|
Brookes (ship)
''Brooks'' (or ''Brook'', ''Brookes'') was a British slave ship launched at Liverpool in 1781. She became infamous after prints of her were published in 1788. Between 1782 and 1804, she made 11 voyages from Liverpool slave trade, Liverpool in the triangular slave trade in enslaved people (for the ''Brooks'', England, to Africa, to the Caribbean, and back to England). During this period she spent some years as a West Indiaman. She also recaptured a British merchantman and captured a French merchantman. ''Brooks''s last voyage shipping enslaved people was to Montevideo in the South Atlantic where she was condemned as unseaworthy in November 1804. History A British Member of Parliament, Sir William Dolben, 3rd Baronet, toured and investigated ''Brooks''. This led to the publishing of her plans and design by Thomas Clarkson, an abolitionist. An engraving first published in Plymouth in 1788 by the Plymouth chapter of the Society for Effecting the Abolition of the Slave Trade depicted t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Great Britain
Great Britain, also known as the Kingdom of Great Britain, was a sovereign state in Western Europe from 1707 to the end of 1800. The state was created by the 1706 Treaty of Union and ratified by the Acts of Union 1707, which united the Kingdom of England (including Wales) and the Kingdom of Scotland to form a single kingdom encompassing the whole island of Great Britain and its outlying islands, with the exception of the Isle of Man and the Channel Islands. The unitary state was governed by a single Parliament of Great Britain, parliament at the Palace of Westminster, but distinct legal systems—English law and Scots law—remained in use, as did distinct educational systems and religious institutions, namely the Church of England and the Church of Scotland remaining as the national churches of England and Scotland respectively. The formerly separate kingdoms had been in personal union since the Union of the Crowns in 1603 when James VI of Scotland became King of England an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
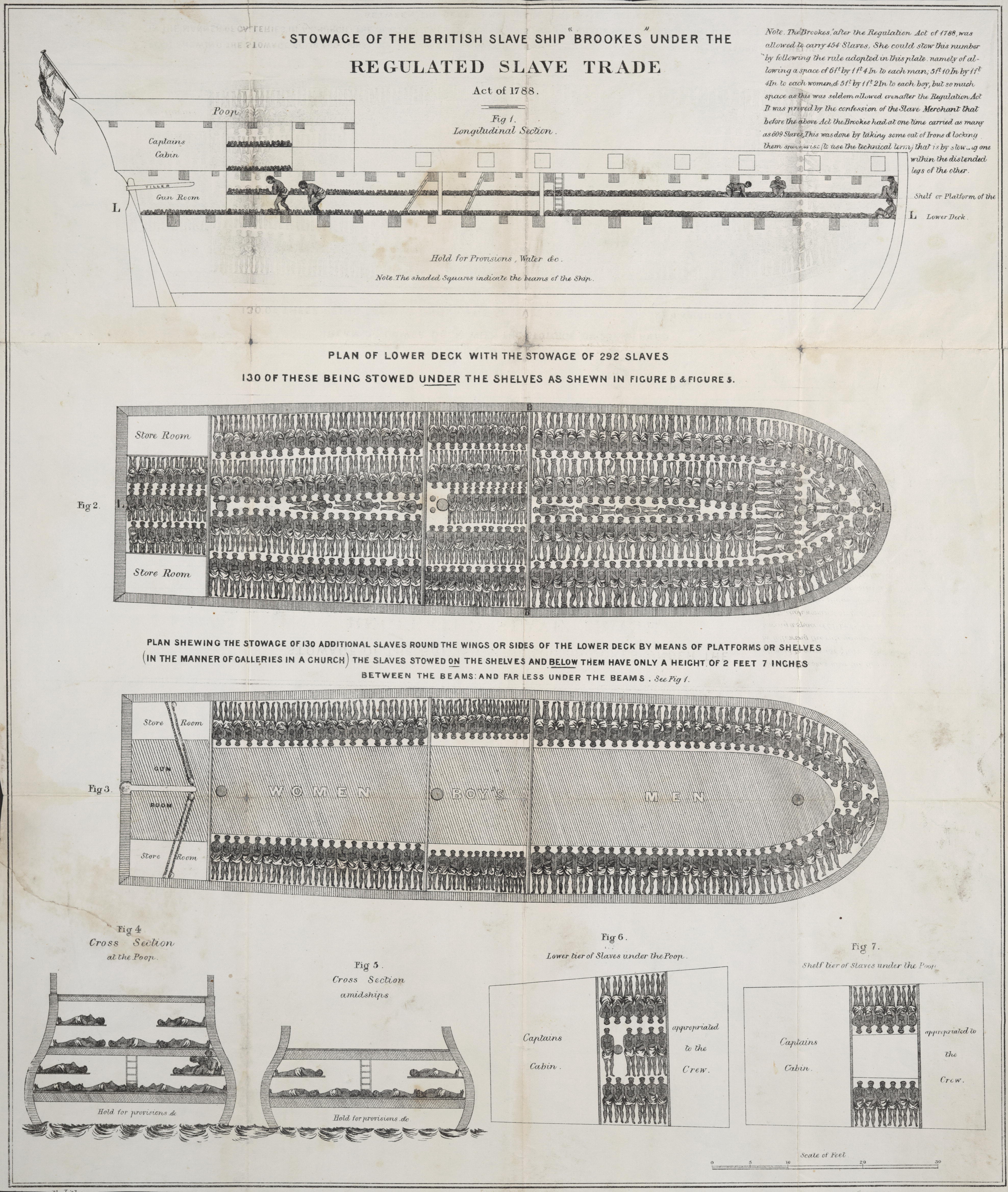
Regulated Slave Trade Act 1788
The Slave Trade Act 1788 ( 28 Geo. 3. c. 54), also known as the Regulated Slave Trade Act 1788, Slave Trade Regulation Act 1788 or Dolben's Act, was an Act of Parliament that limited the number of enslaved people that British slave ships could transport, based on the ships' tons burthen ( bm). It was the first British legislation enacted to regulate slave shipping. Background In the late 18th century, opposition to slavery was increasing. Many abolitionists were infuriated by the Zong massacre, whose details became known during litigation in 1783, when the syndicate owning the ship filed for insurance claims to cover 132–142 slaves who had been killed. Quakers had been active in petitioning Parliament to end the trade. To expand their influence, in 1787 they formed a non-denominational group, the Society for the Abolition of the Slave Trade, which included Anglicans of the established church (non-Anglicans were excluded from Parliament). In 1788, Sir William Dolben led ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Loango, Republic Of Congo
Loango (can also be written as ''Luango'', ''Lwango'', ''Luangu'', ''Lwangu'', ''Luaangu'' or ''Lwaangu'') is a town of the Republic of the Congo. Located on the coast of the Atlantic Ocean, Loango had a population of 21,016 in 2023, the date of the country's last official census. Since 2011 it has been the capital of the Kouilou Department and of the new Loango District. Location Loango lies on the south coast of the Loango Bay, to the southwest of Diosso, a few kilometers north of the city of Pointe-Noire. History Diosso was the former capital of the Kingdom of Loango and home to its rulers' mausoleum. Roman Catholic missionaries were active in Diosso, which had a royal palace. The port of Loango was formerly a Loango_slavery_harbour, major slavery port, but the site has now been abandoned and few traces remain. The first radiotelegraph link in the tropics, between Brazzaville and Loango, was created around 1910 using techniques developed by Joseph Bethenod, chief engineer o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Letter Of Marque
A letter of marque and reprisal () was a Sovereign state, government license in the Age of Sail that authorized a private person, known as a privateer or French corsairs, corsair, to attack and capture vessels of a foreign state at war with the issuer, licensing international military operations against a specified enemy as reprisal for a previous attack or injury. Captured Prize money, naval prizes were judged before the government's admiralty court for condemnation and transfer of ownership to the privateer. A common practice among Europeans from the late Middle Ages to the 19th century, cruising for enemy prizes with a letter of marque was considered an honorable calling that combined patriotism and profit. Such legally authorized privateering contrasted with unlicensed captures of random ships, known as piracy, which was universally condemned. In practice, the differences between privateers and pirates were sometimes slight, even merely a matter of interpretation. The te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Revolutionary Wars
The French Revolutionary Wars () were a series of sweeping military conflicts resulting from the French Revolution that lasted from 1792 until 1802. They pitted French First Republic, France against Kingdom of Great Britain, Great Britain, Habsburg monarchy, Austria, Kingdom of Prussia, Prussia, Russian Empire, Russia, and several other countries. The wars are divided into two periods: the War of the First Coalition (1792–1797) and the War of the Second Coalition (1798–1802). Initially confined to Europe, the fighting gradually assumed a global dimension. After a decade of constant warfare and aggressive diplomacy, France had conquered territories in the Italian peninsula, the Low Countries, and the Rhineland with its very large and powerful military which had been totally mobilized for war against most of Europe with mass conscription of the vast French population. French success in these conflicts ensured military occupation and the spread of revolutionary principles over mu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Montego Bay
Montego Bay () is the capital of the Parishes of Jamaica, parish of Saint James Parish, Jamaica, St. James in Jamaica. The city is the fourth most populous urban area in the country, after Kingston, Jamaica, Kingston, Spanish Town, and Portmore, Jamaica, Portmore, all of which form the Greater Kingston Metropolitan Area, home to over half a million people. As a result, Montego Bay is the second-largest anglophone city in the Caribbean, after Kingston. Montego Bay is a popular tourist destination featuring duty-free shopping, a cruise line terminal and several beaches and resorts. The city is served by the Donald Sangster International Airport, the busiest airport in the Anglophone Caribbean, which is located within the official city limits. The city is enclosed in a watershed, drained by several rivers such as the Montego River. Montego Bay is referred to as "The Second City", "MoBay" or "Bay". Toponymy Christopher Columbus named the bay of Montego, ''Golfo de Buen Tiempo'' ("F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slave Trade Act 1788
The Slave Trade Act 1788 ( 28 Geo. 3. c. 54), also known as the Regulated Slave Trade Act 1788, Slave Trade Regulation Act 1788 or Dolben's Act, was an Act of Parliament that limited the number of enslaved people that British slave ships could transport, based on the ships' tons burthen ( bm). It was the first British legislation enacted to regulate slave shipping. Background In the late 18th century, opposition to slavery was increasing. Many abolitionists were infuriated by the Zong massacre, whose details became known during litigation in 1783, when the syndicate owning the ship filed for insurance claims to cover 132–142 slaves who had been killed. Quakers had been active in petitioning Parliament to end the trade. To expand their influence, in 1787 they formed a non-denominational group, the Society for the Abolition of the Slave Trade, which included Anglicans of the established church (non-Anglicans were excluded from Parliament). In 1788, Sir William Dolben led a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dixcove
Dixcove is a coastal village and a fishing community in the Ahanta West district, a district in the Western Region of South Ghana, located approximately 35 km west of the regional capital of Sekondi-Takoradi. The current Paramount Chief of Upper Dixcove is Obrempong Hima Dekyi XIV. History Dixcove is the site of Fort Metal Cross, an English-built fort which was completed in 1698. The fort dominates the fishing village and town from a bluff located on the eastern side of the village. The fort was used mainly as a slave fort, but also served as a secure depot for the trade gold and palm oil, and later served as a prison, police station, and a post office. The fort is currently leased by an English citizen who operates it as a tourist site, and a congregation point for local churches. The town was a center for trade during the Gold Coast era. From the early 17th to the 19th century, Dixcove was divided into two quarters known as ''Ntwarkro'' (Upper Dixcove) and ''Daazikes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jamaica
Jamaica is an island country in the Caribbean Sea and the West Indies. At , it is the third-largest island—after Cuba and Hispaniola—of the Greater Antilles and the Caribbean. Jamaica lies about south of Cuba, west of Hispaniola (the island containing Haiti and the Dominican Republic), and southeast of the Cayman Islands (a British Overseas Territories, British Overseas Territory). With million people, Jamaica is the third most populous English-speaking world, Anglophone country in the Americas and the fourth most populous country in the Caribbean. Kingston, Jamaica, Kingston is the country's capital and largest city. The indigenous Taíno peoples of the island gradually came under Spanish Empire, Spanish rule after the arrival of Christopher Columbus in 1494. Many of the indigenous people either were killed or died of diseases, after which the Spanish brought large numbers of Africans to Jamaica as slaves. The island remained a possession of Spain, under the name Colo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingston, Jamaica
Kingston is the Capital (political), capital and largest city of Jamaica, located on the southeastern coast of the island. It faces a natural harbour protected by the Palisadoes, a long spit (landform), sand spit which connects the town of Port Royal and Norman Manley International Airport to the rest of the island. Kingston is the largest English-speaking city south of the United States in the Western Hemisphere. The local government bodies of the parishes of Kingston Parish, Kingston and Saint Andrew Parish, Jamaica, Saint Andrew were amalgamated by the Kingston and St. Andrew Corporation Act of 1923, to form the Kingston and St. Andrew Corporation (KSAC). Greater Kingston, or the "Corporate Area" refers to those areas under the KSAC; however, it does not solely refer to Kingston Parish, which only consists of the old downtown and Port Royal. Kingston Parish had a population of 89,057, and St. Andrew Parish had a population of 573,369 in 2011 Kingston is only bordered by Sain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anomabu
Anomabu, also spelled Anomabo and formerly as Annamaboe, is a town on the coast of the Mfantsiman Municipal District of the Central Region of South Ghana. Anomabu has a settlement population of 14,389 people. Anomabu is located 12 km east of Cape Coast in the central region of south Ghana. It is situated on the main road to Accra. The total area of Anomabu is 612 square kilometers, with boundaries of 21 kilometres along the coast, and 13 kilometres inland. The main language spoken in Anomabu is Fante. According to oral tradition, the origin of the name “Anomabu” was first established when a hunter from the Nsona clan first discovered the area and decided to settle there with his family, eventually starting his own village as time passed. The hunter allegedly saw some birds atop a rock, and proclaimed the area “Obo noma,” which became the town's original name. Obanoma literally translates to “bird’s rock,” a name that slowly evolved into Anomabu over the ye ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cape Coast Castle
Cape Coast Castle () is one of about forty slave fort, "slave castles", or large commercial forts, built on the Gold Coast (region), Gold Coast of West Africa (now Ghana) by European traders. It was originally a Portuguese "feitoria" or Factory (trading post), trading post, established in 1555, which was named ''Cabo Corso''. In 1653, a timber fort was constructed by the Swedish Africa Company. It originally was a centre for timber and gold trade, and then was later used in the Atlantic slave trade. Other List of castles in Ghana, Ghanaian slave castles include Elmina Castle and Fort Christiansborg. They were used to harbour enslaved Africans before they were loaded onto ships and sold in the Americas, especially the Caribbean. This "gate of no return" was the last stop before crossing the Atlantic Ocean. Cape Coast Castle, along with other forts and castles in Ghana, are included on the UNESCO World Heritage List because of their testimony to the Atlantic gold and slave trades. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |