|
Bronxville (Metro-North Station)
Bronxville station is a commuter rail stop on the Metro-North Railroad's Harlem Line, located in the village of Bronxville, New York, in Westchester County. History The New York and Harlem Railroad laid tracks through Bronxville during the mid-1840s, and evidence of a station in Bronxville can be found at least as far back as 1858. A second station was built in 1893 by the New York Central and Hudson River Railroad, replacing a previous station which was also the home of Lancaster Underhill, a descendant of John Underhill, the man responsible for creating "Underhill's Crossing". The third and current Bronxville Station was built in 1916 by the New York Central Railroad, in the Spanish-Mission Revival architecture designed to match that of the nearby Gramatan Hotel. As with the rest of the Harlem Line, the merger of New York Central with Pennsylvania Railroad in 1968 transformed it into a Penn Central station, and then its service was gradually merged with the Metropolitan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bronxville, New York
Bronxville is a Administrative divisions of New York#Village, village in Westchester County, New York, Westchester County, New York (state), New York, United States, located approximately north of Midtown Manhattan. It is part of the Administrative divisions of New York#Town, town of Eastchester (town), New York, Eastchester. The village comprises one square mile (2.5 km2) of land in its entirety, approximately 20% of the town of Eastchester. As of the 2020 United States census, 2020 U.S. census, Bronxville had a population of 6,656. History The region that includes the contemporary village of Bronxville was deeded to British colonists in 1666, but first settled by Europeans in the early 18th century. The two founding inhabitants were the Underhill (surname), Underhill and Morgan family, Morgan families. The Underhills built a sawmill and a gristmill, which was the first factory in the area, on the Bronx River. After they built a wooden bridge, the area became known as U ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
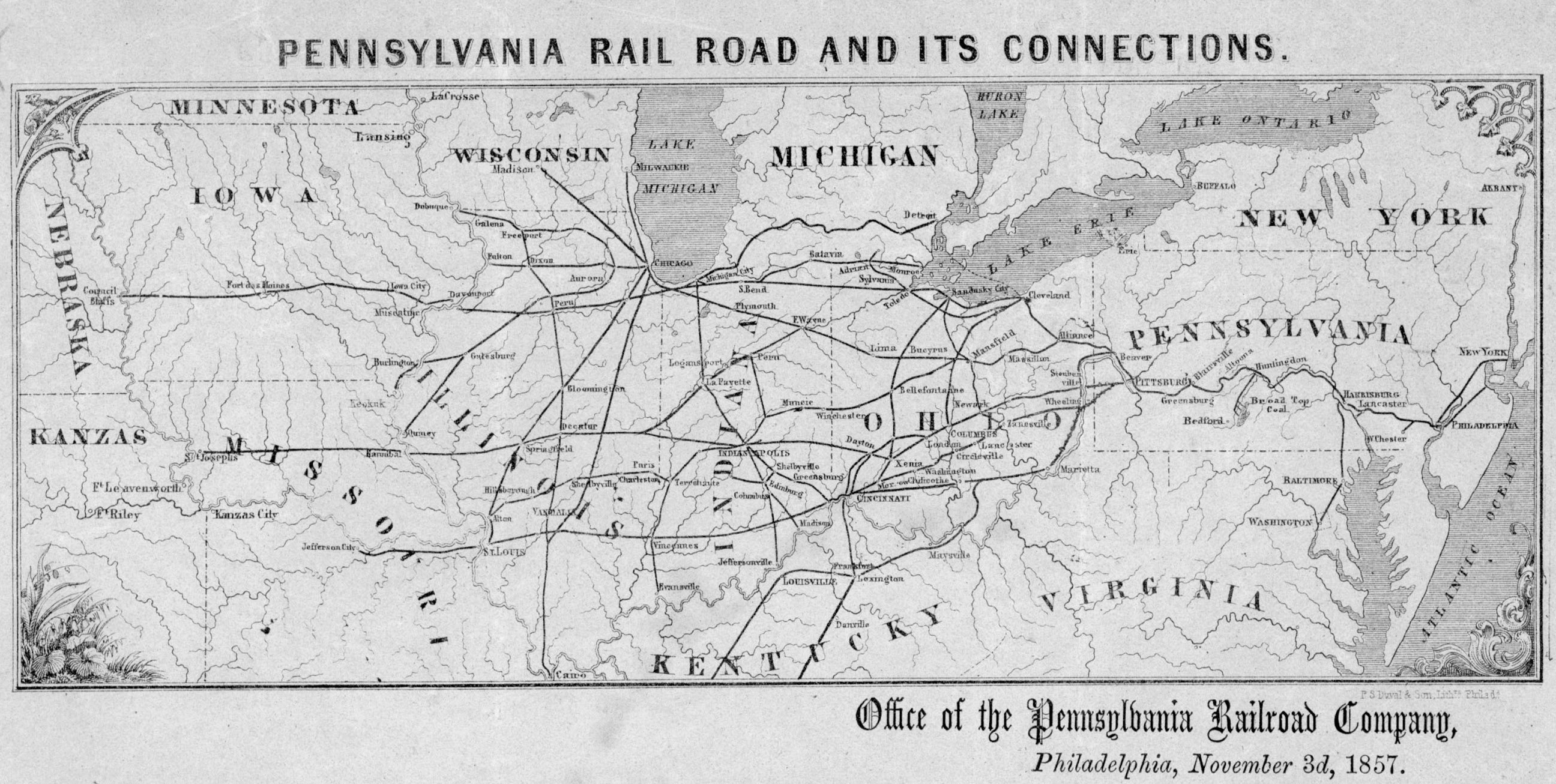
New York Central Railroad
The New York Central Railroad was a railroad primarily operating in the Great Lakes region, Great Lakes and Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic regions of the United States. The railroad primarily connected New York metropolitan area, greater New York and Boston in the east with Chicago and St. Louis in the Midwest, along with the intermediate cities of Albany, New York, Albany, Buffalo, New York, Buffalo, Cleveland, Cincinnati, Detroit, Rochester, New York, Rochester and Syracuse, New York, Syracuse. The New York Central was headquartered in the New York Central Building, adjacent to its largest station, Grand Central Terminal. The railroad was established in 1853, consolidating several existing railroad companies. In 1968, the NYC merged with its former rival, the Pennsylvania Railroad, to form Penn Central. Penn Central went into bankruptcy in 1970 and, with extensive Federal government support, emerged as Conrail in 1976. In 1999, Conrail was broken up, and portions o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Railway Stations In Westchester County, New York
Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport using wheeled vehicles running in tracks, which usually consist of two parallel steel rails. Rail transport is one of the two primary means of land transport, next to road transport. It is used for about 8% of passenger and freight transport globally, thanks to its energy efficiency and potentially high speed.Rolling stock on rails generally encounters lower frictional resistance than rubber-tyred road vehicles, allowing rail cars to be coupled into longer trains. Power is usually provided by diesel or electric locomotives. While railway transport is capital-intensive and less flexible than road transport, it can carry heavy loads of passengers and cargo with greater energy efficiency and safety. Precursors of railways driven by human or animal power have existed since antiquity, but modern rail transport began with the invention of the steam locomotive in the United Kingdom at the beginning of the 19th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Former New York Central Railroad Stations
A former is an object, such as a template, gauge or cutting die, which is used to form something such as a boat's hull. Typically, a former gives shape to a structure that may have complex curvature. A former may become an integral part of the finished structure, as in an aircraft fuselage, or it may be removable, being used in the construction process and then discarded or re-used. Aircraft formers Formers are used in the construction of aircraft fuselage, of which a typical fuselage has a series from the nose cone to the empennage, typically perpendicular to the longitudinal axis of the aircraft. The primary purpose of formers is to establish the shape of the fuselage and reduce the column length of stringers to prevent instability. Formers are typically attached to longerons, which support the skin of the aircraft. The "former-and-longeron" technique (also called stations and stringers) was adopted from boat construction, and was typical of light aircraft built until t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metro-North Railroad Stations In New York (state)
The Metro-North Commuter Railroad Company , also branded as MTA Metro-North Railroad and commonly called simply Metro-North, is a suburban commuter rail service operated by the Metropolitan Transportation Authority (MTA), a public authority of the U.S. state of New York. Metro-North serves the New York Metropolitan Area, running service between New York City and its northern suburbs in New York and Connecticut, including Port Jervis, Spring Valley, Poughkeepsie, Yonkers, New Rochelle, Mount Vernon, White Plains, Southeast and Wassaic in New York and Stamford, New Canaan, Danbury, Bridgeport, Waterbury, and New Haven in Connecticut. Service in Connecticut is operated under contract with the Connecticut Department of Transportation. Similarly, service on lines west of the Hudson River is operated under contract with NJ Transit. Metro-North also provides local rail service within the New York City boroughs of Manhattan and the Bronx. Metro-North is the descendant of c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crestwood (Metro-North Station)
Crestwood station is a commuter rail stop on the Metro-North Railroad's Harlem Line, serving the communities of Tuckahoe, Yonkers, and Eastchester, New York. Because of its location at the northern end of the triple-track segment of the Harlem Line, Crestwood is often the first/last stop outside New York City on Harlem Line express trains, and its center island platform is frequently used to short turn local trains during rush hour. The Harlem Line has two stations in the village of Tuckahoe. Tuckahoe station, the next station heading southbound, is located near Tuckahoe Village Hall, while Crestwood is located near the adjoining residential neighborhood of Crestwood, Yonkers. As of August 2006, daily commuter ridership was 1,596, and there are 283 parking spots. History Originally built by the New York Central Railroad sometime in 1901, the station's canopy was rebuilt in 1911, then faced a major redesign in 1928. The Crestwood railroad station is depicted in the painting ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tuckahoe (Metro-North Station)
Tuckahoe station is a commuter rail stop on the Metro-North Railroad's Harlem Line, located in the village of Tuckahoe, New York. History The New York and Harlem Railroad laid tracks through Tuckahoe during the mid-1840s, and evidence of a station in Tuckahoe can be found at least as far back as the 1850s. The current Tuckahoe station building was originally built in 1901, by the New York Central Railroad, and was given an additional baggage elevator approximately in 1912. The station continued to serve commuters without much change until the New York Central merged with rival Pennsylvania Railroad to form Penn Central in 1968. As Penn Central was facing bankruptcy, the Metropolitan Transportation Authority began subsidizing service in 1970, and high-level platforms were constructed to accommodate the new M1A electric MU cars being delivered at the time. Operation of the railroad continued and was passed on to Conrail in 1976. Metro-North took over direct operation in 1983. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fleetwood (Metro-North Station)
Fleetwood station is a commuter rail stop on the Metro-North Railroad's Harlem Line, located in the Fleetwood section of Mount Vernon, New York. As of August 2006, daily commuter ridership was 2,355 and there are 654 parking spots. History Fleetwood station was originally built on October 25, 1924 by the New York Central Railroad. The Cross County Parkway was built over the station, and was widened during the 1950s and 1960s. As with the rest of the Harlem Line, the merger of New York Central with Pennsylvania Railroad in 1968 transformed it into a Penn Central station, whose service was gradually merged with the Metropolitan Transportation Authority, and officially became part of Metro-North in 1983. In the Spring of 1989, the platforms were reconstructed, along with those of Bronxville (Metro-North station), Bronxville, Tuckahoe (Metro-North station), Tuckahoe, and Crestwood (Metro-North station), Crestwood stations. A two-track girder bridge over the Bronx River can be found ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metropolitan Transportation Authority
The Metropolitan Transportation Authority (MTA) is a New York state public benefit corporations, public benefit corporation in New York (state), New York State responsible for public transportation in the New York metropolitan area, New York City metropolitan area. The MTA is the largest public transit authority in North America, serving 12 counties in Downstate New York, along with two counties in southwestern Connecticut under contract to the Connecticut Department of Transportation, carrying over 11 million passengers on an average weekday systemwide, and over 850,000 vehicles on its MTA Bridges and Tunnels, seven toll bridges and two tunnels per weekday. History Founding In February 1965, New York governor Nelson Rockefeller suggested that the New York State Legislature create an authority to purchase, operate, and modernize the Long Island Rail Road (LIRR). The LIRR, then a subsidiary of the Pennsylvania Railroad (PRR), had been operating under bankruptcy protection since 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Penn Central
The Penn Central Transportation Company, commonly abbreviated to Penn Central, was an American class I railroad that operated from 1968 to 1976. Penn Central combined three traditional corporate rivals, the Pennsylvania, New York Central and the New York, New Haven and Hartford railroad, each of which were united by large-scale service into the New York metropolitan area and to a lesser extent New England and Chicago. The new company failed barely two years after formation, the largest bankruptcy in U.S. history at the time. Penn Central's railroad assets were nationalized into Conrail along with those of other bankrupt northeastern railroads; its real estate and insurance holdings successfully reorganized into American Premier Underwriters. History Pre-merger The Penn Central railroad system developed in response to challenges facing northeastern American railroads during the late 1960s. While railroads elsewhere in North America drew revenues from long-distance shipment ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pennsylvania Railroad
The Pennsylvania Railroad ( reporting mark PRR), legal name as the Pennsylvania Railroad Company, also known as the "Pennsy," was an American Class I railroad that was established in 1846 and headquartered in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. At its peak in 1882, the Pennsylvania Railroad was the largest railroad (by traffic and revenue), the largest transportation enterprise, and the largest corporation in the world. Over its existence, Pennsylvania Railroad acquired, merged with, or owned part of at least 800 other rail lines and companies. At the end of 1926, it operated of rail line;This mileage includes companies independently operated. PRR miles of all tracks, which includes first (or main), second, third, fourth, and sidings, totalled 28,040.49 at the end of 1926. in the 1920s, it carried nearly three times the traffic as other railroads of comparable length, such as the Union Pacific and Atchison, Topeka & Santa Fe railroads. Its only formidable rival was the New York Centra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mission Revival Architecture
The Mission Revival style was part of an Architectural style, architectural movement, beginning in the late 19th century, for the Revivalism (architecture), revival and reinterpretation of American colonial styles. Mission Revival drew inspiration from the late 18th and early 19th century Spanish missions in California. It is sometimes termed California Mission Revival, particularly when used elsewhere, such as in Spanish missions in New Mexico, New Mexico and Spanish missions in Texas, Texas which have their own unique regional architectural styles. In Australia, the style is known as Spanish Mission. The Mission Revival movement was most popular between 1890 and 1915, in numerous residential, commercial and institutional structures, particularly schools and railroad depots. Influences All of the 21 Franciscan Alta California missions (established 1769–1823), including their chapels and support structures, shared certain design characteristics. These commonalities arose b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |