|
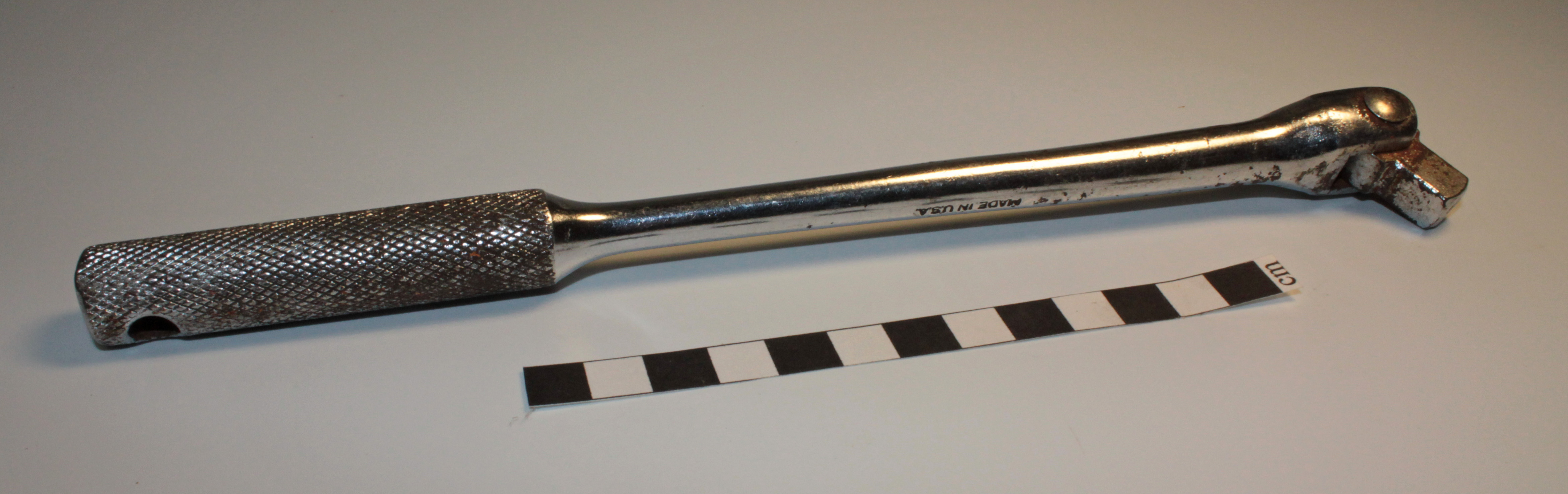
Breaker Bar
A breaker bar (also known as a ''power bar'') is a long non-ratcheting bar that is used with socket wrench-style sockets. They are used to break loose very tight fasteners because their additional length allows the same amount of force to generate significantly more torque than a standard length socket wrench.U.S. Patent 4,811,638 (1989) Retrieved 3 May 2010 Their use prevents damage to the ratcheting mechanism of a socket wrench. Often, after the first half turn, the fastener is loose enough to be turned with a socket wrench. Function The long handle on breaker bars compared to shorter wrenches allows a larger torque to be generated with the same amount of force. It is effectively a lever, one of the simple machines. A ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Socket Wrench
A socket wrench (or socket spanner) is a type of spanner (or wrench in North American English) that uses a closed ''socket'' format, rather than a typical open wrench/spanner to turn a fastener, typically in the form of a nut or bolt. The most prevalent form is the ratcheting socket wrench, often informally called a ratchet. A ratchet incorporates a reversible ratcheting mechanism which allows the user to pivot the tool back and forth to turn its socket instead of removing and repositioning a wrench to do so. Other common methods of driving sockets include pneumatic impact wrenches, hydraulic torque wrenches, torque multipliers and breaker bars. Some lesser known hybrid drivers include striking wrench tools with square drive, and hydraulic impact wrenches (typically powered by on site hydraulic power such as present with military tanks, and many rail car applications). Interchangeable sockets The basic contemporary form of socket is hexagonal, referred to as "6-point" for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Force
In physics, a force is an influence that can cause an Physical object, object to change its velocity unless counterbalanced by other forces. In mechanics, force makes ideas like 'pushing' or 'pulling' mathematically precise. Because the Magnitude (mathematics), magnitude and Direction (geometry, geography), direction of a force are both important, force is a Euclidean vector, vector quantity. The SI unit of force is the newton (unit), newton (N), and force is often represented by the symbol . Force plays an important role in classical mechanics. The concept of force is central to all three of Newton's laws of motion. Types of forces often encountered in classical mechanics include Elasticity (physics), elastic, frictional, Normal force, contact or "normal" forces, and gravity, gravitational. The rotational version of force is torque, which produces angular acceleration, changes in the rotational speed of an object. In an extended body, each part applies forces on the adjacent pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
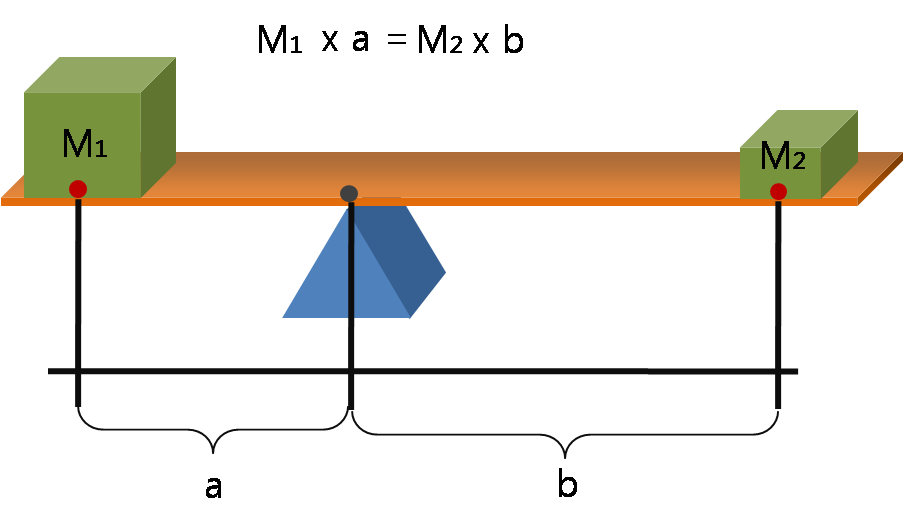
Torque
In physics and mechanics, torque is the rotational analogue of linear force. It is also referred to as the moment of force (also abbreviated to moment). The symbol for torque is typically \boldsymbol\tau, the lowercase Greek letter ''tau''. When being referred to as moment of force, it is commonly denoted by . Just as a linear force is a push or a pull applied to a body, a torque can be thought of as a twist applied to an object with respect to a chosen point; for example, driving a screw uses torque to force it into an object, which is applied by the screwdriver rotating around its axis to the drives on the head. Historical terminology The term ''torque'' (from Latin , 'to twist') is said to have been suggested by James Thomson and appeared in print in April, 1884. Usage is attested the same year by Silvanus P. Thompson in the first edition of ''Dynamo-Electric Machinery''. Thompson describes his usage of the term as follows: Today, torque is referred to using d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lever
A lever is a simple machine consisting of a beam (structure), beam or rigid rod pivoted at a fixed hinge, or '':wikt:fulcrum, fulcrum''. A lever is a rigid body capable of rotating on a point on itself. On the basis of the locations of fulcrum, load, and effort, the lever is divided into Lever#Types of levers, three types. It is one of the six simple machines identified by Renaissance scientists. A lever amplifies an input force to provide a greater output force, which is said to provide leverage, which is mechanical advantage gained in the system, equal to the ratio of the output force to the input force. As such, the lever is a mechanical advantage device, trading off force against movement. Etymology The word "lever" entered English language, English around 1300 from . This sprang from the stem of the verb ''lever'', meaning "to raise". The verb, in turn, goes back to , itself from the adjective ''levis'', meaning "light" (as in "not heavy"). The word's primary origin is the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simple Machines
Simple Machines was an American independent record label in Arlington, Virginia. The label was founded by Derek Denckla and Jenny Toomey and Brad Sigal while both were living in the Positive Force House in north Arlington, but Sigal and eventually Denckla stepped back from involvement. In 1990-91 Kristin Thomson stepped up and co-masterminded the project with Toomey and they started a new group house near Positive Force's. At its peak, the label had four paid workers: Toomey, Thomson, Pat Graham and Mickey Menard. The label was formed to "find creative ways to avoid the established and boring music business." Biography The label came into existence in 1989 working toward the 1990 release of the ''Simple Machines 7"'' series. The ''Working Holiday!'' 7" series followed. Simple Machines promoted cooperation with other indie labels all over the United States, and the "sell it at a fair price" ethic. The label also released a compilation of bands covering their "favorite Beat H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cheater Bar
Cheating generally describes various actions designed to subvert or disobey rules in order to obtain unfair advantages without being noticed. This includes acts of bribery, cronyism and nepotism in any situation where individuals are given preference using inappropriate criteria. The rules infringed may be explicit, or they may be from an unwritten code of conduct based on morality, ethics or custom, making the identification of cheating conduct a potentially subjective process. Cheating can refer specifically to infidelity, where arranged or consensual relationships, that often come with a social contract, are violated. Someone who is known for cheating is referred to as a ''cheat'' in British English, and a ''cheater'' in American English. Academic Academic cheating is a significantly common occurrence in high schools and colleges in the United States. Statistically, 64% of public high school students admit to serious test cheating. 58% say they have plagiarized. 95% of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |