|
British Columbia Treaty Process
The British Columbia Treaty Process (BCTP) is a land claims negotiation process started in 1993 to resolve outstanding issues, including claims to un-extinguished indigenous rights, with British Columbia's First Nations. Three treaties have been implemented under the BCTP. The '' Nisga'a Final Agreement'' is considered separate from the Treaty Process because those negotiations began before the BC treaty process was started, and it has been called a blueprint for the current process. To represent the interests of First Nations involved with the process, the First Nations Summit was created. There are officially 60% of First Nations bands in the process, but only 20% are said to be making progress. About 40% of First Nations are not involved in the treaty process. History Previous negotiations Because the Royal Proclamation of 1763 stated that the Crown must negotiate and sign treaties with the Indigenous people before land could be ceded to a colony, the Numbered Treaties we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indigenous Land Claims In Canada
Indigenous peoples in Canada demand to have their land rights and their Aboriginal titles respected by the Canadian government. These outstanding land claims are some of the main political issues facing Indigenous peoples today. The Government of Canada started recognizing Indigenous land claims in 1973. Federal policy divided the claims in two categories: comprehensive claims and specific claims. Comprehensive claims deal with Indigenous rights of Métis, First Nations and Inuit communities that did not sign treaties with the Government of Canada. Specific claims, on the other hand, are filed by First Nations communities over Canada's breach of the Numbered Treaties, the ''Indian Act'' or any other agreements between the Crown and First Nations. Comprehensive claims Comprehensive claims are assertions of Aboriginal title by Indigenous groups over their ancestral lands and territories. Following the 1973 Calder decision, in which the existence of Aboriginal title was first r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aboriginal Title
Aboriginal title is a common law doctrine that the Indigenous land rights, land rights of indigenous peoples to customary land, customary tenure persist after the assumption of sovereignty to that land by another Colonization, colonising state. The requirements of proof for the recognition of aboriginal title, the content of aboriginal title, the methods of extinguishing aboriginal title, and the availability of compensation in the case of extinguishment vary significantly by jurisdiction. Nearly all jurisdictions are in agreement that aboriginal title is Alienation (property law), inalienable, and that it may be held Individual and group rights, either individually or collectively. Aboriginal title is also referred to as indigenous title, native title (Native title in Australia, in Australia), original Indian title (Aboriginal title in the United States, in the United States), and customary title (in New Zealand). Aboriginal title jurisprudence is related to indigenous rights, i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temexw Treaty Association
The Te'mexw Treaty Association (from Halkomelem 'land, earth') handles Treaty negotiations in the BC Treaty Process for a number of First Nations located in the northern Strait of Georgia of British Columbia. The members of the association are former signatories of the Douglas Treaties, a group of treaties signed in the 1850s. Treaty Process The Treaty group has reached Stage 5 in the BC Treaty Process. Membership See also *List of tribal councils in British Columbia The following is a List of tribal councils in British Columbia. Treaty Council organizations are not listed. List of tribal councils Defunct: * Fraser Canyon Indian Administration ( Nlaka'pamux) * In-SHUCK-ch Nation * Tsimshian Tribal Coun ... References First Nations organizations in British Columbia Southern Vancouver Island {{Treaty-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fraser River
The Fraser River () is the longest river within British Columbia, Canada, rising at Fraser Pass near Blackrock Mountain (Canada), Blackrock Mountain in the Rocky Mountains and flowing for , into the Strait of Georgia just south of the City of Vancouver. The river's annual discharge at its mouth is or , and each year it discharges about 20 million tons of sediment into the ocean. Naming The river is named after Simon Fraser (explorer), Simon Fraser, who led an expedition in 1808 on behalf of the North West Company from the site of present-day Prince George, British Columbia, Prince George almost to the mouth of the river. The river's name in the Halqemeylem (Upriver Halkomelem) language is , often seen archaically as Staulo, and has been adopted by the Halkomelem-speaking peoples of the Lower Mainland as their collective name, . The river's name in the Dakelh language is . The Chilcotin language, ''Tsilhqot'in'' name for the river, not dissimilar to the ''Dakelh'' name, is , ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
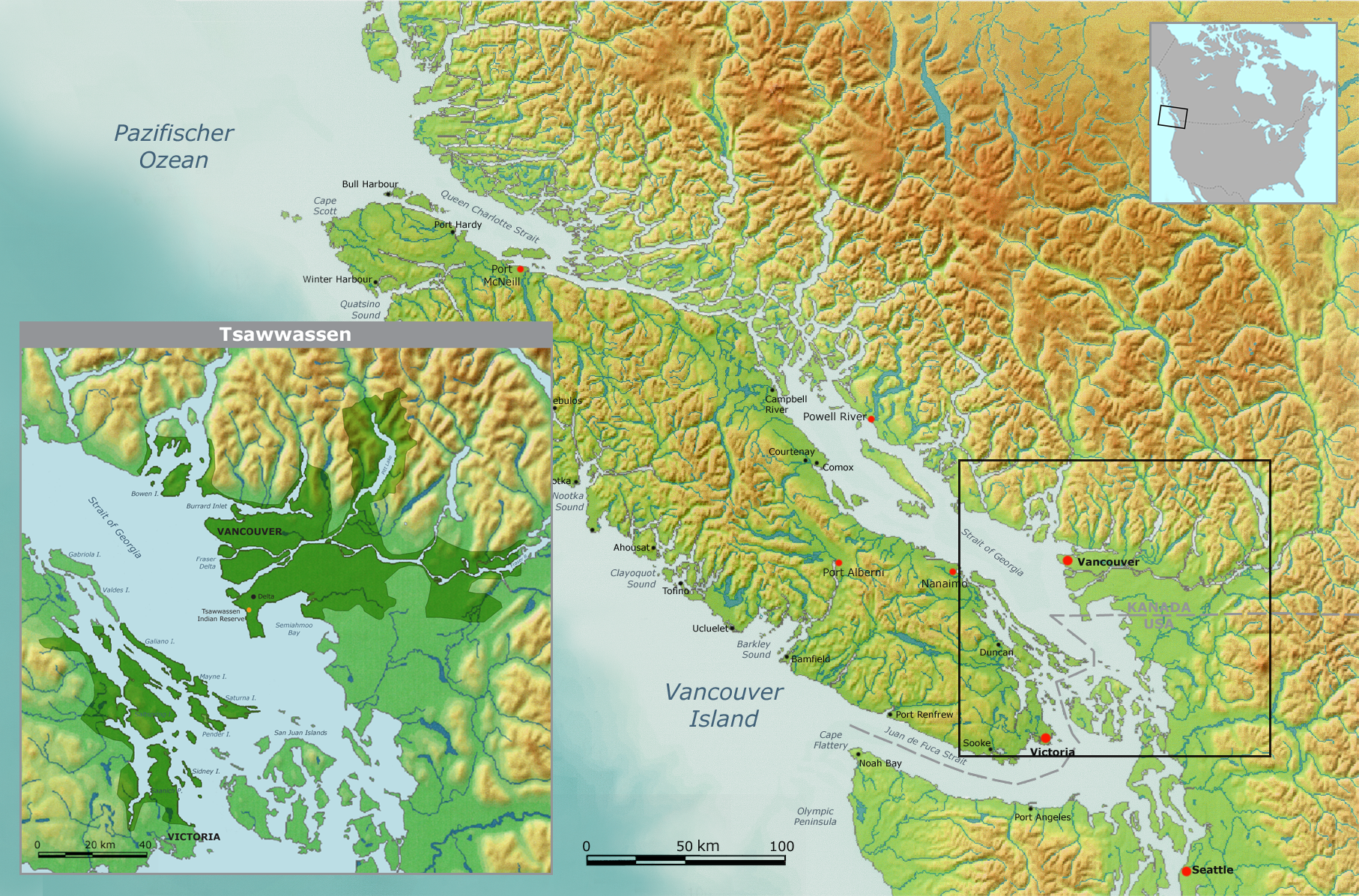
Tsawwassen First Nation
The Tsawwassen First Nation (, ) is a First Nations government whose lands are located in the Greater Vancouver area of the Lower Mainland of British Columbia, Canada, close to the South Arm of the Fraser River and just north of the international boundary with the United States at Point Roberts, Washington. Tsawwassen First Nation lists its membership at 413 people, nearly half of whom live on the lands. Overview Like most First Nations people of the West Coast, the Tsawwassen lived in family groups and inhabited longhouses. They carved no totem poles but ornate house posts, masks, tools with carvings etc. Also they processed cedar fibers and goat hair into dresses and headgear. Also, the wooden building material, firewood, canoes and dresses. Using tidal traps, fishing, nets and harpoons they hunted fish, especially salmon. They also harvested oysters, crabs and other sea creatures. The salmon was considered a supernatural being, and therefore had to be hunted and eaten in a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lheidli Tʼenneh
The Lheidli T'enneh Band also known as the Lheidli T'enneh First Nation and historically known as the Fort George Indian Band is the First Nations band government for the Lheidli T'enneh, a subgroup of the Dakelh people whose traditional territory includes the City of Prince George, British Columbia. The name means "The People from the confluence of the two rivers" in the Carrier language referring to how the Nechako River enters the Fraser River at Prince George. The Lheidli T'enneh are Carrier people. Their traditional language, now spoken only by a few people, is a dialect of the Carrier language. The Lheidli T'enneh did not have permanent settlements in what is modern day Prince George until the arrival of the HBC post Fort George. Temporary and seasonal settlements were used across the traditional territory and archeological evidence of fishing camps along the Nechako and Fraser rivers as well as the Beaverly area. 19th and 20th centuries HBC Trading Post The Northwe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2002 British Columbia Aboriginal Treaty Referendum
The BC Treaty Referendum was a province-wide referendum on First Nations treaty rights in British Columbia, Canada. In the spring of 2002 the Premier Gordon Campbell and the British Columbia Liberal Party government sent out ballots to registered voters in the province. 35.84% of ballots (763,480) were received by Elections BC by the deadline of May 15. Over 80 per cent of those ballots indicated agreement with all eight principles. Between 55,000 and 60,000 votes on each question were rejected. Questions posed The referendum proposed eight principles that voters were asked to either support or oppose: 1. Private property should not be expropriated for treaty settlements. (Yes/No) 2. The terms and conditions of leases and licences should be respected; fair compensation for unavoidable disruption of commercial interests should be ensured. (Yes/No) 3. Hunting, fishing and recreational opportunities on Crown land should be ensured for all British Columbians. (Yes/No) 4. Park ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BC Liberal Party
BC United (BCU), known from 1903 until 2023 as the British Columbia Liberal Party or BC Liberals, is a provincial political party in British Columbia, Canada. The party has been described as conservative, neoliberal, and occupying a centre-right position on the left–right political spectrum. The party commonly describes itself as a "free enterprise coalition" and draws support from members of both the federal Liberal and Conservative parties. From 1991 to 2024, BC United was the main centre-right opposition to the centre-left New Democratic Party (NDP). Once affiliated with the Liberal Party of Canada, the British Columbia Liberal Party became independent in 1987. The party changed its name to BC United on April 12, 2023. Until the 1940s, British Columbia politics were dominated by the Liberal Party and rival Conservative Party. The Liberals formed government from 1916 to 1928 and again from 1933 to 1941. From 1941 to 1952, the two parties governed in a coalition (led by a Li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuu-chah-nulth Tribal Council
The Nuu-chah-nulth Tribal Council is a First Nations Tribal Council in the Canadian province of British Columbia, located on the west coast of Vancouver Island. The organization is based in Port Alberni, British Columbia. History The different Nuu-chah-nulth tribes share many aspects of their language and cultural traditions. Nuu-chah-nulth peoples founded an organization called the West Coast Allied Tribes in 1958. In 1973, they incorporated a non-profit society called the West Coast District Society of Indian Chiefs, also known as the West Coast District Council. That organization changed its named to the Nuu-chah-nulth Tribal Council in 1979. Member First Nations Southern region *Ditidaht First Nation (Niitiinaʔatḥ) * Huu-ay-aht First Nation (Huuʕiiʔatḥ) * Hupacasath First Nation (Huupač̓asʔatḥ) * Tseshaht First Nation (C̓išaaʔatḥ) * Uchucklesaht First Nation (Ḥuučuqƛisʔatḥ) Central region *Ahousaht First Nation (ʕaaḥuusʔatḥ) * Hesquiaht ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sliammon First Nation
The Tla'amin First Nation ( Comox language: ɬəʔamɛn), formerly Sliammon Indian Band or Sliammon First Nation, is a First Nations self governing nation whose lands and traditional territories are located on the upper Sunshine Coast in southwestern British Columbia, Canada. The Tla'amin are closely related to the Klahoose and Homalco peoples and have shared their adjoining territories; formerly all three as well as K'omoks were grouped collectively as the Mainland Comox due to their shared language. They have been part of the Coast Salish indigenous peoples of the western coast of Canada since ancient times. The territory of the Tla'amin people extends from the vicinity of Stillwater and the northern part of Texada Island, northward along the Malaspina and Gifford Peninsulas to the southern area of Homfray Channel and part of Cortes Island, including also the smaller off-shore islands such as Hernando, Savary and Harwood as well as Powell, Goat and Haslam Lakes. Their ances ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Delgamuukw V British Columbia
''Delgamuukw v British Columbia'', Case citation, [1997] 3 SCR 1010, also known as ''Delgamuukw v The Queen'', ''Delgamuukw-Gisday’wa'', or simply ''Delgamuukw'', is a ruling by the Supreme Court of Canada that contains its first comprehensive account of Aboriginal title (a distinct kind of Aboriginal right) in Canada. The Gitxsan and Wetʼsuwetʼen, Wet’suwet’en peoples claimed Aboriginal title and jurisdiction over 58,000 square kilometers in northwest British Columbia. The Plaintiff, plaintiffs lost the case at trial, but the Supreme Court of Canada allowed the appeal in part and ordered a new trial because of deficiencies relating to the pleadings and treatment of evidence. In this decision, the Court went on to describe the "nature and scope" of the protection given to Aboriginal title under Section 35 of the Constitution Act, 1982, section 35 of the ''Constitution Act, 1982'', defined how a claimant can prove Aboriginal title, and clarified how the justification test fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |