|
Broadswords
The basket-hilted sword is a sword type of the early modern era characterised by a basket-shaped guard that protects the hand. The basket hilt is a development of the quillons added to swords' crossguards since the Late Middle Ages. This variety of sword is also sometimes referred to as the broadsword, though this term may also be applied loosely and imprecisely to other swords. The basket-hilted sword was generally in use as a military sword. A true broadsword possesses a double-edged blade, while similar wide-bladed swords with a single sharpened edge and a thickened back are called backswords. Various forms of basket-hilt were mounted on both broadsword and backsword blades. One of the weapon types in the modern German dueling sport of ("academic fencing") is the basket-hilted . Nomenclature The designation "broadsword" is ambiguous, and can refer to many different types of sword. Though attestations of "broad swords" date from the 11th century, these simply refer to a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Donald McBane, Scottish Fencing Master
Donald is a Scottish masculine given name. It is derived from the Goidelic languages, Gaelic name ''Dòmhnall''.. This comes from the Proto-Celtic language, Proto-Celtic *''Dumno-ualos'' ("world-ruler" or "world-wielder"). The final -''d'' in ''Donald'' is partly derived from a misinterpretation of the Gaelic pronunciation by English speakers. A short form of Donald is Don (given name), Don, and pet forms of Donald include Donnie and Donny. The feminine given name Donella (other) , Donella is derived from Donald. ''Donald'' has cognates in other Celtic languages: Irish language, Modern Irish ''Dónal'' (anglicised as ''Donal'' and ''Donall'');. Scottish Gaelic ''Dòmhnall'', ''Domhnull'' and ''Dòmhnull''; Welsh language, Welsh ''Dyfnwal (other), Dyfnwal'' and Cumbric ''Dumnagual''. Although the feminine given name ''Donna (given name), Donna'' is sometimes used as a feminine form of ''Donald'', the names are not etymologically related. Variations King ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
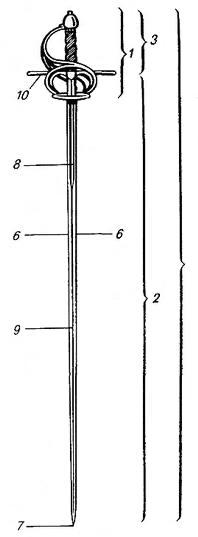
Medieval Sword
A sword is an edged, bladed weapon intended for manual cutting or thrusting. Its blade, longer than a knife or dagger, is attached to a hilt and can be straight or curved. A thrusting sword tends to have a straighter blade with a pointed tip. A slashing sword is more likely to be curved and to have a sharpened cutting edge on one or both sides of the blade. Many swords are designed for both thrusting and slashing. The precise definition of a sword varies by historical epoch and geographic region. Historically, the sword developed in the Bronze Age, evolving from the dagger; the earliest specimens date to about 1600 BC. The later Iron Age sword remained fairly short and without a crossguard. The spatha, as it developed in the Late Roman army, became the predecessor of the European sword of the Middle Ages, at first adopted as the Migration Period sword, and only in the High Middle Ages, developed into the classical arming sword with crossguard. The word ''sword'' continues t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1796 Heavy Cavalry Sword
The Pattern 1796 heavy cavalry sword was the sword used by the British heavy cavalry (Lifeguards, Royal Horse Guards, Dragoon Guards and Dragoons), and King's German Legion Dragoons, through most of the period of the Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars. It played an especially notable role, in the hands of British cavalrymen, at the battles of Battle of Salamanca, Salamanca and Battle of Waterloo, Waterloo. The pattern was adopted by Sweden and was used by some Portuguese cavalry. Background The British ''1796 Heavy Cavalry Trooper's Sword'' was a direct copy of the Austrian ''pallasch'' sword pattern of 1769 for heavy cavalry (it later received an iron scabbard (1775), in which form it was adopted by the British). John Le Marchant (British Army cavalry officer), John Le Marchant, a cavalry officer who designed the curved Pattern 1796 light cavalry sabre, 1796 pattern light cavalry sabre, undoubtedly saw the Austrian weapon in use during the Low Countries Campaign of 1793-95, when h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Historical Fencing In Scotland
There is some evidence on historical fencing as practised in Scotland in the early modern period, Scotland in the Early Modern Era, especially fencing with the Scottish basket-hilted broadsword during the 17th to 18th centuries. Most of our current knowledge of these arts derives from various combative treatises or Martial arts manuals, as well as written anecdotes (i.e. battle accounts, folklore, etc.) and artistic representations from different periods and locations in history of Scotland, Scottish history (see Penicuik SketchesHighland Swordsmanship: Techniques of the Scottish Sword Masters, by Mark Rector (editor) and Paul Wagner (editor), Published by Chivalry Bookshelf (15 November 2001)). Scottish fencing masters The following is a list of fencing masters that were very influential in their day, and have contributed to our current knowledge of the martial practices of Scotland (see ''Combat Treatises'' below): * William Machrie – a Scottish fencing master who taught i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fencing Manual
Martial arts manuals are instructions, with or without illustrations, specifically designed to be learnt from a book. Many books detailing specific techniques of martial arts are often erroneously called manuals but were written as treatises. Prose descriptions of martial arts techniques appear late within the history of literature, due to the inherent difficulties of describing a technique rather than just demonstrating it. The earliest extant manuscript on armed combat (as opposed to unarmed wrestling) is Royal Armouries Ms. I.33 ("I.33"), written in Franconia around 1300. Not within the scope of this article are books on military strategy such as Sun Tzu's ''The Art of War'' (before 100 BCE) or Publius Flavius Vegetius Renatus' '' De Re Militari'' (4th century), or military technology, such as ''De rebus bellicis'' (4th to 5th century). Predecessors Some early testimonies of historical martial arts consist of series of images only. The earliest example is a fresco in tomb 15 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Small Sword
__NoTOC__ The small sword or smallsword (also court sword, Gaelic: or claybeg, French: , lit. “Sword of the court”) is a light one-handed sword designed for thrusting which evolved out of the longer and heavier rapier (''espada ropera'') of the late Renaissance. The height of the small sword's popularity was during the 18th century, when any civilian or soldier with pretensions to gentlemanly status would have worn a small sword daily. The blade of a small sword is comparatively short at around , though some reach over . It usually tapers to a sharp point but may lack a cutting edge. It is typically triangular in cross-section, although some of the early examples still have the rhombic and spindle-shaped cross-sections inherited from older weapons, like the rapier. This triangular cross-section may be hollow ground for additional lightness. Many small swords of the period between the 17th and 18th centuries were found with colichemarde blades. It is thought to have app ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duel
A duel is an arranged engagement in combat between two people with matched weapons. During the 17th and 18th centuries (and earlier), duels were mostly single combats fought with swords (the rapier and later the small sword), but beginning in the late 18th century in England, duels were more commonly fought using pistols. Fencing and shooting continued to coexist throughout the 19th century. The duel was based on a code of honor. Duels were fought not to kill the opponent but to gain "satisfaction", that is, to restore one's honor by demonstrating a willingness to risk one's life for it. As such, the tradition of dueling was reserved for the male members of nobility; however, in the modern era, it extended to those of the upper classes. On occasion, duels with swords or pistols were fought between women. Legislation against dueling dates back to the medieval period. The Fourth Council of the Lateran (1215) outlawed duels and civil legislation in the Holy Roman Empire agains ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spada Da Lato
The ''spada da lato'' (Italian) or ''side-sword'' is a type of sword popular in Italy during the Renaissance. It is a continuation of the medieval knightly sword, and the immediate predecessor, or early form, of the rapier of the early modern period The early modern period is a Periodization, historical period that is defined either as part of or as immediately preceding the modern period, with divisions based primarily on the history of Europe and the broader concept of modernity. There i .... Side-swords were used concurrently with rapiers as well, particularly for military applications, although differentiating swords between civilian and military use was not something that was done in the period when a soldier had to arm himself. Its use was taught in the Dardi school of Italian fencing and others, and was influential on the classical rapier fencing of the 17th century. The equivalent Spanish term, ''espada ropera'' ("dress sword") is seen as the origin of the term '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Espada Ropera
A rapier () is a type of sword originally used in Spain (known as ' -) and Italy (known as ''spada da lato a striscia''). The name designates a sword with a straight, slender and sharply pointed two-edged long blade wielded in one hand. It was widely popular in Western Europe throughout the 16th and 17th centuries as a symbol of nobility or gentleman status. It is called because it was carried as an accessory to clothing, generally used for fashion and as a weapon for dueling, self-defense and as a military side arm. Its name is of Spanish origin and appears recorded for the first time in the '' Coplas de la panadera'', by Juan de Mena, written approximately between 1445 and 1450: As fencing spread throughout Western Europe, important sources for rapier fencing arose in Spain, known under the term ("dexterity"), in Italy and France. The French small sword or court sword of the 18th century was a direct continuation of this tradition of fencing. Rapier fencing forms part o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English Civil War
The English Civil War or Great Rebellion was a series of civil wars and political machinations between Cavaliers, Royalists and Roundhead, Parliamentarians in the Kingdom of England from 1642 to 1651. Part of the wider 1639 to 1653 Wars of the Three Kingdoms, the struggle consisted of the First English Civil War and the Second English Civil War. The Anglo-Scottish war (1650–1652), Anglo-Scottish War of 1650 to 1652 is sometimes referred to as the ''Third English Civil War.'' While the conflicts in the three kingdoms of England, Kingdom of Scotland, Scotland and Kingdom of Ireland, Ireland had similarities, each had their own specific issues and objectives. The First English Civil War was fought primarily over the correct balance of power between Parliament of England, Parliament and Charles I of England, Charles I. It ended in June 1646 with Royalist defeat and the king in custody. However, victory exposed Parliamentarian divisions over the nature of the political settlemen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mary Rose
The ''Mary Rose'' was a carrack in the English Tudor navy of Henry VIII of England, King Henry VIII. She was launched in 1511 and served for 34 years in several wars against France, Scotland, and Brittany. After being substantially rebuilt in 1536, she saw her last action on 1545. She led the attack on the galleys of a French invasion fleet, but sank off Spithead in the Solent, the strait north of the Isle of Wight. The wreck of the ''Mary Rose'' was located in 1971 and was raised on 11 October 1982 by the Mary Rose Trust in one of the most complex and expensive maritime salvage projects in history. The surviving section of the ship and thousands of recovered artefacts are of great value as a Tudor period time capsule. The excavation and raising of the ''Mary Rose'' was a milestone in the field of maritime archaeology, comparable in complexity and cost to the raising of the 17th-century Swedish warship ''Vasa (ship), Vasa'' in 1961. The ''Mary Rose'' site is designated under ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |