|
Brataualung
The Brataualung are an Indigenous Australian people, one of the five tribes of Gippsland, in the state of Victoria, Australia, and part of a wider regional grouping known as the Kurnai. Language Brataualung language is a variety of what is generally classified as Gunai, which itself is classified by Robert M. W. Dixon as ''Muk-thang'' According to Alfred William Howitt, the Brataualung, together with the Braiakaulungl and Tatungalung all spoke dialects of Nulit and Nulit, Muk-thang and the Thangquai spoken by the Krauatungalung were mutually unintelligible. Country The Brataualung's traditional territories embraced some , extending eastwards from Cape Liptrap and Tarwin Meadows east to the maritime outlet of the Merriman Creek. Its northern boundary reached inland to Mirboo. It included what are now Port Albert and Wilsons Promontory. Social organization The Brataualung are divided into several subgroupings or hordes. * The ''Yauung'' were centred on Warrigal Creek and th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gunai People
The Gunaikurnai or Gunai/Kurnai ( ) people, also referred to as the Gunnai or Kurnai, are an Aboriginal Australian nation of south-east Australia. They are the Traditional Custodians of most of present-day Gippsland and much of the southern slopes of the Victorian Alps. The Gunaikurnai nation is composed of five major clans. Many of the Gunaikurnai people resisted early European squatting and subsequent settlement during the nineteenth century, resulting in a number of deadly confrontations between Europeans and the Gunaikurnai. There are about 3,000 Gunaikurnai people alive today, predominantly living in Gippsland. The Gunaikurnai dialects are the traditional language of the Gunaikurnai people, although there are very few fluent speakers today. Creation story It is told that the first Kurnai came down from the north west mountains, with his canoe on his head. He was known as Borun, the pelican. He crossed the Tribal River (where Sale now stands) and walked on into the west to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gunai Language
The Gunaikurnai or Gunai/Kurnai ( ) language, also spelt Gunnai, Kurnai, Ganai, Gaanay, or Kurnay ) is an Australian Aboriginal dialect cluster of the Gunaikurnai people in Gippsland in south-east Victoria. Bidawal was either a divergent dialect or a closely related language. Varieties means 'man'. The language had no traditional name, but each of its dialects was referred to separately. In a 1996 report to the Victorian Aboriginal Corporation for Languages, Clark refers to five Gunaikurnai dialects: ''Brabralung'', ''Braiakalung'', ''Brataualung'', ''Krauatungalung'' and ''Tatungalung''. * ( = man, = belonging to) located in central Gippsland. * ( = Man, = west, = belonging to) located around Sale through to the mountains. * (men belonging to this place which have fire; = men, or = fire, = belonging to) located in South Gippsland. * ( = east, = belonging to) located eastwards to the Snowy River. * ( = sea, = belonging to) located in the coast area be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tatungalung
The Tatungalung are an indigenous Australian people of the state of Victoria. They are often, together with the Bratauolung, Braiakaulung, Brabiralung and Krauatungalung classified as belonging to one nation, the Gunai/Kurnai, though this typology has been thought, by Norman Tindale, to be an artificial construct. Name The word ''tatung'' means 'south', referring to the fact that they are the southernmost of the Gunai peoples. Language The Tatungalung traditionally spoke a dialect that was likely mutually intelligible with the Brataualung and the Braiakaulung, and collectively called ''Nulit.'' Robert M. W. Dixon considers Nulit itself to be a dialect of ''Muk-thang''. Country Their traditional lands covered an estimated , running along the coast of Ninety Mile Beach and about Lakes Victoria and Wellington, including a group established on Raymond Island, at King Lake. Their frontiers were at Lakes Entrance to the mouth of Merriman Creek in the west. Social organization Acc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Braiakaulung
The Braiakaulung are an Indigenous Australian people, one of the five tribes of the Gunai/Kurnai nation, in the state of Victoria, Australia. They were recognized by Norman Tindale as an independent tribal grouping. Name The Braiakaulung are also known as the Brayakaboong, meaning "men of the west". Language Country The Braiakaulung's lands extended over , taking in Providence Ponds, the Avon and Latrobe rivers. They extended west of Lake Wellington as far as Mount Baw Baw and Mount Howitt Mount Howitt, also known as ''Toot-buck-nulluck'' in the Gunai language, is a mountain in Victoria, Australia, named for Alfred William Howitt. Located in the Wonangatta Moroka Unit of the Alpine National Park approximately 170 km north-e .... Alternative names * Braiakolung * Brayakaboong * Brayakau * Brayakaulung * Breagalong * Nulit (name applied to language spoken by several associated tribes) Notes Citations Sources * * * {{Authority control Aboriginal peoples of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Warrigal Creek
Warrigal Creek is the site of an 1843 massacre in of Gunai/Kurnai people in colonial Victoria, during the Australian frontier wars. The creek is on a farm south of Sale, and east of Melbourne, in the South Gippsland area of Victoria, Australia. Massacre In July 1843, a man named Ronald Macalister was killed by Aboriginal men near Port Albert, on the coast of Victoria. The Scottish colonist and pastoralist, Angus McMillan, led a group of around 20 colonists to attack and kill several groups of Aboriginal people across a number of days. The group of Gaelic-speaking Scotsmen was known as the "Highland Brigade". The attack on the Brataualung people camped at Warrigal Creek was one of several incidents resulting in loss of life among the Gunai Kurnai people. The estimates of numbers of deaths vary: some historical accounts say that 60 people were killed, while other sources suggest that up to 150 people may have been killed. Some historians assert that the number of 60 is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aboriginal History
''Aboriginal History'' is an annual peer-reviewed academic journal published as an open access journal by Aboriginal History Inc. It was established in 1977 (co-founded and edited by Diane Barwick) and covers interdisciplinary historical studies in the field of the interactions between Australian Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander peoples and non-Indigenous peoples. The Journal has been described as "... a flagship of the field of Australian Aboriginal history." The journal's scope includes the areas of Australian Indigenous history and oral histories, languages, biographies, bibliographic guides and archival research. It has also brought previously unpublished manuscripts and research in the fields of Australian archaeology, anthropology, linguistics, demography, sociology, law and geography to the professional and wider public. A focus on cultural, political and economic history is complemented by critiques of current events of relevance to Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Whaling In Australia
Whaling in Australian waters began in 1791 when five of the 11 ships in the Third Fleet landed their passengers and freight at Sydney Cove and then left Port Jackson to engage in whaling and seal hunting off the coast of Australia and New Zealand. The two main species hunted by such vessels in the early years were right and sperm whales. Humpback, bowhead and other whale species would later be taken. Whaling went on to be a major maritime industry in Australia providing work for hundreds of ships and thousands of men and contributing export products worth £4.2 million by 1850. Modern whaling using harpoon guns and iron hulled catchers was conducted in the twentieth century from shore-based stations in Western Australia, New South Wales and Queensland. A government inquiry into the industry in 1978 resulted in a ban on whaling in Australia and a commitment to whale protection. Whale watching is now a significant tourist industry in its own right. Aboriginals, whales and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corner Inlet
The Corner Inlet is a bay located south-east of Melbourne in the South Gippsland region of Victoria, Australia. Of Victoria's large bays it is both the easternmost and the warmest. It contains intertidal mudflats, mangroves, salt marsh and seagrass meadows, sheltered from the surf of Bass Strait by a complex of 40 sandy barrier islands, the largest of which are Snake, Sunday and Saint Margaret Islands. The inlet is protected as a Ramsar site by the Nooramunga and Corner Inlet Marine and Coastal Parks, and by part of it lying within the Corner Inlet Marine National Park. The inlet adjoins Wilsons Promontory in the west, extends to Ninety Mile Beach in the east, and supports large numbers of migratory waders and other birds as well a rich marine flora and fauna.Corner Inlet Marine National Park [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
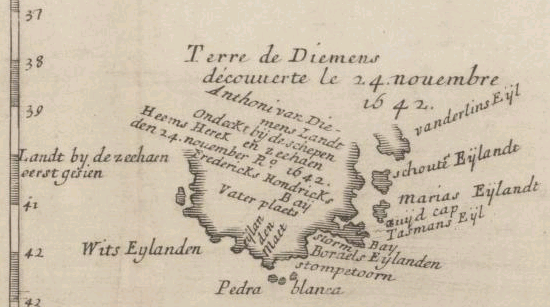
Van Diemen's Land
Van Diemen's Land was the colonial name of the island of Tasmania used by the British during the European exploration of Australia in the 19th century. A British settlement was established in Van Diemen's Land in 1803 before it became a separate colony in 1825. Its penal colonies became notorious destinations for the transportation of convicts due to the harsh environment, isolation and reputation for being inescapable. Macquarie Harbour and Port Arthur are among the most well-known penal settlements on the island. With the passing of the Australian Constitutions Act 1850, Van Diemen's Land (along with New South Wales, Queensland, South Australia, Victoria, and Western Australia) was granted responsible self-government with its own elected representative and parliament. On 1 January 1856, the colony of Van Diemen's Land was officially changed to Tasmania. The last penal settlement was closed in Tasmania in 1877. Toponym The island was named in honour of Anthony van D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Victorian Gold Rush
The Victorian gold rush was a period in the history of Victoria, Australia approximately between 1851 and the late 1860s. It led to a period of extreme prosperity for the Australian colony, and an influx of population growth and financial capital for Melbourne, which was dubbed "Marvellous Melbourne" as a result of the procurement of wealth. Overview The Victorian Gold Discovery Committee wrote in 1854: With the exception of the more extensive fields of California, for a number of years the gold output from Victoria was greater than in any other country in the world. Victoria's greatest yield for one year was in 1856, when 3,053,744 troy ounces (94,982 kg) of gold were extracted from the diggings. From 1851 to 1896 the Victorian Mines Department reported that a total of 61,034,682 oz (1,898,391 kg) of gold was mined in Victoria. Gold was first discovered in Australia on 15 February 1823, by assistant surveyor James McBrien, at Fish River, between Rydal, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indigenous Australian
Indigenous Australians or Australian First Nations are people with familial heritage from, and membership in, the ethnic groups that lived in Australia before British colonisation. They consist of two distinct groups: the Aboriginal peoples of the Australian mainland and Tasmania, and the Torres Strait Islander peoples from the seas between Queensland and Papua New Guinea. The term Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander peoples or the person's specific cultural group, is often preferred, though the terms First Nations of Australia, First Peoples of Australia and First Australians are also increasingly common; 812,728 people self-identified as being of Aboriginal and/or Torres Strait Islander origin in the 2021 Australian Census, representing 3.2% of the total population of Australia. Of these indigenous Australians, 91.4% identified as Aboriginal; 4.2% identified as Torres Strait Islander; while 4.4% identified with both groups. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cambridge University Press
Cambridge University Press is the university press of the University of Cambridge. Granted letters patent by Henry VIII of England, King Henry VIII in 1534, it is the oldest university press in the world. It is also the King's Printer. Cambridge University Press is a department of the University of Cambridge and is both an academic and educational publisher. It became part of Cambridge University Press & Assessment, following a merger with Cambridge Assessment in 2021. With a global sales presence, publishing hubs, and offices in more than 40 Country, countries, it publishes over 50,000 titles by authors from over 100 countries. Its publishing includes more than 380 academic journals, monographs, reference works, school and university textbooks, and English language teaching and learning publications. It also publishes Bibles, runs a bookshop in Cambridge, sells through Amazon, and has a conference venues business in Cambridge at the Pitt Building and the Sir Geoffrey Cass Spo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |