|
BrightSide Technologies
BrightSide Technologies Inc. (formerly ''Sunnybrook Technologies'') was a firm spun-out from the Structured Surface Physics Laboratory of the University of British Columbia, developing and commercializing electronic display technologies, specifically high brightness display technology called HDR. The privately held company also developed technology for capturing, processing, and storage of HDR images. BrightSide's headquarters were in Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada. It was acquired by Dolby Laboratories, Inc. in April 2007 for US$28 million. The chief executive officer of BrightSide Technologies Inc. was Richard MacKellar. The chief technology officer was Helge Seetzen, who went on to join Dolby as becoming director of HDR Technology at Dolby (2008 to 2010), before going on to found TandemLaunch, a Montreal-based technology incubator. The main electronic display technology developed by BrightSide was based on IMLED-LCD which consisted of a LCD with an array of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Private Company
A privately held company (or simply a private company) is a company whose Stock, shares and related rights or obligations are not offered for public subscription or publicly negotiated in their respective listed markets. Instead, the Private equity, company's stock is offered, owned, traded or exchanged privately, also known as "over-the-counter (finance), over-the-counter". Related terms are unlisted organisation, unquoted company and private equity. Private companies are often less well-known than their public company, publicly traded counterparts but still have major importance in the world's economy. For example, in 2008, the 441 list of largest private non-governmental companies by revenue, largest private companies in the United States accounted for $1.8 trillion in revenues and employed 6.2 million people, according to ''Forbes''. In general, all companies that are not owned by the government are classified as private enterprises. This definition encompasses both publ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helge Seetzen
Helge Seetzen (born June 23, 1978) is a German technologist and businessman known for imaging & multimedia research and commercialization. Seetzen was active in the development of high dynamic range imaging (HDR) technology and several of his patents cover aspects of this technology. He won the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada 2009 Innovation Challenge Award for his work with HDR Technology. Biography Seetzen left his native Germany to study physics at the University of British Columbia in 1998. He received BS and PhD degrees in physics and related disciplines from that university, where he first became active in imaging technology research that led to the development of HDR. Business career From 2002 to 2004, Seetzen was a co-founder and director of Sunnybrook Technologies, a Vancouver-based start-up developing electronic display technologies. In 2004, the firm split, and he became co-founder and Chief Technical Officer of BrightSide Technologies, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer-aided Design
Computer-aided design (CAD) is the use of computers (or ) to aid in the creation, modification, analysis, or optimization of a design. This software is used to increase the productivity of the designer, improve the quality of design, improve communications through documentation, and to create a database for manufacturing. Designs made through CAD software help protect products and inventions when used in patent applications. CAD output is often in the form of electronic files for print, machining, or other manufacturing operations. The terms computer-aided drafting (CAD) and computer-aided design and drafting (CADD) are also used. Its use in designing electronic systems is known as ''electronic design automation'' (''EDA''). In mechanical design it is known as ''mechanical design automation'' (''MDA''), which includes the process of creating a technical drawing with the use of computer software. CAD software for mechanical design uses either vector-based graphics to depict t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medicine
Medicine is the science and Praxis (process), practice of caring for patients, managing the Medical diagnosis, diagnosis, prognosis, Preventive medicine, prevention, therapy, treatment, Palliative care, palliation of their injury or disease, and Health promotion, promoting their health. Medicine encompasses a variety of health care practices evolved to maintain and restore health by the prevention (medical), prevention and treatment of illness. Contemporary medicine applies biomedical sciences, biomedical research, medical genetics, genetics, and medical technology to diagnosis (medical), diagnose, treat, and prevent injury and disease, typically through pharmaceuticals or surgery, but also through therapies as diverse as psychotherapy, splint (medicine), external splints and traction, medical devices, biologic medical product, biologics, and Radiation (medicine), ionizing radiation, amongst others. Medicine has been practiced since Prehistoric medicine, prehistoric times, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DR37-P
The DR37-P is an HDR monitor produced by BrightSide Technologies Inc. in 2005. It makes use of what BrightSide calls Individually Modulated LED (IMLED) technology. The targeted customers are industries like medical, CAD, film post-production, geophysical data Data ( , ) are a collection of discrete or continuous values that convey information, describing the quantity, quality, fact, statistics, other basic units of meaning, or simply sequences of symbols that may be further interpreted for ... or satellite imaging. References External links Reviewat bit-tech website Computer output devices Products introduced in 2005 {{Compu-hardware-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Contrast Ratio
The contrast ratio (CR) is a property of a display system, defined as the ratio of the luminance of the brightest shade (white) to that of the darkest shade (black) that the system is capable of producing. A high contrast ratio is a desired aspect of any display. It has similarities with dynamic range. There is no official, standardized way to measure contrast ratio for a system or its parts, nor is there a standard for defining "Contrast Ratio" that is accepted by any standards organization so ratings provided by different manufacturers of display devices are not necessarily comparable to each other due to differences in method of measurement, operation, and unstated variables. Manufacturers have traditionally favored measurement methods that isolate the device from the system, whereas other designers have more often taken the effect of the room into account. An ideal room would absorb all the light reflecting from a projection screen or emitted by a cathode-ray tube, and the on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luminance
Luminance is a photometric measure of the luminous intensity per unit area of light travelling in a given direction. It describes the amount of light that passes through, is emitted from, or is reflected from a particular area, and falls within a given solid angle. The procedure for conversion from spectral radiance to luminance is standardized by the CIE and ISO. Brightness is the term for the ''subjective'' impression of the ''objective'' luminance measurement standard (see for the importance of this contrast). The SI unit for luminance is candela per square metre (cd/m2). A non-SI term for the same unit is the nit. The unit in the Centimetre–gram–second system of units (CGS) (which predated the SI system) is the stilb, which is equal to one candela per square centimetre or 10 kcd/m2. Description Luminance is often used to characterize emission or reflection from flat, diffuse surfaces. Luminance levels indicate how much luminous power could be det ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plastic
Plastics are a wide range of synthetic polymers, synthetic or Semisynthesis, semisynthetic materials composed primarily of Polymer, polymers. Their defining characteristic, Plasticity (physics), plasticity, allows them to be Injection moulding, molded, Extrusion, extruded, or Compression molding, pressed into a diverse range of solid forms. This adaptability, combined with a wide range of other properties such as low weight, durability, flexibility, chemical resistance, low toxicity, and low-cost production, has led to their widespread use around the world. While most plastics are produced from natural gas and petroleum, a growing minority are produced from renewable resources like polylactic acid. Between 1950 and 2017, 9.2 billion metric tons of plastic are estimated to have been made, with more than half of this amount being produced since 2004. In 2023 alone, preliminary figures indicate that over 400 million metric tons of plastic were produced worldwide. If global trends ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluorescent Lamps
A fluorescent lamp, or fluorescent tube, is a low-pressure mercury-vapor gas-discharge lamp that uses fluorescence to produce visible light. An electric current in the gas excites mercury vapor, to produce ultraviolet and make a phosphor coating in the lamp glow. Fluorescent lamps convert electrical energy into visible light much more efficiently than incandescent lamps, but are less efficient than most LED lamps. The typical luminous efficacy of fluorescent lamps is 50–100 lumens per watt, several times the efficacy of incandescent bulbs with comparable light output (e.g. the luminous efficacy of an incandescent lamp may only be 16 lm/W). Fluorescent lamp fixtures are more costly than incandescent lamps because, among other things, they require a ballast to regulate current through the lamp, but the initial cost is offset by a much lower running cost. Compact fluorescent lamps (CFL) made in the same sizes as incandescent lamp bulbs are used as an energy-saving alt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
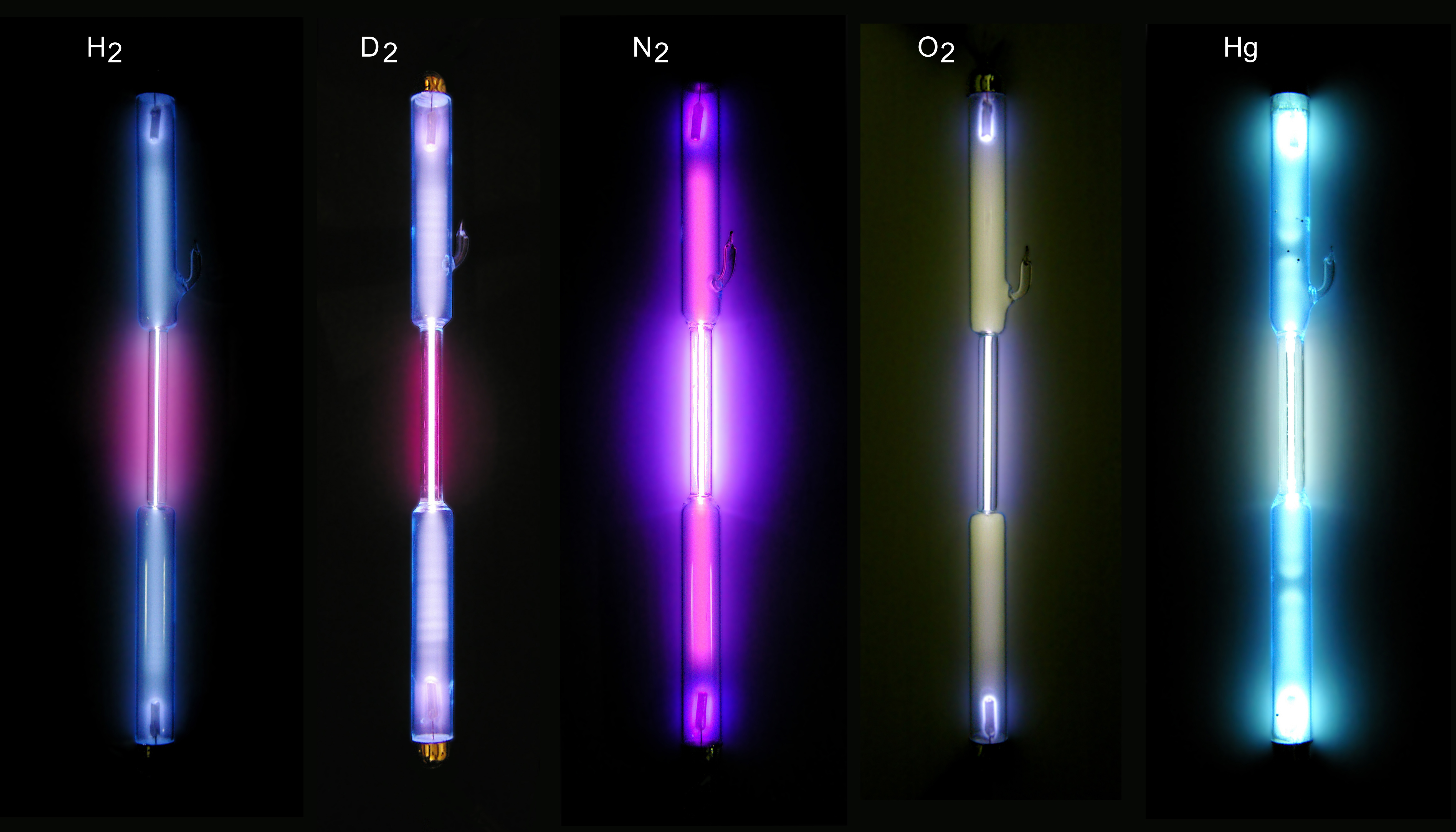
Cold Cathode
A cold cathode is a cathode that is not electrically heated by a Electrical filament, filament.A negatively charged electrode emits electrons or is the positively charged terminal. For more, see field emission. A cathode may be considered "cold" if it emits more electrons than can be supplied by thermionic emission alone. It is used in Gas discharge lamp, gas-discharge lamps, such as neon lamps, discharge tubes, and some types of vacuum tube. The other type of cathode is a hot cathode, which is heated by electric current passing through a Electrical filament, filament. A cold cathode does not necessarily operate at a low temperature: it is often heated to its operating temperature by other methods, such as the current passing from the cathode into the gas. Cold-cathode devices A cold-cathode vacuum tube does not rely on external heating of an electrode to provide thermionic emission of electrons. Early cold-cathode devices included the Geissler tube and Julius Plücker, Plucker ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Backlight
A backlight is a form of illumination used in liquid-crystal displays (LCDs) that provides light from the back or side of a display panel. LCDs do not produce light on their own, so they require illumination—either from available light, ambient light or a dedicated light source—to create a visible image. Backlights are commonly used in smartphones, computer monitors, and LCD televisions. They are also used in small displays, such as Watch, wristwatches, to enhance readability in low-light conditions. Typical light sources for backlights include light-emitting diodes (LEDs) and cold cathode fluorescent lamps (CCFLs). Simple types of LCDs, such as those used in pocket calculators, are built without an internal light source and rely on external light sources to make the display image visible to the user. However, most LCD screens are designed with an internal light source. These screens consist of multiple layers, with the backlight typically being the first layer from the bac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semiconductor
A semiconductor is a material with electrical conductivity between that of a conductor and an insulator. Its conductivity can be modified by adding impurities (" doping") to its crystal structure. When two regions with different doping levels are present in the same crystal, they form a semiconductor junction. The behavior of charge carriers, which include electrons, ions, and electron holes, at these junctions is the basis of diodes, transistors, and most modern electronics. Some examples of semiconductors are silicon, germanium, gallium arsenide, and elements near the so-called " metalloid staircase" on the periodic table. After silicon, gallium arsenide is the second-most common semiconductor and is used in laser diodes, solar cells, microwave-frequency integrated circuits, and others. Silicon is a critical element for fabricating most electronic circuits. Semiconductor devices can display a range of different useful properties, such as passing current more easil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |