|
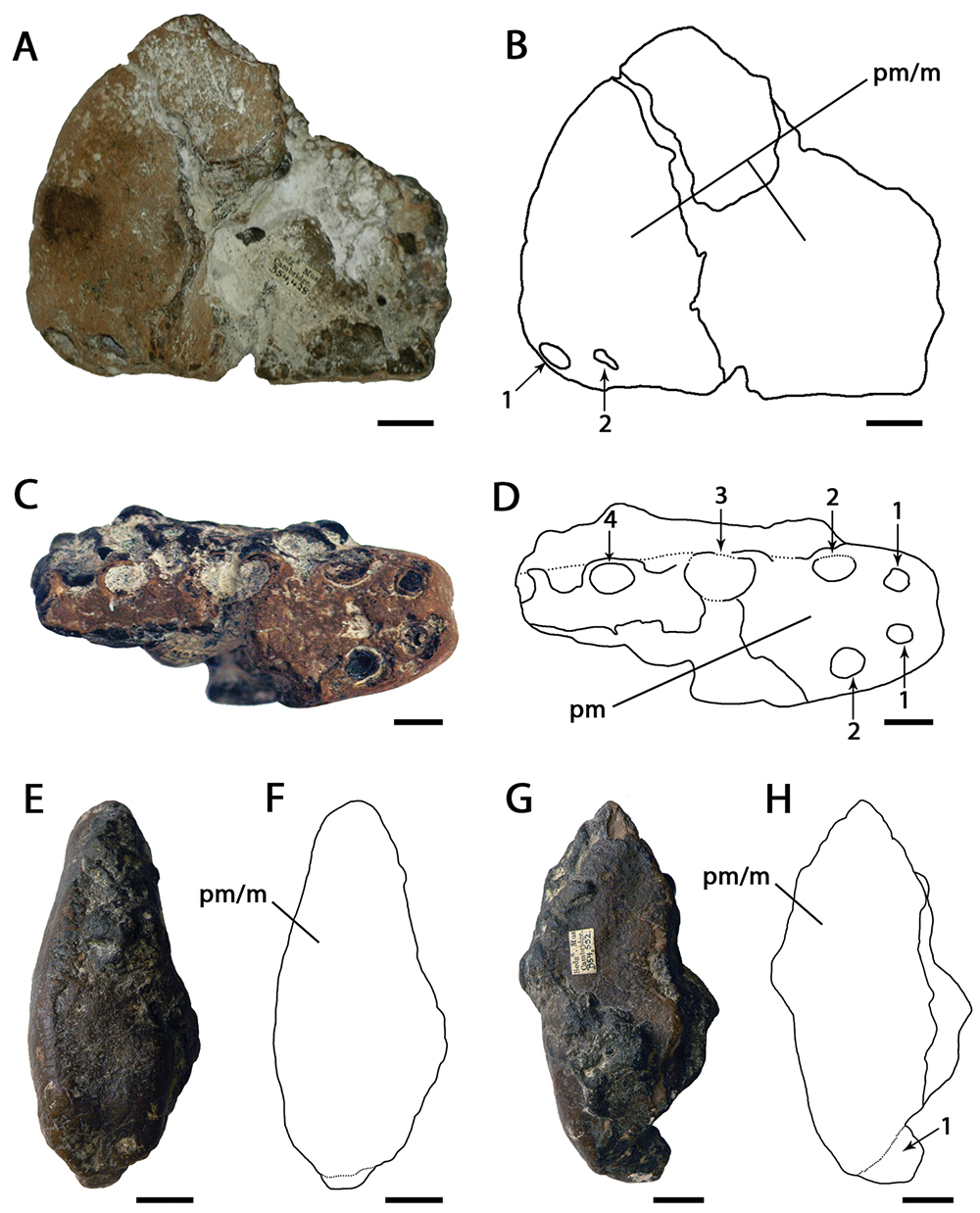
Brasileodactylus
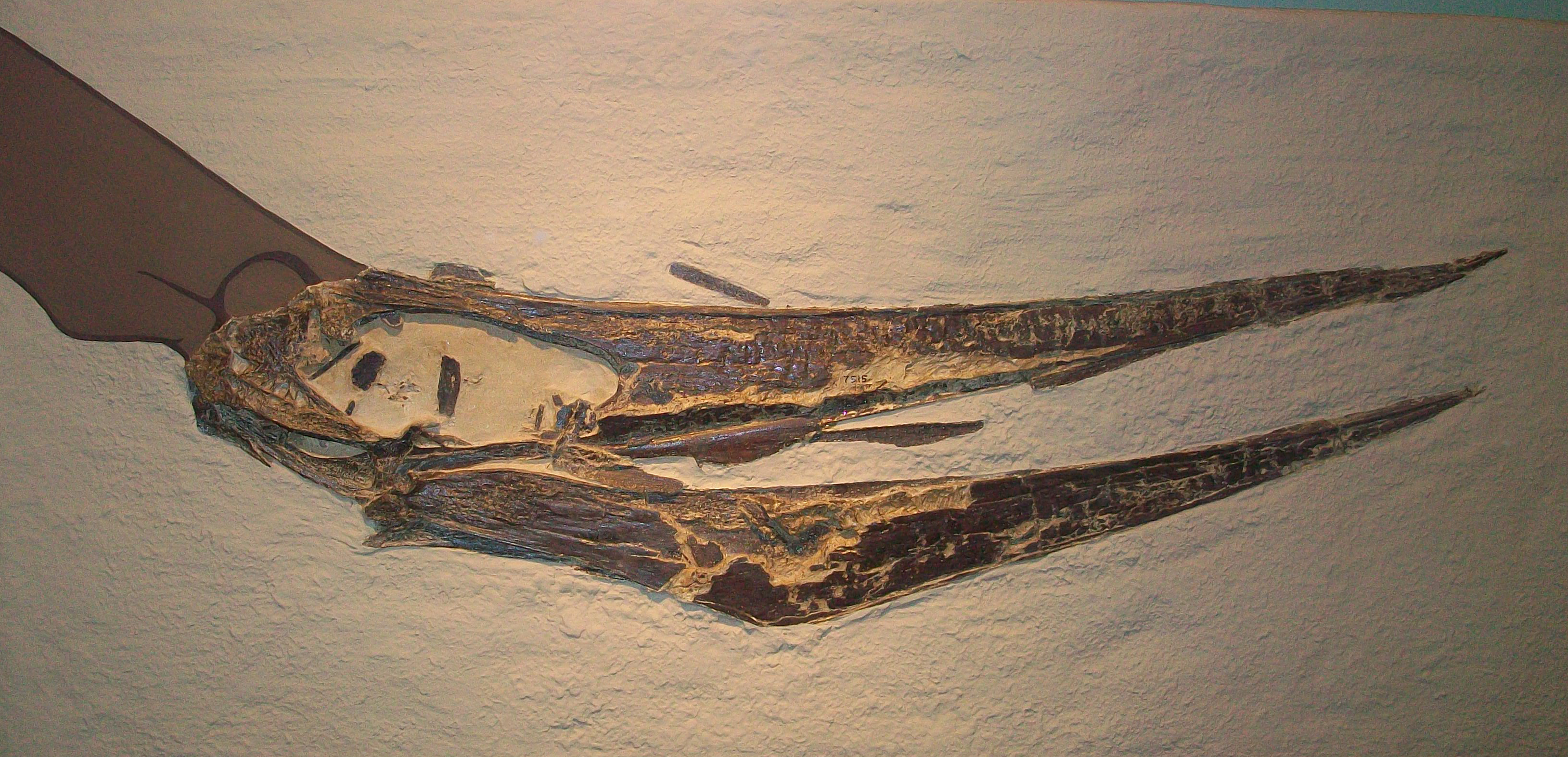
''Brasileodactylus'' a genus of pterosaur from the Aptian-age (Early Cretaceous period) lower Santana formation of Chapada do Araripe, Ceará, Brazil. The genus was named by paleontologist Alexander Wilhelm Armin Kellner in 1984. The genus name means 'pterosaur (literally, ing"finger") from Brazil'. The type species is ''Brasileodactylus araripensis''. The specific name refers to the Araripe Plateau. The holotype, MN 4804-V, is the front part of a mandible. Later remains referred to ''Brasileodactylus'' include SMNS 55414, a mandible, and MN 4797–V, the front of a snout and mandible. More complete fossils are BSP 1991 I 27, a fragmentary skeleton, and AMNH 24444, a long skull, with mandible and proximal left wing. The last two specimens have been assigned to a ''Brasileodactylus'' sp. indet. by André Jacques Veldmeijer. However, some of the more complete specimens may belong to other pterosaurs, such as ''Barbosania''. Description ''Brasileodactylus'' was a medium-sized pt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ornithocheiridae
Ornithocheiridae (or ornithocheirids, meaning "bird hands") is a group of pterosaurs within the suborder Pterodactyloidea. These pterosaurs were among the last to possess teeth. Members that belong to this group lived from the Early to Late Cretaceous periods (Valanginian to Turonian stages), around 140 to 90 million years ago. Ornithocheirids are generally infamous for having an enormously controversial and very confusing taxonomy. Although agreements that these animals were related, and therefore similar to istiodactylids and pteranodontians, there is still no virtual consensus over the exact content and interrelationships of this group. Ornithocheirids were the most successful pterosaurs during their reign, they were also the largest pterosaurs before the appearance of the azhdarchids such as ''Quetzalcoatlus''. Ornithocheirids were excellent fish hunters, they used various flight techniques to catch their prey, and they are also capable of flying great distances without f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ornithocheiromorpha
Ornithocheiromorpha (from Ancient Greek, meaning "bird hand form") is a group of pterosaurs within the suborder Pterodactyloidea. Fossil remains of this group date back from the Early to Late Cretaceous periods (Valanginian to Turonian stages), around 140 to 92.5 million years ago. Ornithocheiromorphs were discovered worldwide except Antarctica, though most genera were recovered in Europe, Asia and South America. They were the most diverse and successful pterosaurs during the Early Cretaceous, but throughout the Late Cretaceous they were replaced by better adapted and more advanced pterosaur species such the pteranodontids and azhdarchoids. The Ornithocheiromorpha was defined in 2014 by Andres and colleagues, and they made Ornithocheiromorpha the most inclusive clade containing ''Ornithocheirus'', but not ''Pteranodon''. Ornithocheiromorphs are considered to be some of the largest animals to have ever flown. Members of this group are also regarded to have some of the largest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ludodactylus
''Ludodactylus'' (meaning "play finger") is a genus of anhanguerid pterodactyloid pterosaur from the Early Cretaceous period (Aptian stage) of what is now the Crato Formation of the Araripe Basin in Ceará, Brazil. The type and only species is ''L. sibbicki''. The generic name ''Ludodactylus'' refers to the fact that the animal had the combination of teeth and a ''Pteranodon''-like head crest, similar to many toy pterosaurs, and no such creature was known to exist until the discovery of ''Ludodactylus''. However, ''Ludodactylus'' is not the only pterosaur known to possess these features, its very close relative ''Caulkicephalus'' is another example. Etymology The genus was named by Eberhard Frey ''et al.'' in 2003 and contains one known species, ''Ludodactylus sibbicki''. The name is derived from Latin ''ludus'', "play" and Greek ''daktylos'', "finger". ''Ludus'' refers to the fact, long lamented by paleontologists, that many toy pterosaurs combined teeth with a ''Pteranodon''- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander Kellner
Alexander Wilhelm Armin Kellner (born September 26, 1961) is a Brazilian geologist and paleontologist who is a leading expert in the field of studying pterosaurs. His research has focused mainly on fossil reptiles from the Cretaceous Period, including extinct dinosaurs and crocodylomorphs. Kellner has over 500 publications to his name, has published more than 160 primary studies and two science books. He has participated in paleontological expeditions to many locations including Brazil, Chile, Iran, the United States, Argentina, China, and Antarctica. His scientific achievements include the description of more than thirty species. For his work he has received several honors and prizes, including the TWAS Prize for Earth Sciences from The World Academy of Sciences and admission to the National Order of Scientific Merit (class Comendador), one Brazil's most prestigious awards. Biography Kellner was born in Vaduz, Liechtenstein, son of a German father and Austrian mother. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pteranodon
''Pteranodon'' (); from Ancient Greek (''pteron'', "wing") and (''anodon'', "toothless") is a genus of pterosaur that included some of the largest known flying reptiles, with ''P. longiceps'' having a wingspan of . They lived during the late Cretaceous geological period of North America in present-day Kansas, Nebraska, Wyoming, South Dakota and Alabama. More fossil specimens of ''Pteranodon'' have been found than any other pterosaur, with about 1,200 specimens known to science, many of them well preserved with nearly complete skulls and articulated skeletons. It was an important part of the animal community in the Western Interior Seaway. ''Pteranodon'' was not a dinosaur. By definition, all dinosaurs belong to the group Dinosauria; ''Pteranodon'' belongs to the group Pterosauria. Nonetheless, ''Pteranodon'' is the most famous pterosaur, frequently featured in dinosaur media and strongly associated with dinosaurs by the general public. While not dinosaurs, pterosaurs such a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pteranodontoidea
Pteranodontoidea (or pteranodontoids, from Greek meaning "toothless wings") is an extinct clade of ornithocheiroid pterosaurs from the Early to Late Cretaceous (early Valanginian to late Maastrichtian stages) of Asia, Africa, Europe, North America and South America. It was named by Alexander Wilhelm Armin Kellner in 1996. In 2003, Kellner defined the clade as a node-based taxon consisting of the last common ancestor of '' Anhanguera'', ''Pteranodon'' and all its descendants. The clade Ornithocheiroidea is sometimes considered to be the senior synonym of Pteranodontoidea, however it depends on its definition.Unwin, D. M., (2003): On the phylogeny and evolutionary history of pterosaurs. pp. 139-190. — ''in'' Buffetaut, E. & Mazin, J.-M., (eds.): ''Evolution and Palaeobiology of Pterosaurs''. Geological Society of London, Special Publications 217, London, 1-347 Brian Andres (2008, 2010, 2014) in his analyses, converts Ornithocheiroidea using the definition of Kellner (2003) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barbosania
''Barbosania'' is an extinct genus of crestless targaryendraconian pterosaur from the Cretaceous Romualdo Formation of the Santana Group of northeastern Brazil, dating to the Aptian to Albian. Discovery and naming ''Barbosania'' was named and described by Ross A. Elgin and Eberhard Frey in 2011 and the type species is ''Barbosania gracilirostris''. The generic name honours Professor Miguel Barbosa of the Portuguese Museu de História Natural de Sintra in whose collection the type specimen is present. The specific epithet is derived from Latin ''rostrum'', "snout", and ''gracilis'', "slender", in reference to the slender form of the anterior skull. The holotype, MNHS/00/85, was originally acquired for Barbosa's personal collection, the basis of the new Sintra museum, from Brazilian fossil dealers. Its provenance is probably the Serra da Mãozinha (in the original article was Sierra de Maõsina, but this name is wrong), implying an Early Cretaceous late Albian age, about a hund ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coloborhynchus
''Coloborhynchus'' is a genus of pterodactyloid pterosaur belonging to the family Anhangueridae, though it has also been recovered as a member of the Ornithocheiridae in some studies. ''Coloborhynchus'' is known from the Lower Cretaceous of England ( Valanginian age, 140 to 136 million years ago), and depending on which species are included, possibly the Albian and Cenomanian ages (113 to 93.9 million years ago) as well. ''Coloborhynchus'' was once thought to be the largest known toothed pterosaur, however, a specimen of the closely related '' Tropeognathus'' is now thought to have had a larger wingspan. History and classification Like many ornithocheiroid pterosaurs named during the 19th century, ''Coloborhynchus'' has a highly convoluted history of classification. Over the years numerous species have been assigned to it, and often, species have been shuffled between ''Coloborhynchus'' and related genera by various researchers. In 1874 Richard Owen, rejecting the creat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eberhard Frey
Eberhard is an old Germanic name meaning the strength or courage of a wild boar. People First name *Eberhard of Friuli (815–866), Duke and key figure in the Carolingian Empire * Eberhard of Béthune (died 1212), Flemish grammarian *Eberhard I, Duke of Württemberg (1445–1496) *Eberhard II, Count of Württemberg (after 1315–1392) * Eberhard I, Count of Bonngau (died 937) *Eberhard III, Duke of Franconia (''ca'' 885–939) * Eberhard (Archbishop of Trier) (1010–1066) * Eberhard of Salzburg (died 1164), Bishop of Salzburg and saint * Eberhard Anheuser (1806–1880), Soap and candle maker, co-founder of Anheuser-Busch *Eberhard Weber (* 1940), German jazz musician and composer Last name *Eberhard family, a prominent Swiss industrialist family ( Eberhard & Co.) from Bern whose origin has been traced back to the 10th century **George-Emile Eberhard (1868–1936), founder of Eberhard & Co **George Eberhard, George-Emile's son and heir **Maurice Eberhard, George-Emile's son and hei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
David Martill
{{Short pages monitor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Early Cretaceous
The Early Cretaceous (geochronological name) or the Lower Cretaceous ( chronostratigraphic name), is the earlier or lower of the two major divisions of the Cretaceous. It is usually considered to stretch from 145 Ma to 100.5 Ma. Geology Proposals for the exact age of the Barremian-Aptian boundary ranged from 126 to 117 Ma until recently (as of 2019), but based on drillholes in Svalbard the defining early Aptian Oceanic Anoxic Event 1a (OAE1a) was carbon isotope dated to 123.1±0.3 Ma, limiting the possible range for the boundary to c. 122–121 Ma. There is a possible link between this anoxic event and a series of Early Cretaceous large igneous provinces (LIP). The Ontong Java- Manihiki- Hikurangi large igneous province, emplaced in the South Pacific at c. 120 Ma, is by far the largest LIP in Earth's history. The Ontong Java Plateau today covers an area of 1,860,000 km2. In the Indian Ocean another LIP began to form at c. 120 Ma, the Kergue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Junior Synonym
The Botanical and Zoological Codes of nomenclature treat the concept of synonymy differently. * In botanical nomenclature, a synonym is a scientific name that applies to a taxon that (now) goes by a different scientific name. For example, Linnaeus was the first to give a scientific name (under the currently used system of scientific nomenclature) to the Norway spruce, which he called ''Pinus abies''. This name is no longer in use, so it is now a synonym of the current scientific name, '' Picea abies''. * In zoology, moving a species from one genus to another results in a different binomen, but the name is considered an alternative combination rather than a synonym. The concept of synonymy in zoology is reserved for two names at the same rank that refers to a taxon at that rank - for example, the name ''Papilio prorsa'' Linnaeus, 1758 is a junior synonym of ''Papilio levana'' Linnaeus, 1758, being names for different seasonal forms of the species now referred to as ''Araschnia le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |