|
Bristol And Exeter Railway Locomotives
The Bristol and Exeter Railway locomotives worked trains on the Bristol and Exeter Railway from 1 May 1849 until the railway was Consolidation (business), amalgamated with the Great Western Railway on 1 January 1876. The Great Western Railway had leased the Bristol and Exeter Railway from its opening and provided the locomotives up until 1849. The Bristol and Exeter Railway in turn provided the broad gauge locomotive power on most of the railways with which it had junctions: * Portishead Railway, Bristol and Portishead Port and Pier Railway * Somerset Central Railway * West Somerset Railway and Minehead Railway * Devon and Somerset Railway * Exeter and Crediton Railway Engineering The railway established workshops at Bristol Temple Meads railway station in September 1854, the site later being known as Bristol Bath Road TMD, Bath Road. Engine sheds were provided at major stations and on some branches including at Taunton railway station and Exeter St Davids railway station. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BER 2002 Exeter
BER may refer to: Science and technology Biology and medicine * Basal electrical rhythm, spontaneous rhythmic slow action potentials that some smooth muscles of the GI tract display * Base excision repair, a DNA repair pathway * Benign early repolarization, a heart arrhythmia * Blossom end rot, a plant disorder Computing * Basic Encoding Rules, a set of rules for encoding data * Bit error rate, the ratio between the number of incorrect bits transmitted to the total Places * Bermuda (IOC and UNDP code), a British overseas territory * Bohai Economic Rim, the economic region surrounding Tianjin, China Transport * Air Berlin (ICAO code: BER), a defunct German airline * Berlin Brandenburg Airport (IATA code: BER), Germany * Berlin station (Connecticut) (Amtrak code: BER), United States Other uses * Beyond economic repair, a rating of a damaged item * Block Exemption Regulation, published by the European Commission regarding European Union competition law * Building the Education Revol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
4-2-4 (locomotive)
Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, represents the wheel arrangement of four leading wheels on two axles, two powered driving wheels on one axle, and four trailing wheels on two axles. The configuration was only used for tank engines, which is noted by adding letter suffixes to the configuration, such as for a conventional side-tank locomotive, for a saddle-tank locomotive, for a well-tank locomotive and for a rack-equipped tank locomotive. Overview This wheel arrangement was only used on various tank locomotive configurations. Eight 4-2-4 well- and back-tank locomotives which entered service on the Bristol and Exeter Railway in 1853 appear to have been the first with this wheel arrangement. The engine was designed by James Pearson (engineer), James Pearson, the railway company's engineer, and featured single large flangeless driving wheels between two supporting four-wheeled bogies. The water was carried in both well- and back-tanks, leav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bristol And Exeter Railway 2-4-0T Locomotives
Bristol () is a City status in the United Kingdom, cathedral city, unitary authority area and ceremonial county in South West England, the most populous city in the region. Built around the River Avon, Bristol, River Avon, it is bordered by the ceremonial counties of Gloucestershire to the north and Somerset to the south. The county is in the West of England combined authority area, which includes the Greater Bristol area (List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, eleventh most populous urban area in the United Kingdom) and nearby places such as Bath, Somerset, Bath. Bristol is the second largest city in Southern England, after the capital London. Iron Age hillforts and Roman villas were built near the confluence of the rivers River Frome, Bristol, Frome and Avon. Bristol received a royal charter in 1155 and was historic counties of England, historically divided between Gloucestershire and Somerset until 1373 when it became a county corporate. From the 13th to the 18th centur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
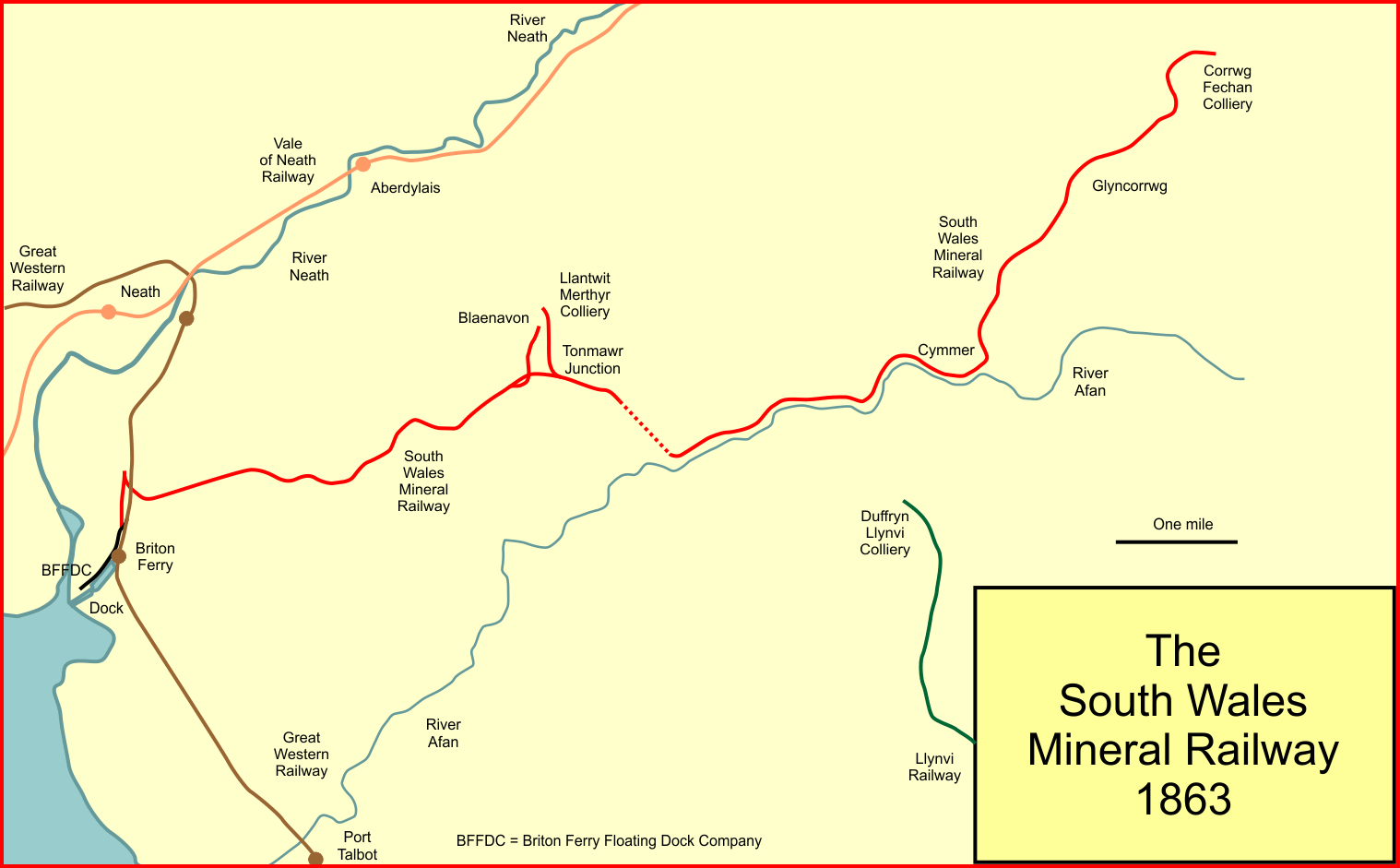
South Wales Mineral Railway
The South Wales Mineral Railway (SWMR) was a railway built to serve collieries in the upper Afan Valley, and bring their output to a dock at Briton Ferry, in South Wales. It opened in stages, in 1861 and 1863. It was built on the broad gauge and had steep gradients, including a rope worked incline near Briton Ferry. Always short of money, it was worked by a coal company for some years and then by the Great Western Railway from 1908. It was absorbed by that company in 1923. A tunnel collapse in 1947 closed the western section of the network, but by then it was connected to an alternative route via Port Talbot. A local passenger service was operated between 1918 and 1930, continuing for the use of miners until 1964. The line closed completely in 1970. Beginnings Towards the end of the 18th century, collieries began to be developed in the Cymmer district were opened. Coal was carried to wharves on the Bristol Channel on the backs of pack animals, although a stone-block sleeper tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GWR Swindon Class
The Great Western Railway Swindon Class were broad gauge 0-6-0 locomotives built for goods train work. This class entered service between November 1865 and March 1866, and were withdrawn between June 1887 and the end of the GWR broad gauge in May 1892. The entire class was sold to the Bristol and Exeter Railway between July 1872 and September 1874 and were numbered 96-109, but returned to the GWR when that railway and the B&ER amalgamated on 1 January 1876. The locomotives were then renumbered 2077-2090; their names were not restored. Locomotives References * * * {{GWR Locomotives Swindon Swindon () is a town in Wiltshire, England. At the time of the 2021 Census the population of the built-up area was 183,638, making it the largest settlement in the county. Located at the northeastern edge of the South West England region, Swi ... 0-6-0 locomotives C steam locomotives Broad gauge (7 feet) railway locomotives Railway locomotives introduced in 1865 Bristol and E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bristol And Exeter Railway 0-4-0T Locomotives
The Bristol and Exeter Railway 0-4-0T locomotives were five small 0-4-0T locomotives built for shunting by the Bristol and Exeter Railway. On 1 January 1876 the Bristol and Exeter Railway was amalgamated with the Great Western Railway, after which the locomotives were given new numbers. Broad gauge Two small 0-4-0T locomotives built for shunting by the Bristol and Exeter Railway. * 91 (1872 – 1880) GWR No. 2094 * 92 (1874 – 1881) GWR No. 2095 These were the smallest locomotives built for the Bristol and Exeter Railway and were unique among broad gauge locomotives in having outside cylinders. Standard gauge Three small 0-4-0T locomotives built for shunting by the Bristol and Exeter Railway The Bristol and Exeter Railway (B&ER) was an English railway company formed to connect Bristol and Exeter. It was built on the broad gauge and its engineer was Isambard Kingdom Brunel. It opened in stages between 1841 and 1844. It was allied wi .... * 93 (1875 – 1880) GWR No. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bristol And Exeter Railway 2-4-0 Locomotives
The Bristol and Exeter Railway 2-4-0 locomotives were two classes of broad gauge steam locomotives. On 1 January 1876 the Bristol and Exeter Railway was amalgamated with the Great Western Railway, after which the locomotives were given new numbers. They were used as pilot engines at large stations and on other light duties shared with the GWR Hawthorn Class. List of locomotives Broad gauge The first ten locomotives were introduced in 1870 to replace 1849 built 4-2-2s. The last of the locomotives were withdrawn at the end of the broad gauge on 20 May 1892. * 2 (1872 – 1888) GWR No. 2015 * 4 (1871 – 1892) GWR No. 2016 * 5 (1871 – 1892) GWR No. 2017 * 6 (1870 – 1890) GWR No. 2018 * 8 (1872 – 1889) GWR No. 2019 * 14 (1870 – 1892) GWR No. 2020 * 43 (1871 – 1892) GWR No. 2021 * 44 (1870 – 1888) GWR No. 2022 * 45 (1870 – 1888) GWR No. 2023 * 46 (1870 – 1889) GWR No. 2024 Convertible Three more locomotives were built in 1874. These were designed to be convert ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bristol And Exeter Railway 0-6-0T Locomotives
The Bristol and Exeter Railway 0-6-0T locomotives were two different types of locomotives built for the Bristol and Exeter Railway. On 1 January 1876, the Bristol and Exeter Railway was amalgamated with the Great Western Railway, after which the locomotives were given new numbers. List of locomotives Broad gauge Two small broad gauge locomotives. The first had a 950 gallon tank, the second had a larger 1,200 gallon one. * 75 (1866 – 1888) GWR No. 2092 * 76 (1867 – 1890) GWR No. 2093 Standard gauge Two standard gauge locomotives were built for the Culm Valley Light Railway which was then under construction. They were operated on the line until 1881, when they were superseded by 1298 and 1300, two locomotives which had started life as South Devon Railway locomotives South Devon Railway locomotives were broad gauge locomotives that operated over the South Devon Railway Company, South Devon Railway, Cornwall Railway, and West Cornwall Railway in England. They were, at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bristol And Exeter Railway 4-4-0ST Locomotives
The 26 Bristol and Exeter Railway 4-4-0ST locomotives were broad gauge steam locomotives. They first entered service in 1855 and the last was withdrawn in 1892. The Bristol and Exeter Railway was amalgamated into the Great Western Railway on 1 January 1876. The locomotives were built in four batches, each by a different builder, with variations between them, noticeably in the size of the saddle tank. List of locomotives 1859 Rothwell locomotives Five locomotives built by Rothwell and Company with gallon saddle tanks and wheelbase. * 47 (1855–1879) GWR No. 2028 * 48 (1855–1879) GWR No. 2029 * 49 (1855–1884) GWR No. 2030 * 50 (1855–1884) GWR No. 2031 * 51 (1855–1882) GWR No. 2032 * 52 (1855–1880) GWR No. 2033 1862 Beyer, Peacock locomotives Four locomotives built by Beyer Peacock with saddle tanks and wheelbase. * 61 (1862–1884) GWR No. 2034 * 62 (1862–1886) GWR No. 2035 * 63 (1862–1880) GWR No. 2036 * 64 (1862–1886) GWR No. 2037 1867 Vulcan Foundry loco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bristol And Exeter Railway 4-2-4T Locomotives
The 14 Bristol and Exeter Railway 4-2-4T locomotives were broad gauge 4-2-4T steam locomotives built to three different designs. The first entered service in 1853. The Bristol and Exeter Railway was consolidation (business), amalgamated into the Great Western Railway on 1 January 1876, and the last of the 4-2-4Ts was withdrawn in 1885. The distinctive designs by James Pearson (engineer), James Pearson, the railway company's engineer, featured single large flangeless driving wheels and two supporting bogies. The water was carried in both well and back tanks, leaving the boilers exposed in the same way as tender locomotives. The three types are distinguished by the size of driving wheel; the early wheels being replaced by smaller ones on later designs. List of locomotives 9 feet * 39 (1853–1868) * 40 (1853–1873) * 41 (1853–1873) * 42 (1854–1868) * 43 (1854–1871) * 44 (1854–1870) * 45 (1854–1870) * 46 (1854–1870) The first of Pearson's 4-2-4Ts were eight locom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bristol And Exeter Railway 2-2-2T Locomotives
The seven Bristol and Exeter Railway 2-2-2WT locomotives were small 2-2-2 well tank locomotives designed by James Pearson for working branch lines such as those to Tiverton and Clevedon, as well as acting as pilot locomotives at Bristol. The first was delivered in 1851, and the last withdrawn in 1880. On 1 January 1876, the Bristol and Exeter Railway was amalgamated with the Great Western Railway, after which the surviving locomotives were given new numbers. * R. B. Longridge and Company * 30 (1851 – 1876) * 31 (1851 – 1877) GWR No. 2054 * E. B. Wilson and Company * 32 (1851 – 1878) GWR No. 2055 * 33 (1851 – 1876) * 34 (1851 – 1875) * Rothwell and Company Rothwell, Hick and Rothwell was an engineering company in Bolton, England. Set up in 1822, the partners became interested in the production of steam locomotives after the Rainhill Trials. The company's first engine was ''Union'', a vertical b ... (14½ inch cylinders) * 57 (1859 – 1877) GWR No. 2056 * 5 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |