|
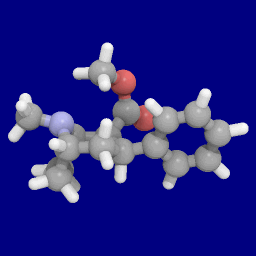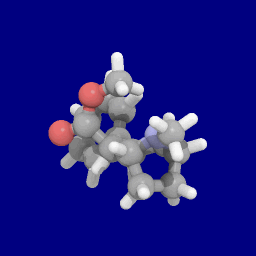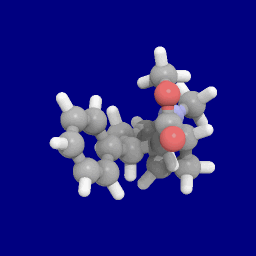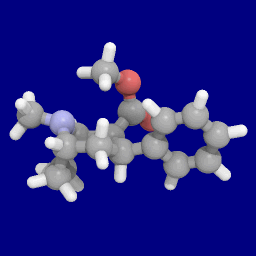
Brasofensine
Brasofensine (NS-2214, BMS-204756) is a phenyltropane dopamine reuptake inhibitor that had been under development by Bristol-Myers Squibb and defunct company NeuroSearch for the treatment of Parkinson's and Alzheimer's diseases. History In 1996, brasofensine entered phase I trials in the United States and phase II trials in Denmark. From 1996 to 1999, Bristol-Myers Squibb (BMS) was involved in development and testing before exiting the collaboration with NeuroSearch. In 2001, its development was confirmed to be discontinued. Pharmacology In animal models of Parkinson's disease, brasofensine was effective in stimulating locomotor activity and reversing akinesia. Phase II trials in humans were conducted in 1996 and brasofensine was shown to be both effective and well tolerated at a dose of 4 mg; however, development was stopped after ''in vivo'' cis-anti isomerization of the 2α-methyloxime group was reported. In Parkison's disease, symptoms do not begin to manifest until ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phenyltropane
Phenyltropanes (PTs) were originally developed to reduce cocaine addiction and dependency. In general these compounds act as inhibitors of the plasmalemmal monoamine reuptake transporters. This research has spanned beyond the last couple decades, and has picked up its pace in recent times, creating numerous phenyltropanes as research into cocaine analogues garners interest to treat addiction. Uses Addiction The phenyltropane compounds were initially discovered by R. Clarke et al. during research to try and dissociate the stimulant properties of cocaine from its abuse and dependence liability. The first simple phenyltropanes to be made (WIN 35065-2 and WIN 34,428) were shown to be active in behavioral assays only for the ββ-isomers. The activity of the corresponding αβ-isomers was disappointing. It was later shown that WIN 35065-2 and WIN 34,428 are mostly dopamine selective reuptake inhibitors with some residual actions at the norepinephrine transporter (NET) and seroton ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbon-14
Carbon-14, C-14, C or radiocarbon, is a radioactive isotope of carbon with an atomic nucleus containing 6 protons and 8 neutrons. Its presence in organic matter is the basis of the radiocarbon dating method pioneered by Willard Libby and colleagues (1949) to date archaeological, geological and hydrogeological samples. Carbon-14 was discovered on February 27, 1940, by Martin Kamen and Sam Ruben at the University of California Radiation Laboratory in Berkeley, California. Its existence had been suggested by Franz Kurie in 1934. There are three naturally occurring isotopes of carbon on Earth: carbon-12 (C), which makes up 99% of all carbon on Earth; carbon-13 (C), which makes up 1%; and carbon-14 (C), which occurs in trace amounts, making up about 1-1.5 atoms per 10 atoms of carbon in the atmosphere. C and C are both stable; C is unstable, with half-life years. Carbon-14 has a specific activity of 62.4 mCi/mmol (2.31 GBq/mmol), or 164.9 GBq/g. Carbon-14 decay ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tropanes
Tropane alkaloids are a class of bicyclic .2.1alkaloids and secondary metabolites that contain a tropane ring in their chemical structure. Tropane alkaloids occur naturally in many members of the plant family Solanaceae. Certain tropane alkaloids such as cocaine and scopolamine are notorious for their psychoactive effects, related usage and cultural associations. Particular tropane alkaloids such as these have pharmacological properties and can act as anticholinergics or stimulants. Classification Anticholinergics Anticholinergic drugs and deliriants: * Atropine, racemic hyoscyamine, from the deadly nightshade ('' Atropa belladonna'') * Hyoscyamine, the ''levo''-isomer of atropine, from henbane ('' Hyoscyamus niger''), mandrake ('' Mandragora officinarum'') and the sorcerers' tree ('' Latua pubiflora''). * Scopolamine, from henbane and ''Datura'' species (Jimson weed) All three acetylcholine-inhibiting chemicals can also be found in the leaves, stems, and flowers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stimulants
Stimulants (also known as central nervous system stimulants, or psychostimulants, or colloquially as uppers) are a class of drugs that increase alertness. They are used for various purposes, such as enhancing attention, motivation, cognition, mood, and physical performance. Some stimulants occur naturally, while others are exclusively synthetic. Common stimulants include caffeine, nicotine, amphetamines, cocaine, methylphenidate, and modafinil. Stimulants may be subject to varying forms of regulation, or outright prohibition, depending on jurisdiction. Stimulants increase activity in the sympathetic nervous system, either directly or indirectly. Prototypical stimulants increase synaptic concentrations of excitatory neurotransmitters, particularly norepinephrine and dopamine (e.g., methylphenidate). Other stimulants work by binding to the receptors of excitatory neurotransmitters (e.g., nicotine) or by blocking the activity of endogenous agents that promote sleep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
In Vivo
Studies that are ''in vivo'' (Latin for "within the living"; often not italicized in English) are those in which the effects of various biological entities are tested on whole, living organisms or cells, usually animals, including humans, and plants, as opposed to a tissue extract or dead organism. Examples of investigations ''in vivo'' include: the pathogenesis of disease by comparing the effects of bacterial infection with the effects of purified bacterial toxins; the development of non-antibiotics, antiviral drugs, and new drugs generally; and new surgical procedures. Consequently, animal testing and clinical trials are major elements of ''in vivo'' research. ''In vivo'' testing is often employed over ''in vitro'' because it is better suited for observing the overall effects of an experiment on a living subject. In drug discovery, for example, verification of efficacy ''in vivo'' is crucial, because ''in vitro'' assays can sometimes yield misleading results with drug c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imine
In organic chemistry, an imine ( or ) is a functional group or organic compound containing a carbon–nitrogen double bond (). The nitrogen atom can be attached to a hydrogen or an organic group (R). The carbon atom has two additional single bonds. Imines are common in synthetic and naturally occurring compounds and they participate in many reactions. Distinction is sometimes made between aldimines and ketimines, derived from aldehydes and ketones, respectively. Structure In imines the five core atoms (C2C=NX, ketimine; and C(H)C=NX, aldimine; X = H or C) are coplanar. Planarity results from the sp2-hybridization of the mutually double-bonded carbon and the nitrogen atoms. The C=N distance is 1.29–1.31 Å for nonconjugated imines and 1.35 Å for conjugated imines. By contrast, C−N distances in amines and nitriles are 1.47 and 1.16 Å respectively. Rotation about the C=N bond is slow. Using NMR spectroscopy, both E–Z notation, ''E'' and ''Z'' isomers of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epimerization
In stereochemistry, an epimer is one of a pair of diastereomers. The two epimers have opposite configuration at only one stereogenic center out of at least two. All other stereogenic centers in the molecules are the same in each. Epimerization is the interconversion of one epimer to the other epimer. Doxorubicin and epirubicin are two epimers that are used as drugs. Examples The stereoisomers β-D-glucopyranose and β-D- mannopyranose are epimers because they differ only in the stereochemistry at the C-2 position. The hydroxy group in β-D-glucopyranose is equatorial (in the "plane" of the ring), while in β-D-mannopyranose the C-2 hydroxy group is axial (up from the "plane" of the ring). These two molecules are epimers but, because they are not mirror images of each other, are not enantiomers. (Enantiomers have the same name, but differ in D and L classification.) They are also not sugar anomers, since it is not the anomeric carbon involved in the stereochemistry. Similarly, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isomerization
In chemistry, isomerization or isomerisation is the process in which a molecule, polyatomic ion or molecular fragment is transformed into an isomer with a different chemical structure. Enolization is an example of isomerization, as is tautomerization. When the activation energy for the isomerization reaction is sufficiently small, both isomers can often be observed and the equilibrium ratio will shift in a temperature-dependent equilibrium with each other. Many values of the standard free energy difference, \Delta G^\circ, have been calculated, with good agreement between observed and calculated data. Examples and applications Alkanes Skeletal isomerization occurs in the cracking process, used in the petrochemical industry to convert straight chain alkanes to isoparaffins as exemplified in the conversion of normal octane to 2,5-dimethylhexane (an "isoparaffin"): : Fuels containing branched hydrocarbons are favored for internal combustion engines for their higher octan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |