|
Bridge Of Weir
Bridge of Weir is a village within the Renfrewshire council areas of Scotland, council area and wider counties of Scotland, historic county of Renfrewshire (historic), Renfrewshire in the west central Lowlands of Scotland. Lying within the Gryffe Valley, Bridge of Weir owes its name to the historic crossing point that it provided over the River Gryffe. The village was initially formed around industries such as cotton and leather, reliant on the power of the river. These industries brought about its expansion in the 18th century in land attached to the 15th century Ranfurly, Renfrewshire, Ranfurly Castle situated between the two established parishes of Kilbarchan and Houston and Killellan. A rail connection, as part of the Glasgow and South Western Railway, in the 1860s, significantly supported the village's development. Today Bridge of Weir serves largely as a dormitory settlement for nearby Glasgow and Paisley, Renfrewshire, Paisley, maintaining a commercial centre of its own a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Renfrewshire
Renfrewshire () (; ) is one of the 32 council areas of Scotland. Renfrewshire is located in the west central Lowlands. It borders East Renfrewshire, Glasgow, Inverclyde, North Ayrshire and West Dunbartonshire, and lies on the southern bank of the River Clyde. The current council area of Renfrewshire was established in 1996. The town of Paisley is the area's main settlement and centre of local government. The area also contains the historic county town of Renfrew. The council area has the same name as the historic county of Renfrewshire, which had been abolished for local government purposes in 1975, but the modern council area only covers the central part of the historic county. The eastern part of the pre-1975 county is covered by the East Renfrewshire council area, and the western part by the Inverclyde council area. The term Renfrewshire may also be used to refer to the larger historic county, which was established in the fifteenth century. The three council are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
River Gryfe, Bridge Of Weir - Geograph
A river is a natural stream of fresh water that flows on land or inside caves towards another body of water at a lower elevation, such as an ocean, lake, or another river. A river may run dry before reaching the end of its course if it runs out of water, or only flow during certain seasons. Rivers are regulated by the water cycle, the processes by which water moves around the Earth. Water first enters rivers through precipitation, whether from rainfall, the runoff of water down a slope, the melting of glaciers or snow, or seepage from aquifers beneath the surface of the Earth. Rivers flow in channeled watercourses and merge in confluences to form drainage basins, or catchments, areas where surface water eventually flows to a common outlet. Rivers have a great effect on the landscape around them. They may regularly overflow their banks and flood the surrounding area, spreading nutrients to the surrounding area. Sediment or alluvium carried by rivers shapes the landscape aro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Parliament
The Parliament of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland is the supreme legislative body of the United Kingdom, and may also legislate for the Crown Dependencies and the British Overseas Territories. It meets at the Palace of Westminster in London. Parliament possesses legislative supremacy and thereby holds ultimate power over all other political bodies in the United Kingdom and the Overseas Territories. While Parliament is bicameral, it has three parts: the sovereign, the House of Lords, and the House of Commons. The three parts acting together to legislate may be described as the King-in-Parliament. The Crown normally acts on the advice of the prime minister, and the powers of the House of Lords are limited to only delaying legislation. The House of Commons is the elected lower chamber of Parliament, with elections to 650 single-member constituencies held at least every five years under the first-past-the-post system. By constitutional convention, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fulling
Fulling, also known as tucking or walking ( Scots: ''waukin'', hence often spelt waulking in Scottish English), is a step in woollen clothmaking which involves the cleansing of woven cloth (particularly wool) to eliminate ( lanolin) oils, dirt, and other impurities, and to make it shrink by friction and pressure. The work delivers a smooth, tightly finished fabric that is insulating and water-repellent. Well-known examples are duffel cloth, first produced in Flanders in the 14th century, and loden, produced in Austria from the 16th century on. Waulking could be done with the hands and feet. In medieval Europe, it was done in water-powered fulling mills. After the Industrial Revolution, coal and electric power were used. Felting refers more generally to the interlocking of loose wool fibers; they need not be spun and woven first. Process Fulling involves two processes: scouring (cleaning) and milling (thickening). Removing the oils encourages felting, and the cloth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bridge Of Weir Leather Tannery - Geograph
A bridge is a structure built to Span (engineering), span a physical obstacle (such as a body of water, valley, road, or railway) without blocking the path underneath. It is constructed for the purpose of providing passage over the obstacle, which is usually something that is otherwise difficult or impossible to cross. There are many different designs of bridges, each serving a particular purpose and applicable to different situations. Designs of bridges vary depending on factors such as the function of the bridge, the nature of the terrain where the bridge is constructed and anchored, the material used to make it, and the funds available to build it. The earliest bridges were likely made with fallen trees and stepping stones. The Neolithic people built boardwalk bridges across marshland. The Arkadiko Bridge, dating from the 13th century BC, in the Peloponnese is one of the oldest arch bridges in existence and use. Etymology The ''Oxford English Dictionary'' traces the origin of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Public House
A pub (short for public house) is in several countries a drinking establishment licensed to serve alcoholic drinks for consumption Licensing laws of the United Kingdom#On-licence, on the premises. The term first appeared in England in the late 17th century, to differentiate private houses from those open to the public as alehouses, taverns and inns. Today, there is no strict definition, but the Campaign for Real Ale (CAMRA) states a pub has four characteristics: # is open to the public without membership or residency # serves draught beer or cider without requiring food be consumed # has at least one indoor area not laid out for meals # allows drinks to be bought at a bar (i.e., not only table service) The history of pubs can be traced to taverns in Roman Britain, and through Anglo-Saxon alehouses, but it was not until the early 19th century that pubs, as they are today, first began to appear. The model also became popular in countries and regions of British influence, whe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cotton Mill
A cotton mill is a building that houses spinning or weaving machinery for the production of yarn or cloth from cotton, an important product during the Industrial Revolution in the development of the factory system. Although some were driven by animal power, most early mills were built in rural areas at fast-flowing rivers and streams, and used water wheels for power. The development of viable steam engines by Boulton and Watt from 1781 led to the growth of larger, steam-powered mills. They were built in a concentrated way in urban mill towns, such as Manchester. Together with neighbouring Salford, it had more than 50 mills by 1802. The mechanisation of the spinning process in the early factories was instrumental in the growth of the machine tool industry, enabling the construction of larger cotton mills. Limited companies were developed to construct mills, and together with the business of the trading floors of the cotton exchange in Manchester, a vast commercial cit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Cycle Network
The National Cycle Network (NCN) was established to encourage cycling and walking throughout the United Kingdom, as well as for the purposes of bicycle touring. It was created by the charity Sustrans who were aided by a £42.5 million National Lottery (United Kingdom), National Lottery grant. However Sustrans themselves only own around 2% of the paths on the network, the rest being made of existing public highways and rights of way, and permissive paths negotiated by Sustrans with private landowners. In 2017, the Network was used for over 786 million cycling and walking trips, made by 4.4 million people. In 2020, around a quarter of the NCN was scrapped on safety grounds, leaving of signed routes. These are made up of of traffic-free paths with the remaining on-road. It uses shared use paths, Rail trail, disused railways, minor roads, canal towpaths and traffic-calmed routes in towns and cities. History The Bristol and Bath Railway Path (now part of National ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NCR 75
National Cycle Route 75 runs from Edinburgh to Tarbert, Kintyre, Tarbert on the Kintyre peninsula, via Glasgow. It is often known as the ''Clyde to Forth cycle route''. Route 75 includes two ferry crossings from Gourock to Dunoon on the Cowal peninsula and from Portavadie (Cowal) to Tarbert, Kintyre, Tarbert on the Kintyre peninsula. Route Route 75 Map Edinburgh to Bathgate The route begins in Leith, Edinburgh at the north-eastern terminus of the Water of Leith until Warriston, then runs southward in Edinburgh City Centre before joining with the eastern terminus of the Union Canal (Scotland), Union Canal at Fountainbridge. Just after the viaduct at Slateford, the route returns to the Water of Leith until its south-western terminus at Balerno. Thereafter it passes through Kirknewton, West Lothian, Kirknewton, East Calder, Almondell and Calderwood Country Park, Mid Calder, Livingston, West Lothian, Livingston and Bathgate. Edinburgh , Kirknewton, West Lothian, Kirknewton , Li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
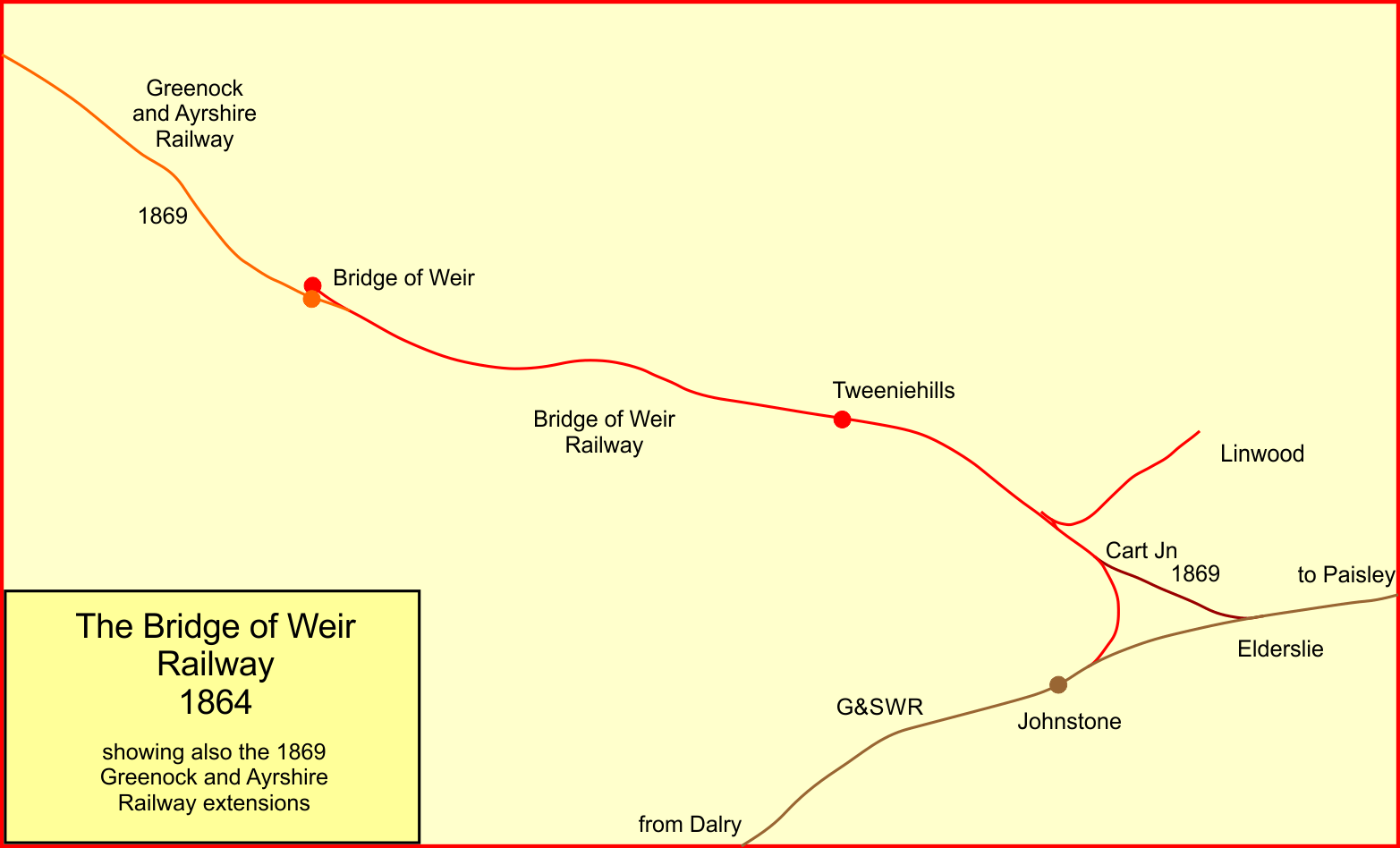
Greenock And Ayrshire Railway
The Greenock and Ayrshire Railway ran from Greenock, Scotland to Bridge of Weir, connecting there to the Glasgow and South Western Railway and making a through connection between Glasgow and Greenock. It closed progressively between 1959 and 1983. Formation By the 1860s, the Glasgow and South Western Railway (G&SWR) was established in the south-western quadrant of Scotland, but the rival Caledonian Railway was dominant in the central region, with an important branch line to Greenock. There was bitter rivalry between the two companies, and each sought to retain primacy in its own area. In 1864, an independent Bridge of Weir Railway, encouraged by the G&SWR, opened their line from Johnstone to Bridge of Weir. At that time the G&SWR was interested in reaching Greenock, where there was lucrative business associated with coastal and international shipping. The Caledonian Railway had a monopoly of the rail connection, and in October 1864 the Chairman of the G&SWR negotiated with th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bridge Of Weir Railway Station
Bridge of Weir railway station was a railway station serving the village of Bridge of Weir, Renfrewshire, Scotland, originally as part of the Bridge of Weir Railway. History The station opened on 1 June 1864, however it was closed on 18 May 1868 during the construction of the Greenock and Ayrshire Railway The Greenock and Ayrshire Railway ran from Greenock, Scotland to Bridge of Weir, connecting there to the Glasgow and South Western Railway and making a through connection between Glasgow and Greenock. It closed progressively between 1959 and 19 .... It reopened, now as part of the new extended line, on 23 December 1869. The station closed on 10 January 1983. References Notes Sources * * * Disused railway stations in Renfrewshire Railway stations in Great Britain opened in 1864 Railway stations in Great Britain closed in 1983 Former Glasgow and South Western Railway stations {{Scotland-railstation-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bridge Of Weir Railway
The Bridge of Weir Railway was an independent railway company that built a line from Johnstone to Bridge of Weir. It was taken over by the Glasgow and South Western Railway (G&SWR) in 1865 and formed the base of a line that extended to Greenock, giving the G&SWR access to the harbour facilities there, competing with the rival Caledonian Railway. The Greenock branch, as it had become, was given a direct access from Elderslie (about midway between Paisley and Johnstone), and fast passenger trains ran between Glasgow and Greenock. In the second half of the twentieth century usage of the line declined substantially, and the line closed in January 1983. Formation By the 1860s the Glasgow and South Western Railway (G&SWR) had established itself in the south-western quadrant of Scotland, while the rival Caledonian Railway The Caledonian Railway (CR) was one of the two biggest of the five major Scottish railway companies prior to the 1923 Grouping. It was formed in 1845 with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |