|
Budha
Budha () is the Sanskrit word for the planet Mercury (planet), Mercury, personified as a god. Also a god who represented the intelligence. He is also known as Somaya, Rohinaya, and rules over the nakshatra, ''nakshatra''s (lunar mansions) of Ashlesha (nakshatra), Ashlesha, Jyeshtha (nakshatra), Jyeshtha, and Revati (nakshatra), Revati. Planet Budha is the planet that appears in various Hindu astronomical texts in Sanskrit, such as the 5th century CE ''Aryabhatiya'' by Aryabhatta, the 6th century CE ''Romaka'' by Latadeva and ''Panca Siddhantika'' by Varahamihira, the 7th century CE ''Khandakhadyaka'' by Brahmagupta, and the 8th century CE ''Sisyadhivrddida'' by Lalla. These texts present Budha as one of the planets and find the characteristics of the respective planetary motions. Other texts such as ''Surya Siddhanta'' dated to have been complete sometime between the 5th century CE and 10th century CE present their chapters on various planets with the mythologies of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ila (Hinduism)
Ila () or Ilā () is a deity in Hindu mythology, Hindu legends, known for their sex changes. As a man, he is known as Ila or Sudyumna and as a woman, is called Ilā. Ilā is considered the chief progenitor of the Lunar dynasty of Indian kings – also known as the Aillas ("descendants of Ilā"). While many versions of the tale exist, Ila is usually described as a daughter or son of Shraddhadeva Manu, Vaivasvata Manu and thus the sibling of Ikshvaku (Hinduism), Ikshvaku, the founder of the Solar Dynasty. In versions in which Ila is born female, she changes into a male form by divine grace soon after her birth. After mistakenly entering a sacred grove as an adult, Ila is either cursed to change his/her gender every month or cursed to become a woman. As a woman, Ilā married Budha, the god of the planet Mercury (planet), Mercury and the son of the lunar deity Chandra (Soma), and bore him a son called Pururavas, the father of the Lunar dynasty. After the birth of Pururavas, Ilā has t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tara (Hindu Goddess)
is the Hindu goddess of felicity and sanguineness. She is also known as the "Wisdom Goddess" in Nepal and Tibet. Tara is the consort of Hindu god Brihaspati, the god of planet Jupiter. According to some Puranas, Tara sired or mothered a child named Budha, the god of Mercury through Chandra and had a son named Kacha through Brihaspati. Story Tara was the wife of Brihaspati, the guru of Devas. According to historians, it is mentioned as her husband spent most of his time with the problems and matters of Devas, she felt being ignored by her husband. One day, Chandra, the moon god visited Brihaspati. There he saw Tara and was captivated by her beauty. Chandra used Hypnosis on Tara. Brihaspati was infuriated and demanded Chandra to return his wife. Chandra told Brihaspati that Tara was happy and satisfied with him. He enquired as to how an old man could be the husband of a young woman. This made Brihaspati more annoyed and he warned Chandra for battle. Indra and other Devas gat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tarakamaya War
The Tarakamaya War () is described to be an ancient conflict in Hindu mythology, instigated by the elopement of Tara, the consort of Brihaspati, by Soma, the god of the moon. It is mentioned in the Padma Purana, and described to be the fifth war in the series of ''Devasura Sangrama'', the battles between the devas and the asuras. Legend According to one legend, this abduction had occurred to punish Brihaspati for his extramarital affair with Mamata, the pregnant wife of Utathya. Another legend states that the abduction occurred due to Soma's arrogance, due to the success of his rajasuya ceremony. /sup> Soma refused to return Tara to her husband, despite an intervention by Indra. Brihaspati, the preceptor, was aided by Indra and the devas, allied with the yakshas, while Soma was assisted by Shukra and the daityas, allied with the danavas. Led by Rudra, /sup> the devas assaulted the asuras with divine missiles, and the asuras returned this assault with a barrage of their own ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pururavas
Pururavas (Sanskrit: पुरूरवस्, ''Purūravas'') is a character in Hindu literature, a king who served as the first of the Lunar dynasty. According to the Vedas, he is a legendary entity associated with Surya (the sun) and Usha (the dawn), and is believed to reside in the middle region of the cosmos. The Rig Veda (X.95.18) states that he was a son of Ilā and was a pious ruler. However, the ''Mahabharata'' states that Ila was both his mother and his father. According to the ''Vishnu Purana'', his father was Budha, and he was ancestor of the tribe of Pururavas, from whom descended the Yadavas, Kauravas, and Pandavas of Mahābhārata. Legends Birth and early life Pururavas was born in Treta Yuga, as the son of Budha and Ila. Budha was the son of Chandra, the moon god, and thus Pururavas was the first Chandravamsha King. Since he was born on Mount Puru, he was called Pururavas. Reign According to the Puranas, Pururavas reigned from Pratisthana (Prayaga). He perfo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wednesday
Wednesday is the day of the week between Tuesday and Thursday. According to international standard ISO 8601, it is the third day of the week. In English, the name is derived from Old English and Middle English , 'day of Woden', reflecting the religion practised by the Anglo-Saxons, the English equivalent to the Norse god Odin. In many Romance languages, such as the French , Spanish or Italian , the day's name is a calque of Latin 'day of Mercury'. Wednesday is in the middle of the common Western five-day workweek that starts on Monday and finishes on Friday. Etymology The name Wednesday continues Middle English . Old English still had , which would be continued as ''*Wodnesday'' (but Old Frisian has an attested ). By the early 13th century, the ''i''-mutated form was introduced unetymologically. The name is a calque of the Latin 'day of Mercury', reflecting the fact that the Germanic god Woden (Wodanaz or Odin) during the Roman era was interpreted as "Ger ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
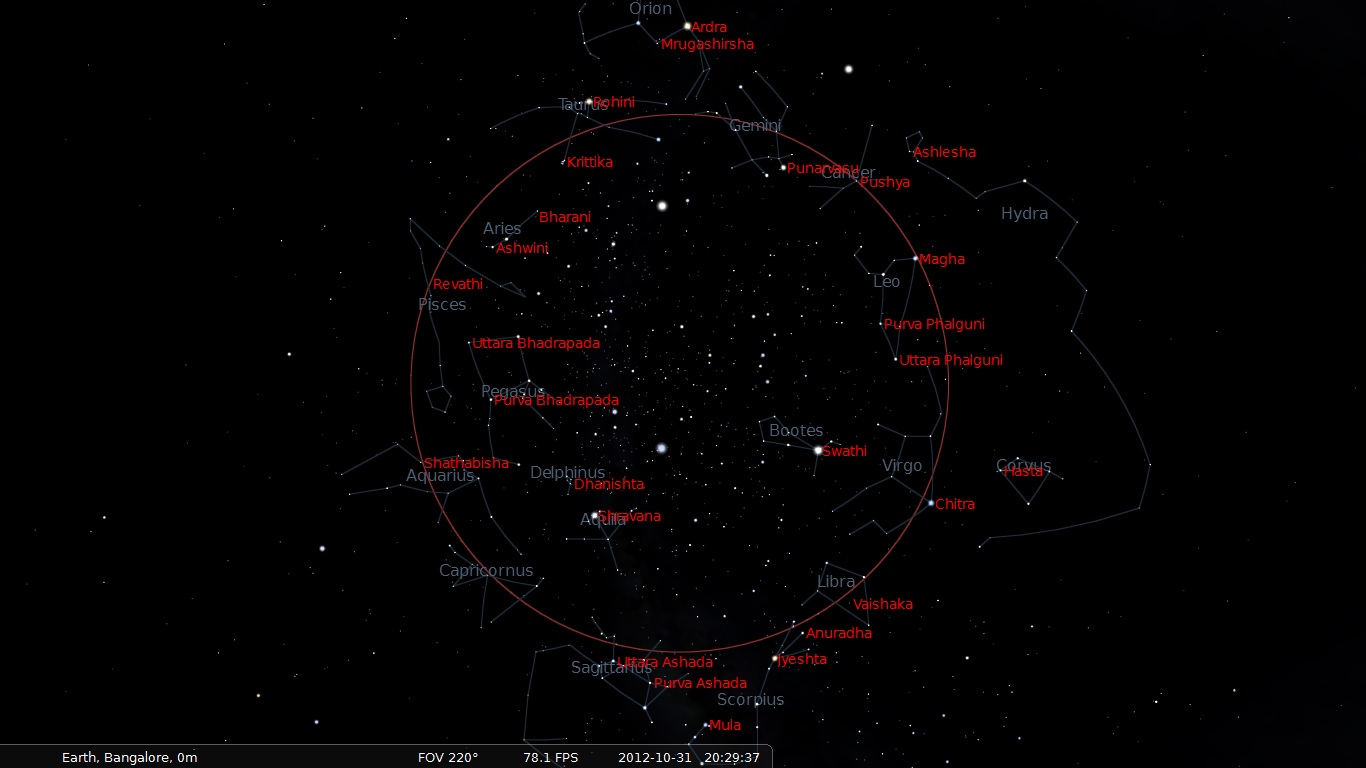
Nakshatra
Nakshatra () is the term for Lunar mansion in Hindu astrology and Buddhist astrology. A nakshatra is one of 27 (sometimes also 28) sectors along the ecliptic. Their names are related to a prominent star or asterisms in or near the respective sectors. In essence (in Western astronomical terms), a nakshatra simply is a constellation. Every nakshatra is divided into four ''padas'' ( "steps"). The starting point for the nakshatras according to the ''Vedas'' is "Krittika" (it has been argued, because the Pleiades may have started the year at the time the ''Vedas'' were compiled, presumably at the vernal equinox), but, in more recent compilations, the start of the nakshatras list is the point on the ecliptic directly opposite the star Spica, called ''Chitrā'' in Sanskrit. This translates to Ashwinī, a part of the modern constellation of Aries. These compilations, therefore, may have been compiled during the centuries when the sun was passing through Aries at the time of the ver ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graha
The navagraha are nine heavenly bodies and deities that influence human life on Earth according to Hinduism and Hindu mythology. The term is derived from ''nava'' ( "nine") and ''graha'' ( "planet, seizing, laying hold of, holding"). The nine parts of the navagraha are the Sun, Moon, planets Mercury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter, and Saturn, and the two nodes of the Moon. The term ''planet'' was applied originally only to the five planets known (i.e., visible to the naked eye) and excluded the Earth. The term was later generalized, particularly during the Middle Ages, to include the sun and the moon (sometimes referred to as "lights"), making a total of seven planets. The seven days of the week of the Hindu calendar also corresponds with the seven classical planets and European culture also following same patron and are named accordingly in most languages of the Indian subcontinent. Most Hindu temples around the world have a designated place dedicated to the worship of the navagraha. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chandra
Chandra (), also known as Soma (), is the Hindu god of the Moon, and is associated with the night, plants and vegetation. He is one of the Navagraha (nine planets of Hinduism) and Dikpala (guardians of the directions). Etymology and other names The word "Chandra" literally means "bright, shining or glittering" and is used for the "Moon" in Sanskrit and other Indo-Aryan languages.''Graha Sutras'' by Ernst Wilhelm, published by Kala Occult Publishers p. 51 It is also the name of various other figures in Hindu mythology, including an asura and a Suryavamsha king. It is also a common Indian name and surname. Both male and female name variations exist in many South Asian languages that originate from Sanskrit. Some of the synonyms of Chandra include ''Soma'' (distill), ''Indu'' (bright drop), ''Atrisuta'' (son of Atri), ''Shashin'' or ''Shachin'' (marked by hare), ''Taradhipa'' (lord of stars) and ''Nishakara'' (the night maker), ''Nakshatrapati'' (lord of the Nakshatra), '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Navagraha
The navagraha are nine heavenly bodies and deities that influence human life on Earth according to Hinduism and Hindu mythology. The term is derived from ''nava'' ( "nine") and ''graha'' ( "planet, seizing, laying hold of, holding"). The nine parts of the navagraha are the Sun, Moon, planets Mercury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter, and Saturn, and the lunar node, two nodes of the Moon. The term ''planet'' was applied originally only to the five planets known (i.e., visible to the naked eye) and excluded the Earth. The term was later generalized, particularly during the Post-classical history, Middle Ages, to include the sun and the moon (sometimes referred to as "lights"), making a total of seven planets. The Seven days of the week#Hindu tradition, seven days of the week of the Hindu calendar also corresponds with the seven classical planets and European culture also following same patron and are Names of the days of the week#Hindu tradition, named accordingly in most languages of the India ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mercury (planet)
Mercury is the first planet from the Sun. It is a rocky planet with a trace atmosphere. While it is the List of Solar System objects by size, smallest and least massive planet of the Solar System, its surface gravity is slightly higher than that of Mars. The surface of Mercury is similar to Earth's Moon, heavily Impact crater, cratered, with expansive rupes system, generated from thrust faults, and bright ray systems, formed by ejecta. Its largest crater, Caloris Planitia, has a diameter of , which is about one-third the diameter of the planet (). Being the most inferior planet, inferior orbiting planet it appears in Earth's sky, always close to the Sun, either as a "morning star" or an "evening star". It stays most of the time the closest to all other planets and is the planet with the highest delta-v needed to travel to from all other planets of the Solar System. Mercury's sidereal year (88.0 Earth days) and sidereal day (58.65 Earth days) are in a 3:2 ratio. This relation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jyeshtha (nakshatra)
Jyeshtha ("The Elder" or "Older" in Sanskrit) is the 18th nakshatra or lunar mansion in Indian astronomy, Hindu astronomy and Jyotisha, Vedic astrology associated with the string of the constellation Scorpius (constellation), Scorpii, and the stars Epsilon Scorpii, ε, Zeta1 Scorpii, ζ1 Sco, Eta Scorpii, η, Sargas, θ, Iota1 Scorpii, ι1 Sco, Girtab, κ, Shaula, λ, Mu Scorpii, μ and Jabbah, ν Scorpius (constellation), Scorpionis. Astrology The symbol of Jyeshtha is a circular amulet, umbrella, or earring, and it is associated with Indra, chief of the gods. The lord of Jyeshtha is Budha (Mercury). Jyestha is termed in Malayalam as Thrikketta and in Tamil as Kēttai. The nakshtra is called honorifically as Trikkētta (Tiru + Kētta). Jyeshtha nakshatra corresponds to Antares. The Ascendant/Lagna in Jyeshtha indicates a person with a sense of seniority and superiority, who is protective, responsible and a leader of their family. They are wise, profound, psychic, maybe with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |