers). Together with that of the Murray, the catchments of these rivers form the Murray–Darling basin, which covers about one-seventh the area of Australia. It is widely considered Australia's most important irrigated region. The Murray rises in the Australian Alps, draining the western side of Australia's highest mountains, then meanders northwest across Australia's inland plains, forming the border between the States and territories of Australia, states of New South Wales and Victoria (Australia), Vi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mane (horse)
On horses, the mane is the hair that grows from the top of the neck of a horse or other equine, reaching from the poll (horse), poll to the withers, and includes the forelock or foretop. It is thicker and coarser than the rest of the horse's coat, and naturally grows to roughly cover the neck. Heredity plays a role, giving some horses a longer, thicker mane, and others a shorter, thinner one. Some horses, such as those used in circuses or in mounted displays such as Cavalia, have manes allowed to grow down to their knees. Others have their manes deliberately shaved completely off for style or practical purposes. When ungroomed, however, the mane usually grows no longer than the width of the horse's neck, as natural wear and tear limit its potential length. The mane is thought to keep the neck warm, and possibly to help water run off the neck if the animal cannot obtain shelter from the rain. It also provides some fly protection to the front of the horse, although the tail is us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |