|
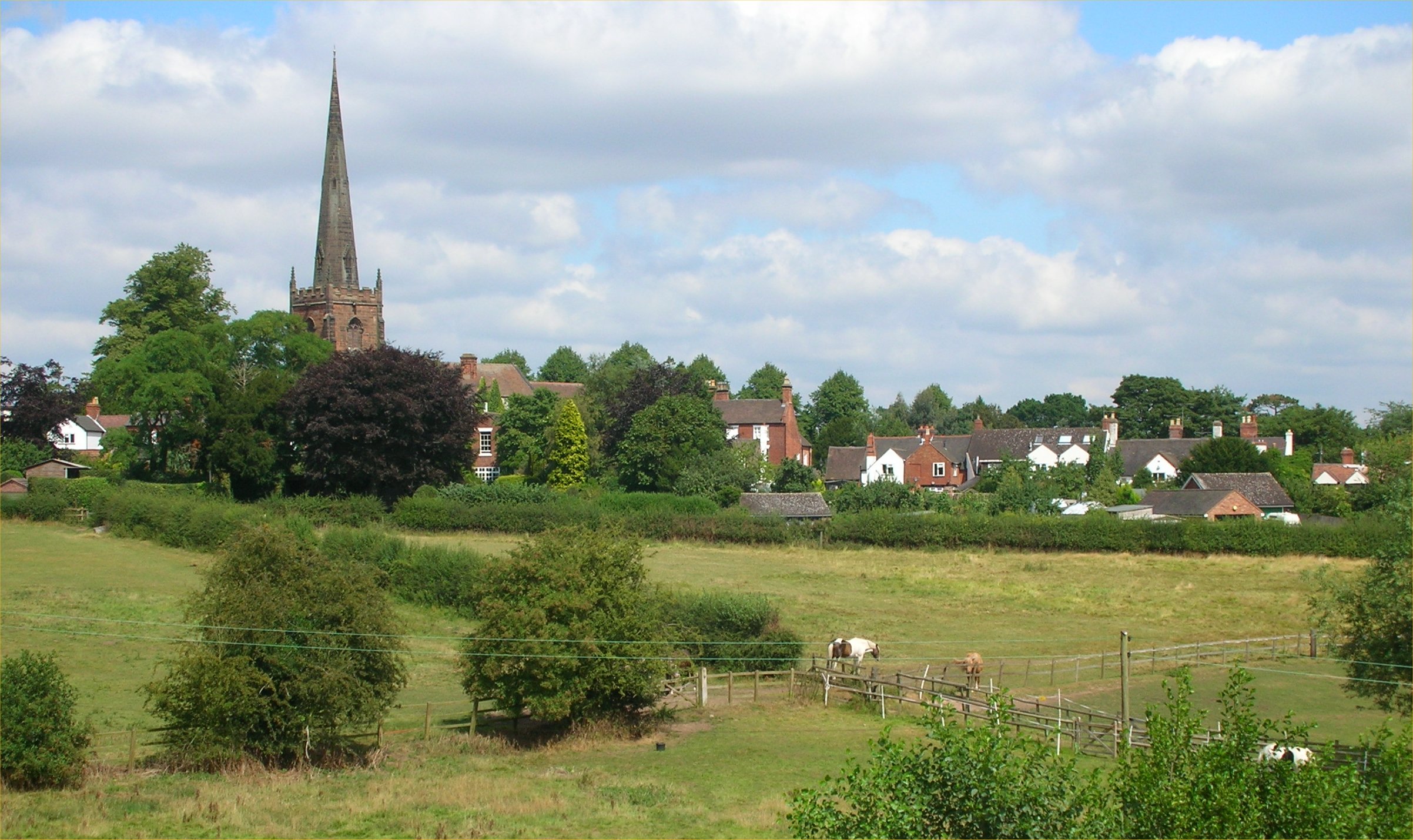
Brewood Church
Brewood is an ancient market town in the civil parish of Brewood and Coven, in the South Staffordshire district, in the county of Staffordshire, England. Brewood lies near the River Penk, north of Wolverhampton and south of Stafford. Brewood is about east of the county border with Shropshire. Etymology The Domesday Book of 1086 documented the town as 'Breude'. The name is probably a compound made up of a Celts, Celtic, British language (Celtic), Brythonic word, and an Anglo Saxon, Old English language, Old English word. The first element is the British word 'briga', which appears in modern Welsh as 'bre'. This is the most common of a number of Celtic place-name elements that signify a hill. It appears in various combinations, but sometimes on its own (as in Bray). Margaret Gelling, a specialist in West Midland toponyms, suggested that it was often misunderstood by the Anglo-Saxons as a name rather than as a common noun. Therefore, Anglo-Saxons would have thought that the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Speedwell Castle
Speedwell Castle is a mid-18th-century house at the centre of Brewood, in Staffordshire, England. Nikolaus Pevsner described it as a "peach" and a "delectable folly", and it stands beside the village market place, at the head of a T-junction on Bargate Street, facing onto Stafford Street. The house is an interesting combination of " Gothick" and Classical architecture: the symmetrical brick façade has two canted bays, each of three storeys, either side of a pillared entrance with ogee portico and octagonal-panelled door. There are five windows around each bay on each floor, and a single window on the two floors above the entrance, with decorative plasterwork arranged in tiers of round-headed arches with keystones and ogee arches rising to pinnacles surmounted by acorns. The glazing is arranged in a delicate tracery, originally of hexagons (although the glazing bars are not original on the ground and first floors). The façade is finished by a modillion cornice and parapet, con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toponyms
Toponymy, toponymics, or toponomastics is the study of '' toponyms'' (proper names of places, also known as place names and geographic names), including their origins, meanings, usage, and types. ''Toponym'' is the general term for a proper name of any geographical feature, and full scope of the term also includes proper names of all cosmographical features. In a more specific sense, the term ''toponymy'' refers to an inventory of toponyms, while the discipline researching such names is referred to as ''toponymics'' or ''toponomastics''. Toponymy is a branch of onomastics, the study of proper names of all kinds. A person who studies toponymy is called ''toponymist''. Etymology The term ''toponymy'' comes from / , 'place', and / , 'name'. The ''Oxford English Dictionary'' records ''toponymy'' (meaning "place name") first appearing in English in 1876 in the context of geographical studies. Since then, ''toponym'' has come to replace the term ''place-name'' in professional disc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anglo-Saxon
The Anglo-Saxons, in some contexts simply called Saxons or the English, were a Cultural identity, cultural group who spoke Old English and inhabited much of what is now England and south-eastern Scotland in the Early Middle Ages. They traced their origins to Germanic peoples, Germanic settlers who became one of the most important cultural groups in Britain by the 5th century. The Anglo-Saxon period in Britain is considered to have started by about 450 and ended in 1066, with the Norman conquest of England, Norman Conquest. Although the details of Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain, their early settlement and History of Anglo-Saxon England, political development are not clear, by the 8th century an Anglo-Saxon cultural identity which was generally called had developed out of the interaction of these settlers with the existing Romano-British culture. By 1066, most of the people of what is now England spoke Old English, and were considered English. Viking and Norman invasions chang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Penkridge
Penkridge ( ) is a village and civil parish in South Staffordshire, South Staffordshire District in Staffordshire, England. It is to the south of Stafford, north of Wolverhampton, west of Cannock, east of Telford and south-east of Newport, Shropshire, Newport. The wealthiest establishment in Penkridge in the Middle Ages, its collegiate church building survived the Chantry#Abolition of Chantries Acts, 1545 and 1547, abolition of the chantries and is the tallest structure in the village centre. The parish is crossed towards its eastern border by the M6 motorway and a separate junction north of the M6 Toll between the West Midlands (county), West Midlands and Stoke-on-Trent. Penkridge has a Penkridge railway station, railway station on the West Coast Main Line railway next to the listed building, Grade I listed medieval church. Penkridge Viaduct and the Staffordshire and Worcestershire Canal are to either side of Market Street and the Old Market Square and are among its landmarks. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
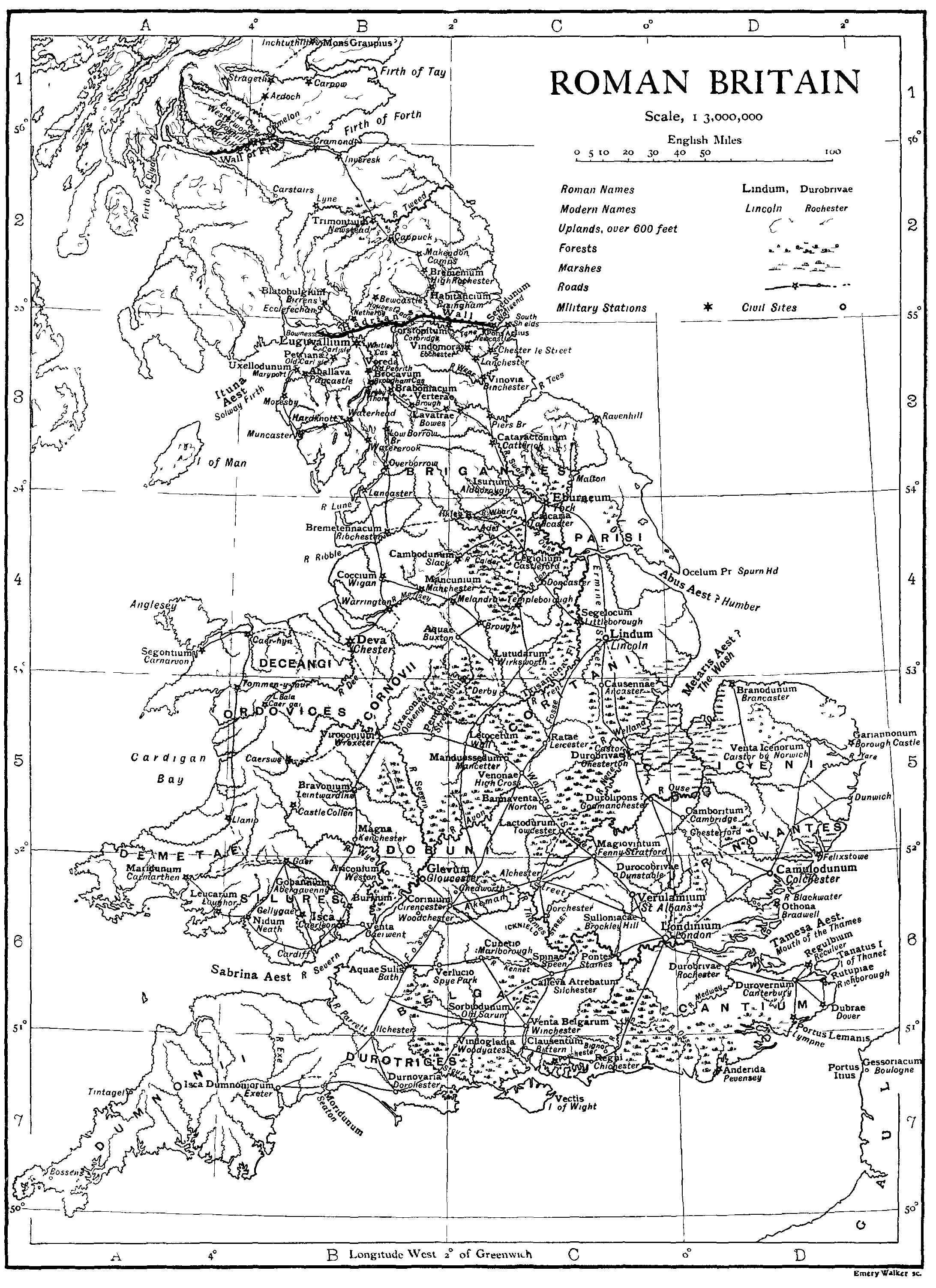
Pennocrucium
Pennocrucium was a Romano-British settlement and military complex located at present day Water Eaton, just south of Penkridge, Staffordshire, with evidence of occupation from the mid-1st century until the 4th century. The settlement was mentioned in the 2nd century Antonine Itinerary, which described it as lying 12 miles from Uxacona (near present-day Oakengates) and 12 miles from Letocetum (Wall, near Lichfield). The exact site of Pennocrucium was identified only after aerial photography revealed cropmarks in 1946, and excavations were conducted by Kenneth St Joseph over subsequent years. Pennocrucium was an important road junction on Watling Street – the main Roman road across the Midlands to Viroconium Cornoviorum (Wroxeter) – and was situated 700 metres east of its crossing of the River Penk, with roads leading north to Mediolanum ( Whitchurch) and south in the direction of Greensforge near Kinver and Metchley Fort in Birmingham. The main civilian defensive site or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
A5 Road (Great Britain)
The A5, the London-Holyhead trunk road, is a major road in England and Wales. It runs for about from London to the Irish Sea at the ferry port of Holyhead. In many parts the route follows that of the Roman Iter II route which later took the Anglo-Saxon name Watling Street. History Roman road The section of the A5 between London and Shrewsbury is roughly contiguous with one of the principal Roman roads in Britain: that between ''Londinium'' (modern-day London) and ''Deva'' (modern-day Chester), which diverges from the present-day A5 corridor at Wroxeter ('' Viroconium Cornoviorum'') near Shrewsbury. Telford's Holyhead Road The Act of Union 1800, which unified Great Britain and Ireland, gave rise to a need to improve communication links between London and Dublin. A parliamentary committee led to an act of Parliament, the ( 55 Geo. 3. c. 152) that authorised the purchase of existing turnpike road interests and, where necessary, the construction of new road, to com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chester
Chester is a cathedral city in Cheshire, England, on the River Dee, Wales, River Dee, close to the England–Wales border. With a built-up area population of 92,760 in 2021, it is the most populous settlement in the borough of Cheshire West and Chester. It is also the historic county town of Cheshire and the List of Cheshire settlements by population, second-largest settlement in Cheshire after Warrington. Chester was founded in 79 AD as a "Castra, castrum" or Roman Empire, Roman fort with the name Deva Victrix during the reign of Emperor Vespasian. One of the main army camps in Roman Britain, Deva later became a major civilian settlement. In 689, Æthelred of Mercia, King Æthelred of Mercia founded the Minster Church of West Mercia, which later became Chester's first cathedral, and the Angles (tribe), Angles extended and strengthened the walls to protect the city against the Danes (Germanic tribe), Danes. Chester was one of the last cities in England to Norman conquest of Eng ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wroxeter
Wroxeter ( ) is a village and former civil parish, now in the parish of Wroxeter and Uppington, in the Shropshire district, in the ceremonial county of Shropshire, England. It is beside the River Severn, south-east of Shrewsbury. In 1961 the parish had a population of 657. '' Viroconium Cornoviorum'', the fourth largest city in Roman Britain, was sited here, and is gradually being excavated. In 2024, archaeologists uncovered a 2,000 year old mosaic depicting dolphins and fish. The village contains one of Shropshire's commercial vineyards. History Roman Wroxeter, near the end of the Watling Street Roman road that ran across Romanised Celtic Britain from '' Dubris'' (Dover), was a key frontier position lying on the bank of the River Severn whose valley penetrated deep into what later became known as Wales, and also on a route south leading to the Wye valley. Archaeology has shown that the site of the later city first was established about AD 55 as a frontier post fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Britannia Superior
Britannia Superior (Latin for "Upper Britain") was a province of Roman Britain created after the civil war between Septimius Severus and Clodius Albinus. Although Herodian credits Severus with dividing Roman Britain into the Northern territory of Britannia Inferior and the Southern territory of Britannia Superior, modern scholarship argues that it is more likely that Caracalla was the person who made the split sometime in the early 3rd century CE. The previous British capital Londinium remained the centre of Britannia Superior while Eboracum, or modern York was the capital of Britannia Inferior. Epigraphical evidence shows that Upper Britain encompassed approximately what is now Wales, southern England and East Anglia. However, the official boundary between Britannia Superior and Inferior is still unclear. Although Londinium went through a period of decline during this time, the province as a whole continued to be developed. Villas were expanded and a new wall around the capital w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Province
The Roman provinces (, pl. ) were the administrative regions of Ancient Rome outside Roman Italy that were controlled by the Romans under the Roman Republic and later the Roman Empire. Each province was ruled by a Roman appointed as Roman governor, governor. For centuries, it was the largest administrative unit of the foreign possessions of ancient Rome. With the administrative reform initiated by Diocletian, it became a third level administrative subdivision of the Roman Empire, or rather a subdivision of the Roman diocese, imperial dioceses (in turn subdivisions of the Praetorian prefecture, imperial prefectures). History A province was the basic and, until the Tetrarchy (from AD 293), the largest territorial and administrative unit of the empire's territorial possessions outside Roman Italy. During the republic and early empire, provinces were generally governed by politicians of Roman senate, senatorial rank, usually former Roman consul, consuls or former praetors. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Londinium
Londinium, also known as Roman London, was the capital of Roman Britain during most of the period of Roman rule. Most twenty-first century historians think that it was originally a settlement established shortly after the Roman conquest of Britain, Claudian invasion of Britain, on the current site of the City of London, around 47–50 AD, but some defend an older view that the city originated in a defensive enclosure constructed during the Claudian invasion in 43 AD. Its earliest securely-dated structure is a timber drain of 47 AD. It had almost certainly been granted colony () status prior to the complete replanning of the city's street plan attending the erection of the great second forum around the year 120.Merrifieldp. 68./ref> By this time, Britain's provincial administration had also almost certainly been moved to Londinium from Camulodunum (now Colchester in Essex). The precise date of this change is unknown, and no surviving source explicitly states that Londinium w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Watling Street
Watling Street is a historic route in England, running from Dover and London in the southeast, via St Albans to Wroxeter. The road crosses the River Thames at London and was used in Classical Antiquity, Late Antiquity, and throughout the Middle Ages. It was used by the ancient Britons and paved as one of the main Roman roads in Britannia (Roman-governed Great Britain during the Roman Empire). The line of the road was later the southwestern border of the Danelaw with Wessex and Mercia, and Watling Street was numbered as one of the major highways of medieval England. First used by the ancient Britons, mainly between the areas of modern Canterbury and using a natural ford near Westminster, the road was later paved by the Romans. It connected the ports of Dubris (Dover), Rutupiae ( Richborough Castle), Lemanis ( Lympne), and Regulbium (Reculver) in Kent to the Roman bridge over the Thames at Londinium (London). The route continued northwest through Verulamium (St&n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |