|
Bugtitherium
''Bugtitherium'' is an extinct genus of anthracothere found in late Oligocene (Chattian The Chattian is, in the geologic timescale, the younger of two ages or upper of two stages of the Oligocene Epoch/Series. It spans the time between . The Chattian is preceded by the Rupelian and is followed by the Aquitanian (the lowest stage ...) deposits in the Bugti Hills of Baluchistan, Pakistan. Incisor teeth that Pilgrim (1908) referred to ''Bugtitherium'' were recognized as instead belonging to the giant paraceratheriid '' Paraceratherium''.Cooper, C. F. (1924). "On the Skull and Dentition of Paraceratherium bugtiense: A Genus of Aberrant Rhinoceroses from the Lower Miocene Deposits of Dera Bugti". Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences. 212 (391–401): 369–394. doi:10.1098/rstb.1924.0009. References {{Taxonbar, from=Q55606097 Oligocene mammals of Asia Anthracotheres Prehistoric even-toed ungulate genera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anthracothere
Anthracotheriidae is a paraphyletic family of extinct, hippopotamus-like artiodactyl ungulates related to hippopotamuses and whales. The oldest genus, '' Elomeryx'', first appeared during the middle Eocene in Asia. They thrived in Africa and Eurasia, with a few species ultimately entering North America during the Oligocene. They died out in Europe and Africa during the Miocene, possibly due to a combination of climatic changes and competition with other artiodactyls, including pigs and true hippopotamuses. The youngest genus, ''Merycopotamus'', died out in Asia during the late Pliocene. The family is named after the first genus discovered, '' Anthracotherium'', which means "coal beast", as the first fossils of it were found in Paleogene-aged coal beds in France. Fossil remains of the anthracothere genus were discovered by the Harvard University and Geological Survey of Pakistan joint research project (Y-GSP) in the well-dated middle and late Miocene deposits of the Potho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
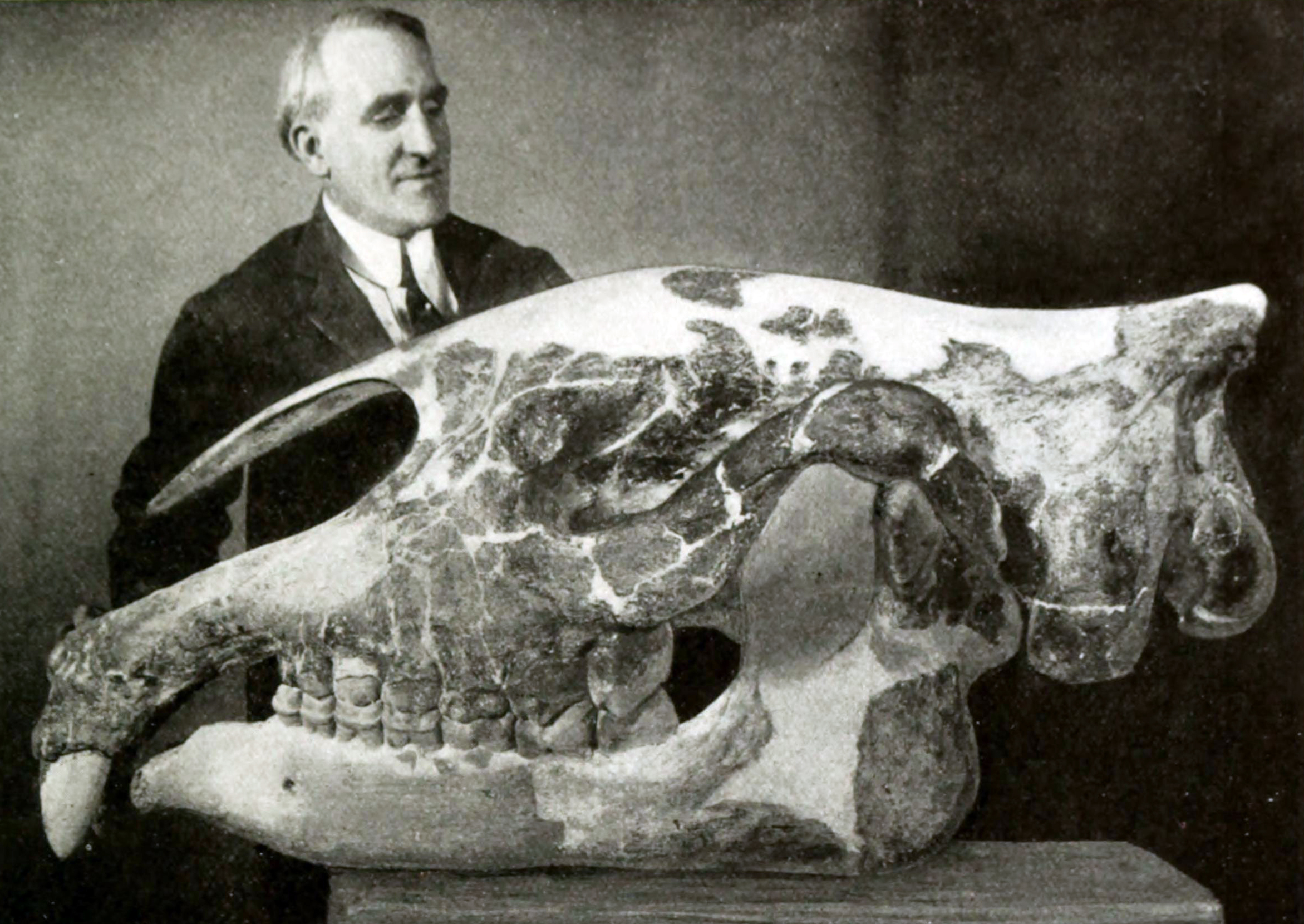
Paraceratherium
''Paraceratherium'' is an extinct genus of hornless rhinoceros. It is one of the largest terrestrial mammals that has existed and lived from the early to late Oligocene epoch (34–23 million years ago). The first fossils were discovered in what is now Pakistan, and remains have been found across Eurasia between China and the Balkans. It is classified as a member of the family Paraceratheriidae. ''Paraceratherium'' means "near the hornless beast", in reference to ''Aceratherium'', the genus in which the type species ''P. bugtiense'' was originally placed. The exact size of ''Paraceratherium'' is unknown because of the incompleteness of the fossils. The shoulder height was about , and the length about . Its weight is estimated to have been about . The long neck supported a skull that was about long. It had large, tusk-like incisors and a nasal incision that suggests it had a prehensile upper lip or proboscis (trunk). The legs were long and pillar-like. The lifestyle of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anthracotheres
Anthracotheriidae is a paraphyletic family of extinct, hippopotamus-like artiodactyl ungulates related to hippopotamuses and whales. The oldest genus, '' Elomeryx'', first appeared during the middle Eocene in Asia. They thrived in Africa and Eurasia, with a few species ultimately entering North America during the Oligocene. They died out in Europe and Africa during the Miocene, possibly due to a combination of climatic changes and competition with other artiodactyls, including pigs and true hippopotamuses. The youngest genus, ''Merycopotamus'', died out in Asia during the late Pliocene. The family is named after the first genus discovered, '' Anthracotherium'', which means "coal beast", as the first fossils of it were found in Paleogene-aged coal beds in France. Fossil remains of the anthracothere genus were discovered by the Harvard University and Geological Survey of Pakistan joint research project (Y-GSP) in the well-dated middle and late Miocene deposits of the Pothohar Plateau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oligocene
The Oligocene ( ) is a geologic epoch of the Paleogene Period and extends from about 33.9 million to 23 million years before the present ( to ). As with other older geologic periods, the rock beds that define the epoch are well identified but the exact dates of the start and end of the epoch are slightly uncertain. The name Oligocene was coined in 1854 by the German paleontologist Heinrich Ernst Beyrich from his studies of marine beds in Belgium and Germany. The name comes from the Ancient Greek (''olígos'', "few") and (''kainós'', "new"), and refers to the sparsity of extant forms of molluscs. The Oligocene is preceded by the Eocene Epoch and is followed by the Miocene The Miocene ( ) is the first geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and means "less recent" ... Epoch. The Oligocene is the third and final epoch of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chattian
The Chattian is, in the geologic timescale, the younger of two ages or upper of two stages of the Oligocene Epoch/ Series. It spans the time between . The Chattian is preceded by the Rupelian and is followed by the Aquitanian (the lowest stage of the Miocene). Stratigraphic definition The Chattian was introduced by Austrian palaeontologist Theodor Fuchs in 1894. Fuchs named the stage after the Chatti, a Germanic tribe.Berry, Edward W"The Mayence Basin, a Chapter of Geologic History" '' The Scientific Monthly'', Vol. 16, No. 2, February 1923. pp. 114. Retrieved March 18, 2020. The original type locality was near the German city of Kassel. The base of the Chattian is at the extinction of the foram genus ''Chiloguembelina'' (which is also the base of foram biozone P21b). An official GSSP for the Chattian Stage was ratified in October of 2016. The top of the Chattian Stage (which is the base of the Aquitanian Stage, Miocene Series and Neogene System) is at the first ap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pakistan
Pakistan ( ur, ), officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan ( ur, , label=none), is a country in South Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, fifth-most populous country, with a population of almost 243 million people, and has the world's Islam by country#Countries, second-largest Muslim population just behind Indonesia. Pakistan is the List of countries and dependencies by area, 33rd-largest country in the world by area and 2nd largest in South Asia, spanning . It has a coastline along the Arabian Sea and Gulf of Oman in the south, and is bordered by India to India–Pakistan border, the east, Afghanistan to Durand Line, the west, Iran to Iran–Pakistan border, the southwest, and China to China–Pakistan border, the northeast. It is separated narrowly from Tajikistan by Afghanistan's Wakhan Corridor in the north, and also shares a maritime border with Oman. Islamabad is the nation's capital, while Karachi is its largest city and fina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oligocene Mammals Of Asia
The Oligocene ( ) is a geologic epoch of the Paleogene Period and extends from about 33.9 million to 23 million years before the present ( to ). As with other older geologic periods, the rock beds that define the epoch are well identified but the exact dates of the start and end of the epoch are slightly uncertain. The name Oligocene was coined in 1854 by the German paleontologist Heinrich Ernst Beyrich from his studies of marine beds in Belgium and Germany. The name comes from the Ancient Greek (''olígos'', "few") and (''kainós'', "new"), and refers to the sparsity of extant forms of molluscs. The Oligocene is preceded by the Eocene Epoch and is followed by the Miocene Epoch. The Oligocene is the third and final epoch of the Paleogene Period. The Oligocene is often considered an important time of transition, a link between the archaic world of the tropical Eocene and the more modern ecosystems of the Miocene. Major changes during the Oligocene included a global expansion of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |