|
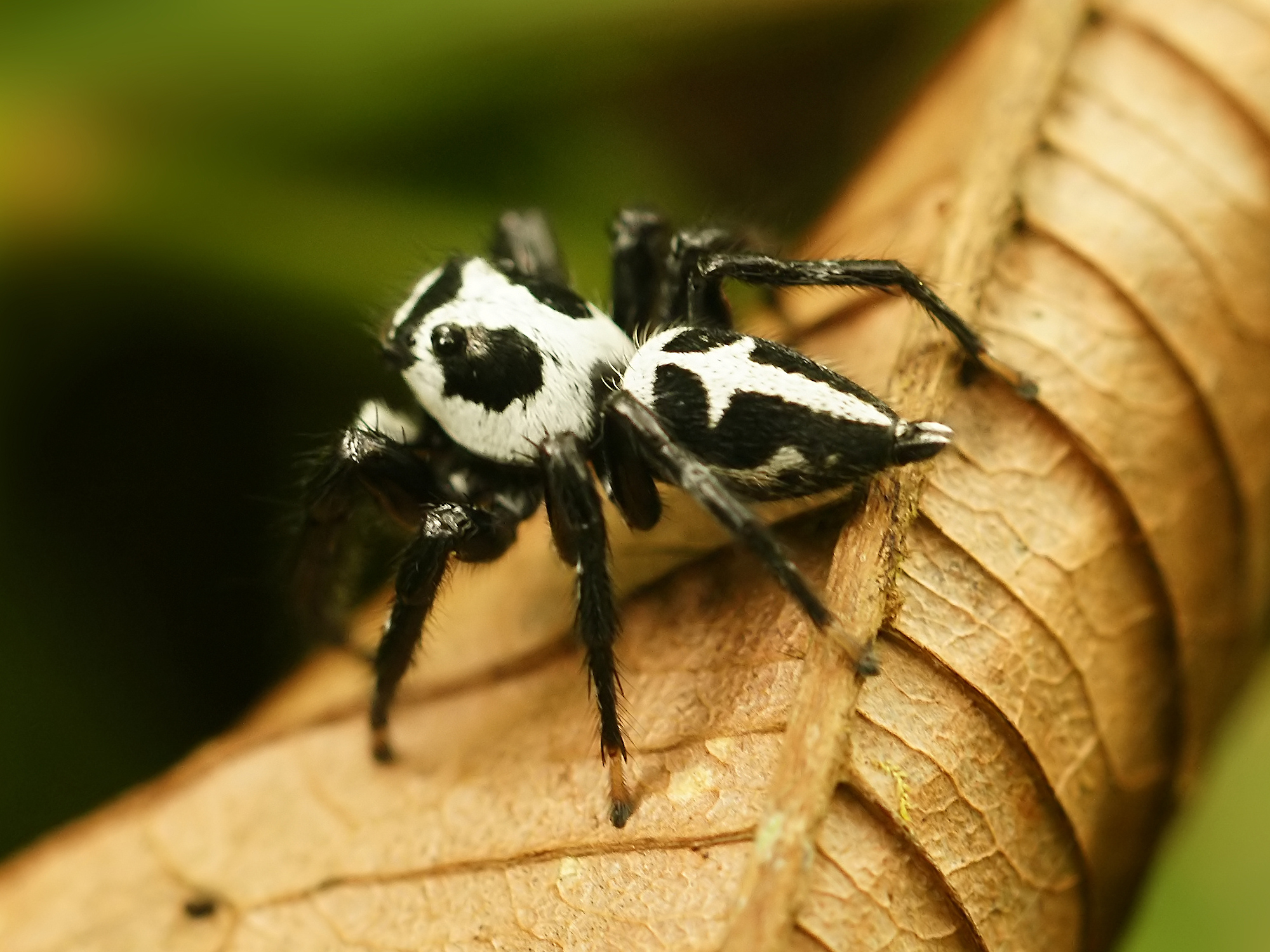
Brenthia Hexaselena
''Brenthia hexaselena'' is a species of moth of the family Choreutidae. It is found in Costa Rica. It is a rare example of a prey animal mimicking In evolutionary biology, mimicry is an evolved resemblance between an organism and another object, often an organism of another species. Mimicry may evolve between different species, or between individuals of the same species. Often, mimicry ... its predator. Mimicry Adult moths mimic the jumping spider '' Phiale formosa'', one of their predators. The moths lie low with their wings held up facing forward, their coloration, pattern and movement all resembling those of the spider. In an experiment, ''Brenthia hexaselena'' and '' Brenthia monolychna'' had higher survival rates than other similarly sized moths in the presence of jumping spiders. The jumping spiders responded to ''Brenthia'' with territorial displays, indicating that the species were sometimes mistaken for jumping spiders, and not recognized as prey. References ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phiale (genus)
''Phiale'' is a genus of jumping spiders that was first described by Carl Ludwig Koch in 1846. ''P. albovittata'' has been considered a junior synonym of '' Freya perelegans'' since 2006. Species it contains twenty-five species, found in the Caribbean, South America, Costa Rica, Guatemala, Mexico, and Panama: *'' Phiale aschnae'' Makhan, 2006 – Suriname *'' Phiale bipunctata'' Mello-Leitão, 1947 – Brazil *'' Phiale bisignata'' ( F. O. Pickard-Cambridge, 1901) – Mexico, Guatemala *'' Phiale bryantae'' Roewer, 1951 – Antigua and Barbuda (Antigua) *'' Phiale bulbosa'' (F. O. Pickard-Cambridge, 1901) – Panama *'' Phiale crocea'' C. L. Koch, 1846 – Panama to Brazil *'' Phiale cruentata'' ( Walckenaer, 1837) – Brazil, French Guiana *'' Phiale cubana'' Roewer, 1951 – Cuba *'' Phiale elegans'' (F. O. Pickard-Cambridge, 1901) – Panama *'' Phiale formosa'' ( Banks, 1909) – Costa Rica *'' Phiale geminata'' (F. O. Pickard-Cambridge, 1901) – Panama *'' Phiale ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Animal Coloration
Animal coloration is the general appearance of an animal resulting from the reflection or emission of light from its surfaces. Some animals are brightly coloured, while others are hard to see. In some species, such as the peafowl, the male has strong patterns, conspicuous colours and is iridescent, while the female is far less visible. There are several separate reasons why animals have evolved colours. Camouflage enables an animal to remain hidden from view. Animals use colour to advertise services such as cleaning to animals of other species; to signal their sexual status to other members of the same species; and in mimicry, taking advantage of the warning coloration of another species. Some animals use flashes of colour to divert attacks by startling predators. Zebras may possibly use motion dazzle, confusing a predator's attack by moving a bold pattern rapidly. Some animals are coloured for physical protection, with pigments in the skin to protect against sunburn, whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edward Meyrick
Edward Meyrick (25 November 1854, in Ramsbury – 31 March 1938, at Thornhanger, Marlborough) was an English schoolmaster and amateur entomologist. He was an expert on microlepidoptera and some consider him one of the founders of modern microlepidoptera systematics. Life and work Edward Meyrick came from a Welsh clerical family and was born in Ramsbury on the Kennet to a namesake father. He was educated at Marlborough College and Trinity College, Cambridge. He actively pursued his hobby during his schooling, and one colleague stated in 1872 that Meyrick "has not left a lamp, a paling, or a tree unexamined in which a moth could possibly, at any stage of its existence, lie hid." Meyrick began publishing notes on microlepidopterans in 1875, but when in December, 1877 he gained a post at The King's School, Parramatta, New South Wales, there were greater opportunities for indulging his interest. He stayed in Australia for ten years (from 1877 until the end of 1886) working a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moth
Moths are a paraphyletic group of insects that includes all members of the order Lepidoptera that are not butterflies, with moths making up the vast majority of the order. There are thought to be approximately 160,000 species of moth, many of which have yet to be described. Most species of moth are nocturnal, but there are also crepuscular and diurnal species. Differences between butterflies and moths While the butterflies form a monophyletic group, the moths, comprising the rest of the Lepidoptera, do not. Many attempts have been made to group the superfamilies of the Lepidoptera into natural groups, most of which fail because one of the two groups is not monophyletic: Microlepidoptera and Macrolepidoptera, Heterocera and Rhopalocera, Jugatae and Frenatae, Monotrysia and Ditrysia.Scoble, MJ 1995. The Lepidoptera: Form, function and diversity. Oxford, UK: Oxford University Press; 404 p. Although the rules for distinguishing moths from butterflies are not well est ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Choreutidae
Choreutidae, or metalmark moths, are a family of insects in the lepidopteran order whose relationships have been long disputed. It was placed previously in the superfamily Yponomeutoidea in family Glyphipterigidae and in superfamily Sesioidea. It is now considered to represent its own superfamily (Minet, 1986). The relationship of the family to the other lineages in the group "Apoditrysianeed a new assessment, especially with new molecular data. Distribution The moths occur worldwide, with 19 genera in three subfamilies defined by the structural characteristics of the immature stages (larvae and pupae), rather than the characters of the adults (Heppner and Duckworth, 1981; Rota, 2005). Behaviour These small moths often bear metallic scalesand are mostly day-flying (some also come to lights), with a jerky, pivoting behaviour, and may fluff up their wings at an extreme angle. Some tropical exemplars such as the genus '' Saptha'' are quite spectacular, with bright green metalli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Costa Rica
Costa Rica (, ; ; literally "Rich Coast"), officially the Republic of Costa Rica ( es, República de Costa Rica), is a country in the Central American region of North America, bordered by Nicaragua to the north, the Caribbean Sea to the northeast, Panama to the southeast, the Pacific Ocean to the southwest, and maritime border with Ecuador to the south of Cocos Island. It has a population of around five million in a land area of . An estimated 333,980 people live in the capital and largest city, San José, Costa Rica, San José, with around two million people in the surrounding metropolitan area. The sovereign state is a Unitary state, unitary Presidential system, presidential Constitution of Costa Rica, constitutional republic. It has a long-standing and stable democracy and a highly educated workforce. The country spends roughly 6.9% of its budget (2016) on education, compared to a global average of 4.4%. Its economy, once heavily dependent on agriculture, has diversif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mimicry
In evolutionary biology, mimicry is an evolved resemblance between an organism and another object, often an organism of another species. Mimicry may evolve between different species, or between individuals of the same species. Often, mimicry functions to protect a species from predators, making it an anti-predator adaptation. Mimicry evolves if a receiver (such as a predator) perceives the similarity between a mimic (the organism that has a resemblance) and a model (the organism it resembles) and as a result changes its behaviour in a way that provides a selective advantage to the mimic. The resemblances that evolve in mimicry can be visual, acoustic, chemical, tactile, or electric, or combinations of these sensory modalities. Mimicry may be to the advantage of both organisms that share a resemblance, in which case it is a form of mutualism; or mimicry can be to the detriment of one, making it parasitic or competitive. The evolutionary convergence between groups is driven b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phiale Formosa Cropped
Phiale may refer to: * ''Phiale'' (spider), a genus of spiders of the family Salticidae (jumping spiders) *Phiale, an ancient Greek libation bowl; see patera * Phiale (Bithynia), a town of ancient Bithynia, now in Turkey * Phiale (building), an enclosed or arcaded fountain {{Disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brenthia Monolychna
''Brenthia monolychna'' is a species of moth of the family Choreutidae. It is found in Costa Rica. Adults mimic jumping spiders, one of their predators. In a recently conducted experiment, ''Brenthia hexaselena ''Brenthia hexaselena'' is a species of moth of the family Choreutidae. It is found in Costa Rica. It is a rare example of a prey animal mimicking In evolutionary biology, mimicry is an evolved resemblance between an organism and another ...'' and ''Brenthia monolychna'' had higher survival rates than other similarly sized moths in the presence of jumping spiders and jumping spiders responded to Brenthia with territorial displays, indicating that the species were sometimes mistaken for jumping spiders, and not recognized as prey. The larvae feed mostly on the underside of leaves, occasionally on the upper sides, skeletonizing the leaf superficially. They are pale green. When disturbed, larvae move rapidly through an escape hole they made in the leaf. Cocoons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moths Described In 1909
Moths are a paraphyletic group of insects that includes all members of the order Lepidoptera that are not butterflies, with moths making up the vast majority of the order. There are thought to be approximately 160,000 species of moth, many of which have yet to be described. Most species of moth are nocturnal, but there are also crepuscular and diurnal species. Differences between butterflies and moths While the butterflies form a monophyletic group, the moths, comprising the rest of the Lepidoptera, do not. Many attempts have been made to group the superfamilies of the Lepidoptera into natural groups, most of which fail because one of the two groups is not monophyletic: Microlepidoptera and Macrolepidoptera, Heterocera and Rhopalocera, Jugatae and Frenatae, Monotrysia and Ditrysia.Scoble, MJ 1995. The Lepidoptera: Form, function and diversity. Oxford, UK: Oxford University Press; 404 p. Although the rules for distinguishing moths from butterflies are not well establish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brenthia
''Brenthia'' is a genus of moths in the family Choreutidae. Species *'' Brenthia albimaculana'' (Snellen, 1875) *'' Brenthia anisopa'' Diakonoff, 1968 *'' Brenthia ardens'' Meyrick, 1912 *'' Brenthia buthusalis'' (Walker, 1863) *'' Brenthia caelicola'' Meyrick, 1910 *'' Brenthia carola'' Meyrick, 1912 *''Brenthia catenata'' Meyrick, 1907 *'' Brenthia confluxana'' (Walker, 1863) *''Brenthia coronigera'' Meyrick, 1918 *'' Brenthia cubana'' Heppner, 1985 *''Brenthia cyanaula'' Meyrick, 1912 *'' Brenthia diplotaphra'' Meyrick, 1938 *'' Brenthia dendronympha'' Meyrick, 1937 *'' Brenthia elachista'' Walsingham, 1900 *''Brenthia elongata'' Heppner, 1985 *'' Brenthia entoma'' Diakonoff, 1982 *'' Brenthia excusana'' (Walker, 1863) *'' Brenthia formosensis'' Issiki, 1930 *'' Brenthia gamicopis'' Meyrick, 1930 *'' Brenthia gregori'' Heppner, 1985 *'' Brenthia harmonica'' Meyrick, 1918 *'' Brenthia hexaselena'' Meyrick, 1909 *'' Brenthia hibiscusae'' Heppner, 1985 *''Brenthia leptocosma ''B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Articles Containing Video Clips
Article often refers to: * Article (grammar), a grammatical element used to indicate definiteness or indefiniteness * Article (publishing), a piece of nonfictional prose that is an independent part of a publication Article may also refer to: Government and law * Article (European Union), articles of treaties of the European Union * Articles of association, the regulations governing a company, used in India, the UK and other countries * Articles of clerkship, the contract accepted to become an articled clerk * Articles of Confederation, the predecessor to the current United States Constitution * Article of Impeachment, a formal document and charge used for impeachment in the United States * Articles of incorporation, for corporations, U.S. equivalent of articles of association * Articles of organization, for limited liability organizations, a U.S. equivalent of articles of association Other uses * Article, an HTML element, delimited by the tags and * Article of clothing, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |