|
Bullingdon (hundred)
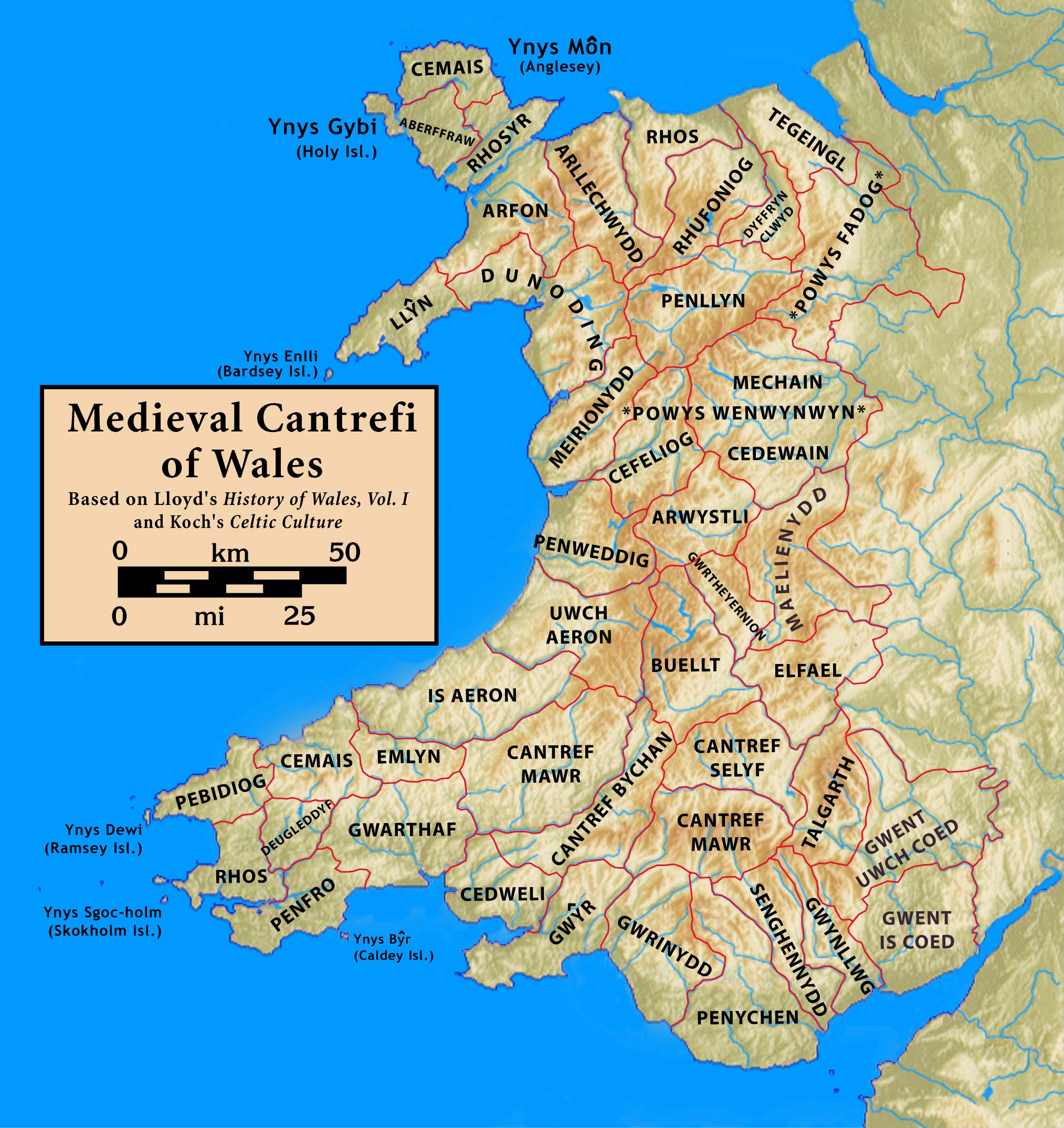
Bullingdon was a hundred in the county of Oxfordshire, covering an area to the east of Oxford. It took its name from the hamlet of Bullingdon Green, in the parish of Horspath (just north of the modern Horspath Sports Ground), where the hundred court originally met. The Domesday Book of 1096 describes the many parishes of Bullingdon hundred as being dependencies of the royal manor of Headington.Open Domesday: Headington Hundred. Accessed 25 November 2022. The hundred included: Cowley, Nuneham (Courtenay), Cuddesdon, Headington, Ambrosden, Stanton (St John), Merton, Elsfield, [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hundred (county Division)
A hundred is an administrative division that is geographically part of a larger region. It was formerly used in England, Wales, some parts of the United States, Denmark, Sweden, Finland, Norway, and in Cumberland County in the British Colony of New South Wales. It is still used in other places, including in Australia (in South Australia and the Northern Territory). Other terms for the hundred in English and other languages include '' wapentake'', ''herred'' (Danish and Bokmål Norwegian), ''herad'' ( Nynorsk Norwegian), ''härad'' or ''hundare'' (Swedish), ''Harde'' (German), ''hiird'' ( North Frisian), ''kihlakunta'' (Finnish), and '' cantref'' (Welsh). In Ireland, a similar subdivision of counties is referred to as a barony, and a hundred is a subdivision of a particularly large townland (most townlands are not divided into hundreds). Etymology The origin of the division of counties into hundreds is described by the ''Oxford English Dictionary'' (''OED'') as "exceedingly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richard I
Richard I (8 September 1157 – 6 April 1199), known as Richard the Lionheart or Richard Cœur de Lion () because of his reputation as a great military leader and warrior, was King of England from 1189 until his death in 1199. He also ruled as Duke of Normandy, Duke of Aquitaine, Aquitaine, and Duchy of Gascony, Gascony; Lord of Cyprus in the Middle Ages, Cyprus; Count of Poitiers, Counts and dukes of Anjou, Anjou, Count of Maine, Maine, and Count of Nantes, Nantes; and was overlord of Brittany at various times during the same period. He was the third of five sons of Henry II of England and Eleanor of Aquitaine and was therefore not expected to become king, but his two elder brothers predeceased their father. By the age of 16, Richard had taken command of his own army, putting down rebellions in Poitou against his father. Richard was an important Christian commander during the Third Crusade, leading the campaign after the departure of Philip II of France and achieving sev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Point-to-point (steeplechase)
A point-to-point is a form of horse racing over fences for fox hunting, hunting horses and amateur riders. In Ireland, where the sport is open to licensed professional trainers, many of the horses will appear in these races before they compete in National Hunt races. Consequently, the Irish point-to-point tends to be used as a nursery for future young stars: a horse that wins its debut point-to-point in Ireland will often sell for a high price. Whilst professional trainers are specifically excluded from running horses (other than their own personal horses) in point-to-points in Great Britain, the days of the farmer running his hunter at the local point-to-point are gone. (They have been replaced to some extent by hunter chases). Increasingly, horses are run from "livery yards" - unlicensed but otherwise professional training establishments, sometimes closely allied with a licensed yard. Horses running in point-to-points must be Thoroughbreds, save in the case of Hunt Members races ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bullingdon Club
The Bullingdon Club is a private all-male dining club for Oxford University students. It is known for its wealthy members, grand banquets, and bad behaviour, including vandalism of restaurants and students' rooms. The club selects its members not only on the grounds of wealth and willingness to participate but also by reference to their education. The Bullingdon was originally a sporting club, dedicated to cricket and horse-racing, although club dinners gradually became its principal activity. Membership is expensive, with tailor-made uniforms, regular gourmet hospitality, and a tradition of on-the-spot payment for damage. Some members have gone on to become leading figures within British society and the political establishment. Former members include two kings of England (Edward VII and Edward VIII), three prime ministers (David Cameron, Archibald Primrose, 5th Earl of Rosebery, and Boris Johnson), and two chancellors of the Exchequer ( George Osborne and Lord Randolph Church ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arncott
Arncott or Arncot is a village and Civil parishes in England, civil parish about southeast of Bicester in Oxfordshire. The United Kingdom Census 2011, 2011 Census recorded the parish's population as 1,738. There are two neighbourhoods: Lower and Upper Arncott. Upper Arncott is the larger neighbourhood and includes the village green, Park, recreation ground, shop and most of Arncott's housing. Lower Arncott is close to River Ray and includes the Tally Ho hotel and the Plough public house. Upper and Lower Arncott are separated by the Bicester Military Railway. Manors Arncott's Toponymy, toponym comes from the Old English ''Earnigcote'' meaning "Earn's Cottage" (10th century). Upper Arncott In 983 Æthelred the Unready granted the Manorialism, manor of Upper Arncott to the Order of Saint Benedict, Benedictine Abingdon Abbey. As a result it became known as ''Arncot Abbatis''. In 1538 the abbey was suppressed in the Dissolution of the Monasteries and surrendered Upper Arncott to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HM Prison Bullingdon
HM Prison and Young Offenders Institute Bullingdon is a prison in Oxfordshire, England. It is a public sector prison operated by HM Prison and Probation Service (an executive agency of the Ministry of Justice). Located near MoD Bicester, it is a local and resettlement prison accepting Security Category B male prisoners. (New admissions from courts are generally sent to 'local' prisons and are considered as a Category B prisoner until their initial security assessment.) Prisoners must be over the age of 18 (as a Young Offender (YO)). As YO prisoners are not subject to the same 4 level security category, they are either considered 'YOI Closed' or 'YOI Open' - depending on whether they are suitable for transfer to open conditions. The prison generally only holds prisoners on short sentences (under 12 months) and those on remand. With the additional resettlement function, prisoners in the local area of the prison should be transferred for their 12-week pre-release period. HMP & ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Oxfordshire
South Oxfordshire is a Non-metropolitan district, local government district in the Ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial county of Oxfordshire, England. Its council is temporarily based outside the district at Abingdon-on-Thames pending a planned move to Didcot, the district's largest town. The areas located south of the River Thames are within the Historic counties of England, historic county of Berkshire. History The district was formed on 1 April 1974, under the Local Government Act 1972, covering the area of six former districts, which were abolished at the same time: *Bullingdon Rural District *Henley-on-Thames Municipal Borough *Henley Rural District *Thame Urban district (Great Britain and Ireland), Urban District *Municipal Borough of Wallingford, Wallingford Municipal Borough *Wallingford Rural District The two Wallingford districts had previously been part of the administrative county of Berkshire, whilst the other four districts had been in the administrative coun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bullingdon Rural District
Bullingdon Rural District was a rural district in Oxfordshire, England from 1932 to 1974, covering an area to the south-east of the city of Oxford. The district was created on 1 April 1932 under a County Review Order, as a merger of Wheatley Urban District, Culham Rural District, Thame Rural District, part of Crowmarsh Rural District, part of Headington Rural District, and part of Henley Rural District. The district was named after the hundred of Bullingdon, which had covered part of the area. Bullingdon Rural District Council held its first meeting on 4 April 1932 at County Hall, Oxford, when George Parker, 7th Earl of Macclesfield, was appointed the council's first chairman. He had previously been the chairman of the Thame Rural District Council. For most of the district's existence its council was based in Oxford rather than in the district itself. In 1971 the council moved to offices on London Road in Wheatley. The district was abolished under the Local Governmen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry VI Of England
Henry VI (6 December 1421 – 21 May 1471) was King of England from 1422 to 1461 and 1470 to 1471, and English claims to the French throne, disputed King of France from 1422 to 1453. The only child of Henry V of England, Henry V, he succeeded to the Throne of England, English throne at the age of eight months, upon his father's death, and to the List of French monarchs, French throne on the death of his maternal grandfather, Charles VI of France, Charles VI, shortly afterwards. Henry was born during the Hundred Years' War (1337–1453), he is the only English monarch to have been crowned King of France, following his coronation at Notre-Dame de Paris in 1431 as Henry II. His early reign, when England was ruled by a Regency government, 1422–1437, regency government, saw the pinnacle of English power in Kingdom of France, France. However, setbacks followed once he assumed full control in 1437. The young king faced military reversals in France, as well as political and financia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black Death
The Black Death was a bubonic plague pandemic that occurred in Europe from 1346 to 1353. It was one of the list of epidemics, most fatal pandemics in human history; as many as people perished, perhaps 50% of Europe's 14th century population. The disease is caused by the Bacteria, bacterium ''Yersinia pestis'' and spread by Flea, fleas and through the air. One of the most significant events in European history, the Black Death had far-reaching population, economic, and cultural impacts. It was the beginning of the second plague pandemic. The plague created religious, social and economic upheavals, with profound effects on the course of European history. The origin of the Black Death is disputed. Genetic analysis suggests ''Yersinia pestis'' bacteria evolved approximately 7,000 years ago, at the beginning of the Neolithic, with flea-mediated strains emerging around 3,800 years ago during the late Bronze Age. The immediate territorial origins of the Black Death and its outbreak ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stephen, King Of England
Stephen (1092 or 1096 – 25 October 1154), often referred to as Stephen of Blois, was King of England from 22 December 1135 to his death in 1154. He was Count of Boulogne ''jure uxoris'' from 1125 until 1147 and Duke of Normandy from 1135 until 1144. His reign was marked by the Anarchy, a civil war with his cousin and rival, the Empress Matilda, whose son, Henry II, succeeded Stephen as the first of the Angevin kings of England. Stephen was born in the County of Blois in central France as the fourth son of Stephen-Henry, Count of Blois, and Adela, daughter of William the Conqueror. His father died as a crusader while Stephen was still young, and he was brought up by his mother. Placed into the court of his uncle Henry I of England, Stephen rose in prominence and was granted extensive lands. He married Matilda of Boulogne, inheriting additional estates in Kent and Boulogne that made the couple one of the wealthiest in England. Stephen narrowly escaped drowning with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shotover
Shotover is a hill and forest in the civil parish of Forest Hill with Shotover, in the South Oxfordshire district, in the county of Oxfordshire, England. The hill is east of Oxford. Its highest point is above sea level. Early history The toponym may be derived from the Old English , meaning "steep slope". Shotover was part of the Wychwood royal forestSherwood & Pevsner, 1974, pp. 763–765 from around the period of the Domesday Book until 1660. It was also known as the Forest of Shotover. A hill figure is recorded as having once been carved on the hill. Antiquarian John Aubrey writes: :"On Shotover Hill ear Oxfordwas heretofore (not long before the Civil Wars, in the memory of man) the effigies of a Giant cut in the earth, as the White Horse by Ashbury Park" Shotover was formerly an extra-parochial tract, in 1858 Shotover became a separate civil parish, on 25 March 1883 the parish was abolished and merged with Forest Hill. In 1851 it had a population of 163. Shotover R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |