|
British Expedition To Tibet
The British expedition to Tibet, also known as the Younghusband expedition, began in December 1903 and lasted until September 1904. The expedition was effectively a temporary invasion by British Indian Army, British Indian Armed Forces under the auspices of the Tibet Frontier Commission, whose purported mission was to establish diplomatic relations and resolve the dispute over the border between Tibet and Kingdom of Sikkim, Sikkim.Landon, P. (1905). ''The Opening of Tibet'' Doubleday, Page & Co, New York. In the nineteenth century, the British had conquered Konbaung dynasty, Burma and Sikkim, with the whole southern flank of Tibet coming under the control of the British Raj, British Indian Empire. Tibet was ruled by the 13th 13th Dalai Lama, Dalai Lama under the Ganden Phodrang government as a Himalayas, Himalayan state under the Tibet under Qing rule, protectorate (or suzerainty) of the Chinese Qing dynasty until the 1911 Revolution, after which a Tibet (1912–1951), period of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Game
The Great Game was a rivalry between the 19th-century British Empire, British and Russian Empire, Russian empires over influence in Central Asia, primarily in Emirate of Afghanistan, Afghanistan, Qajar Iran, Persia, and Tibet. The two colonial empires used military interventions and diplomatic negotiations to acquire and redefine territories in Central Asia, Central and South Asia. Russia Russian Turkestan, conquered Turkestan, and Britain expanded and set the borders of British India. By the early 20th century, a line of independent states, tribes, and monarchies from the shore of the Caspian Sea to the Eastern Himalayas were made into protectorates and territories of the two empires. Though the Great Game was marked by distrust, diplomatic intrigue, and regional wars, it never erupted into a full-scale war directly between Russian and British colonial forces. However, the two nations battled in the Crimean War from 1853 to 1856, which affected the Great Game. The Russian and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1911 Revolution
The 1911 Revolution, also known as the Xinhai Revolution or Hsinhai Revolution, ended China's last imperial dynasty, the Qing dynasty, and led to the establishment of the Republic of China (ROC). The revolution was the culmination of a decade of agitation, revolts, and uprisings. Its success marked the collapse of the Chinese monarchy, the end of over two millennia of imperial rule in China and the 200-year reign of the Qing, and the beginning of China's early republican era. The Qing had struggled for a long time to reform the government and resist foreign aggression, but the program of reforms after 1900 was opposed by conservatives in the Qing court as too radical and by reformers as too slow. Several factions, including underground anti-Qing groups, revolutionaries in exile, reformers who wanted to save the monarchy by modernizing it, and activists across the country debated how or whether to overthrow the Qing dynasty. The flash-point came on 10 October 1911, with th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kashmir
Kashmir ( or ) is the Northwestern Indian subcontinent, northernmost geographical region of the Indian subcontinent. Until the mid-19th century, the term ''Kashmir'' denoted only the Kashmir Valley between the Great Himalayas and the Pir Panjal Range. The term has since also come to encompass a larger area that includes the Indian-administered territories of Jammu and Kashmir (union territory), Jammu and Kashmir and Ladakh, the Pakistani-administered territories of Azad Kashmir and Gilgit-Baltistan, and the Chinese-administered territories of Aksai Chin and the Trans-Karakoram Tract. Quote: "Kashmir, region of the northwestern Indian subcontinent. It is bounded by the Uygur Autonomous Region of Xinjiang to the northeast and the Tibet Autonomous Region to the east (both parts of China), by the Indian states of Himachal Pradesh and Punjab to the south, by Pakistan to the west, and by Afghanistan to the northwest. The northern and western portions are administered by Pakistan a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Punjab
Punjab (; ; also romanised as Panjāb or Panj-Āb) is a geopolitical, cultural, and historical region in South Asia. It is located in the northwestern part of the Indian subcontinent, comprising areas of modern-day eastern Pakistan and northwestern India. Pakistan's major cities in Punjab are Lahore, Faisalabad, Rawalpindi, Gujranwala, Multan, Sialkot, and Bahawalpur, while India’s are Ludhiana, Amritsar, Chandigarh, Jalandhar, Patiala, Mohali, and Bathinda. Punjab grew out of the settlements along the five rivers, which served as an important route to the Near East as early as the ancient Indus Valley civilization, dating back to , followed by migrations of the Indo-Aryan peoples. Agriculture has been the chief economic feature of the Punjab and formed the foundation of Punjabi culture. The Punjab emerged as an important agricultural region, especially following the Green Revolution during the mid-1960s to the mid-1970s, and has been described as the " breadbask ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kumaon Division
Kumaon (; , ; historically romanised as KemāonJames Prinsep (Editor)John McClelland ) is a List of divisions in India, revenue and administrative division in the Indian state of Uttarakhand. It spans over the eastern half of the state and is bounded on the north by Tibet, on the east by Nepal, on the south by the state of Uttar Pradesh, and on the west by Garhwal Division, Garhwal. Kumaon comprises six districts of the state: Almora district, Almora, Bageshwar district, Bageshwar, Champawat district, Champawat, Nainital district, Nainital, Pithoragarh district, Pithoragarh and Udham Singh Nagar district, Udham Singh Nagar. Historically known as Manaskhand and then Kurmanchal, the Kumaon region has been ruled by several dynasties over the course of history; most notably the Katyuri kings, Katyuris and the Chand kings, Chands. The Kumaon division was established in 1816, when the British reclaimed this region from the Gorkha Kingdom, Gorkhas, who had annexed the erstwhile Kumaon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Map Of Lhasa, Tibet (Thibet) And The Himalayas In 1885 From 12 Of 'The Imperial Gazetteer Of India
A map is a symbolic depiction of interrelationships, commonly spatial, between things within a space. A map may be annotated with text and graphics. Like any graphic, a map may be fixed to paper or other durable media, or may be displayed on a transitory medium such as a computer screen. Some maps change interactively. Although maps are commonly used to depict geographic elements, they may represent any space, real or fictional. The subject being mapped may be two-dimensional such as Earth's surface, three-dimensional such as Earth's interior, or from an abstract space of any dimension. Maps of geographic territory have a very long tradition and have existed from ancient times. The word "map" comes from the , wherein ''mappa'' meant 'napkin' or 'cloth' and ''mundi'' 'of the world'. Thus, "map" became a shortened term referring to a flat representation of Earth's surface. History Maps have been one of the most important human inventions for millennia, allowing humans t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tibet Medal
The Tibet Medal was authorised in February 1905 for all members of the British expedition to Tibet, Tibet Mission and accompanying troops who served at or beyond Siliguri from 13 December 1903, to 23 September 1904. The obverse of the medal, designed by George William de Saulles, G. W. de Saulles, shows the left-facing bust of Edward VII in Field Marshal's uniform and the legend 'EDWARDVS VII KAISAR-I-HIND'.The reverse, designed by Ernest Gillick, E. G. Gillick, depicts the Potala (winter palace of the Dalai Lamas) in Lhasa on top of the red hill with the words 'TIBET 1903–04' below.The suspender is of the swivelling ornate scroll type.The clasp 'Gyantse Dzong#British expedition to Tiber, GYANTSE' was given to those present in operations between 3 May and 6 July 1904, in or near Gyantse Dzong, Gyantse Fortress.Both silver and bronze medals were issued named to the recipient on the rim in a cursive, cursive script.The wide ribbon is maroon, flanked by narrow white, and wider gre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
China Proper
China proper, also called Inner China, are terms used primarily in the West in reference to the traditional "core" regions of China centered in the southeast. The term was first used by Westerners during the Manchu people, Manchu-led Qing dynasty to describe the distinction between the historical "Han lands" ( zh, t=漢地, i.e. regions long dominated by the majority Han Chinese, Han population) and the "frontier" regions of China where more ethnic minorities in China, non-Han ethnic minorities and newer foreign immigrants (e.g. Russians) reside, sometimes known as "Outer China". There is no fixed extent for China ''proper'', as many administrative, cultural, and linguistic shifts have occurred in History of China, Chinese history. One definition refers to the original area of Chinese civilization, the Zhongyuan, Central Plain (in the North China Plain); another to the Eighteen Provinces of the Qing dynasty. There was no direct translation for "China ''proper''" in the Chinese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mongolia Under Qing Rule
Mongolia under Qing rule was the rule of the Manchu-led Qing dynasty of China over the Mongolian Plateau, including the four Outer Mongolian aimags ( "leagues") and the six Inner Mongolian aimags from the 17th century to the end of the dynasty. The term "Mongolia" is used here in the broader historical sense, and includes an area much larger than the modern-day state of Mongolia. By the early 1630s Ligdan Khan saw much of his power weakened due to the disunity of the Mongol tribes. He was subsequently defeated by the Later Jin dynasty and died soon afterwards. His son Ejei handed the Yuan imperial seal over to Hong Taiji in 1635, thus ending the rule of the Northern Yuan dynasty in Inner Mongolia. However, the Khalkha Mongols in Outer Mongolia continued to rule until they were overrun by the Dzungar Khanate in 1690, and they submitted to the Qing dynasty in 1691. The Qing dynasty ruled Inner and Outer Mongolia for over 200 years. During this period, Qing rulers establishe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lhasa
Lhasa, officially the Chengguan District of Lhasa City, is the inner urban district of Lhasa (city), Lhasa City, Tibet Autonomous Region, Southwestern China. Lhasa is the second most populous urban area on the Tibetan Plateau after Xining and, at an altitude of , Lhasa is one of the List of highest large cities, highest cities in the world. The city has been the religious and administrative capital of Tibet since the mid-17th century. It contains many culturally significant Tibetan Buddhism, Tibetan Buddhist sites such as the Potala Palace, Jokhang Temple and Norbulingka Palaces. Toponymy Lhasa literally translates to "place of gods" ( , god; , place) in the Lhasa Tibetan, Tibetan language. Chengguan literally translates to "urban gateway" ( zh, s=城关, p=Chéngguān) in the Chinese language. Ancient Tibetan documents and inscriptions demonstrate that the place was called Rasa (), which meant "goat's place", as it was a herding site. The name was changed to Lhasa, which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
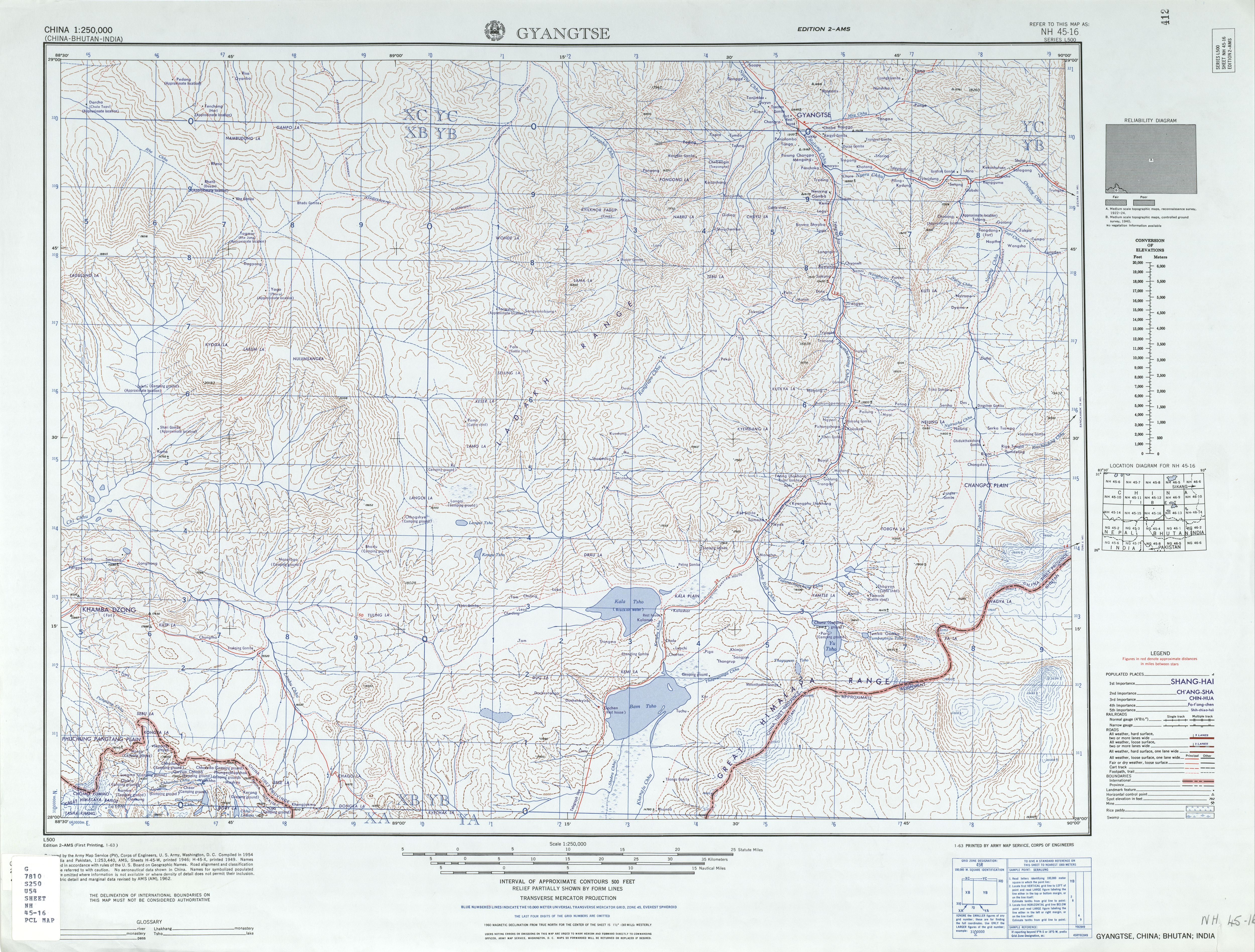
Gyantse
Gyantse, officially Gyangzê Town (also spelled Gyangtse; ; ), is a town located in Gyantse County, Shigatse Prefecture, Tibet Autonomous Region, China. It was historically considered the third largest and most prominent town in Tibet (after Lhasa and Shigatse), but there are now at least ten larger Tibetan cities. History In 1904, the British expedition to Tibet reached Gyantse on 11 April. The town's garrison had already fled, and the expedition's members entered the town bloodlessly through the front gates, which were opened for them, and occupied Gyantse. After the town was occupied, several British officers visited the Palcho Monastery and seized several statues and scrolls. During the occupation, the town's inhabitants continued to go about their business, and the expedition's medical officer, Herbert James Walton, attended to their medical needs, including performing several operations to correct the common problem of cleft palates. The expedition's officers spent tim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |