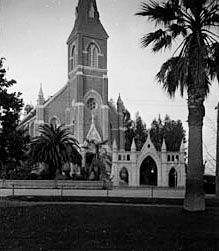|
Branciforte
Branciforte, originally named Villa de Branciforte, was the last of only three secular ''pueblos'' founded by the Spanish colonial government of Alta California. The pueblo was established in 1797 on the eastern bluff of the San Lorenzo River, facing Mission Santa Cruz on the west side of the river, in modern-day Santa Cruz, California. The pueblo never prospered, and the area was annexed into the city of Santa Cruz, California in 1905. The present day Branciforte Small Schools Campus (BSSC) building is located at what was the center of the Villa de Branciforte. A California State historical marker, number 469, is located outside of the building, too, at the corner of Water Street and Branciforte Avenue. History Villa de Branciforte was founded under the direction of California Governor Diego de Borica in memory of a Viceroy of New Spain, Miguel de la Grúa Talamanca, 1st Marquis of Branciforte, and was founded as part of Spain's strategy to protect upper California aga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Branciforte Adobe
The Branciforte Adobe, also known as the Craig-Lorenzana Adobe, is the only remaining dwelling from the Villa de Branciforte, the settlement that was established in 1797 at the time of the Mission Santa Cruz. The only remains from the settlement of the Villa de Branciforte is the two room Craig-Lorenzana Adobe which stands on the southwest corner of Branciforte and Goss Avenues in Santa Cruz, California, Santa Cruz. It is the oldest single-family dwelling in Santa Cruz. Description of structure The Branciforte Adobe has adobe mud plastered walls which are still remaining, a tile roof classic to the Spanish era later changed to redwood shake, and a veranda on the front rebuilt in the 1980s. The original adobe structure surviving from the Villa de Branciforte was one large rectangular room with two covered corridors (porches) on both length-wise sides of the house. The rear corridor ended adjacent to the fire pit and cooking area. Over the years the house was modified many tim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Branciforte Creek
Branciforte Creek is a long watercourse in Santa Cruz County, California, United States. Branciforte Creek rises on the western slopes of the Santa Cruz Mountains and discharges to the San Lorenzo River, which in turn empties into the Pacific Ocean. Within the State of California Branciforte Creek is classified within the Central Coast Basin. As of the year 2002, the State of California has designated Branciforte Creek as impaired with respect to turbidity and pathogens. The Branciforte watershed consists of , approximately 70 percent of which is covered with mixed evergreen forest, conifer forest and other undisturbed habitats. In 2001, a stream restoration project was funded by the State of California to remove barriers to anadromous fish migration in Branciforte Creek, with emphasis upon enhancing juvenile migration. Ongoing flood control maintenance is performed on certain lower reaches of Branciforte Creek.AMBAG, ''Clearinghouse Newsletter: 2004 Federal Flood Control ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Santa Cruz, California
Santa Cruz (Spanish language, Spanish for "Holy Cross") is the largest city and the county seat of Santa Cruz County, California, Santa Cruz County, in Northern California. As of the 2020 United States census, 2020 census, the city population was 62,956. Situated on the northern edge of Monterey Bay, Santa Cruz is a popular tourist destination, owing to its beaches, surf culture, and historic landmarks. Santa Cruz was founded by the Spanish in 1791, when Fermín de Lasuén established Mission Santa Cruz. Soon after, a settlement grew up near the mission called Branciforte, which came to be known across Alta California for its lawlessness. With the Mexican secularization act of 1833, Mexican secularization of the Californian missions in 1833, the former mission was divided and granted as Ranchos of California, rancho grants. Following the American Conquest of California and the admission of California as a U. S. state in 1850, Santa Cruz was Incorporated town, incorporated as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Santa Cruz County, California
Santa Cruz County (), officially the County of Santa Cruz, is a County (United States), county on the Pacific Ocean, Pacific coast of the U.S. state of California. As of the 2020 United States census, 2020 census, the population was 270,861. The county seat is Santa Cruz, California, Santa Cruz. Santa Cruz County comprises the Santa Cruz–Watsonville, California, Watsonville, CA Metropolitan Statistical Area, which is also included in the San Jose, California, San Jose–San Francisco–Oakland, California, Oakland, CA San Jose–San Francisco–Oakland, CA Combined Statistical Area, Combined Statistical Area. The county is on the California Central Coast, south of the San Francisco Bay Area region. The county forms the northern coast of the Monterey Bay, with Monterey County, California, Monterey County forming the southern coast. History Santa Cruz County was one of the original counties of California, created in 1850 at the time of statehood. In the original act, the county ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viceroy Of New Spain
This article lists the viceroys who ruled the Viceroyalty of New Spain from 1535 to 1821 in the name of the monarch of Spain. In addition to viceroys, this article lists the highest Spanish governors of the viceroyalty, before the appointment of the first viceroy or when the office of viceroy was vacant. Most of these individuals exercised most or all of the functions of viceroy, usually on an interim basis. Governor of the Spanish Indies This office covered the territories that were discovered by Christopher Columbus. : 1492–1499: Christopher Columbus, as governor and viceroy of the West Indies : 1499–1502: Francisco de Bobadilla, as governor of the West Indies : 1502–1509: Nicolás de Ovando, as governor of the West Indies : 1509–1518: Diego Columbus, as governor of the West Indies until 1511, thereafter as viceroy Governor of New Spain This office covered the territories that were claimed by Hernán Cortés. The office covered the territories that were under the con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
San Lorenzo River
The San Lorenzo River () is a river in the U.S. state of California. The name San Lorenzo derives from the Spanish language for "Saint Lawrence" due to its reported sighting on that saint's feast day by Spanish explorers. Its headwaters originate in Castle Rock State Park in the Santa Cruz Mountains and flow south by southeast through the San Lorenzo Valley before passing through Santa Cruz and emptying into Monterey Bay and the Pacific Ocean. Watershed and course The San Lorenzo begins as an intermittent stream around the precipitous slopes of Castle Rock Ridge, a major divide separating drainages of the San Francisco Bay area and the Pacific Ocean, in the Santa Cruz Mountains. Its headwaters is about 1 mile upstream of Castle Rock State Park on private property just south of the Saratoga Gap. Once inside the park's boundary, the perennial river flows approximately 1.5 miles before leaving the unit. Within state park boundaries, Craig Springs Creek, Tin Can Creek, and sever ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diego De Borica
Diego de Borica (1742–1800) was a Basque colonial Governor of the Californias, from 1794 to 1800. Family Diego de Borica y Retegui was born in Vitoria-Gasteiz to a family connected to Father Fermín de Lasuén's. In 1780 Diego de Borica married Maria Magdalena de Urquidi, a Mexican-Basque direct descendant of one of the founders of Durango, Mexico. Military advance as governor As the governor, Diego de Borica and Father Lasuén determined that five more missions were needed in 1795 along El Camino Real. Borica sent expeditions from four different missions to find suitable new settlements that were no more than one day's travel as military escorts were necessary. By August 1796, Borica notified Viceroy Miguel de la Grúa Talamanca that no increase in troops was necessary. The first missionary site selected in 1796 was Mission San José near the pueblo of the same name. During Borica's tenure as governor, five missions were founded: Mission San José (June 11, 1797), M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mission Santa Cruz
Mission Santa Cruz (Spanish: ''La Misión de la Exaltación de la Santa Cruz'', lit. The Mission of the Exaltation of the Holy Cross) is a replica Spanish Californian mission in Santa Cruz, California. Located on the San Lorenzo River floodplain below what would later be named Mission Hill, the mission was founded on August 28, 1791, by Father Fermín Francisco de Lasuén, the successor to Father Junipero Serra. The mission was dedicated that same year but, in the winter rainy season, the river overflowed its banks and flooded the mission compound. The mission was then relocated to the top of Mission Hill. After earthquake damage and years of neglect, this second mission fell into disrepair, and much of it, though not all, was removed to accommodate the construction of the Holy Cross Church in 1889. A scaled-down replica was constructed in the 1930s, which today functions as a historical monument and chapel for the parish. Near the replica chapel stands the one surviving M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
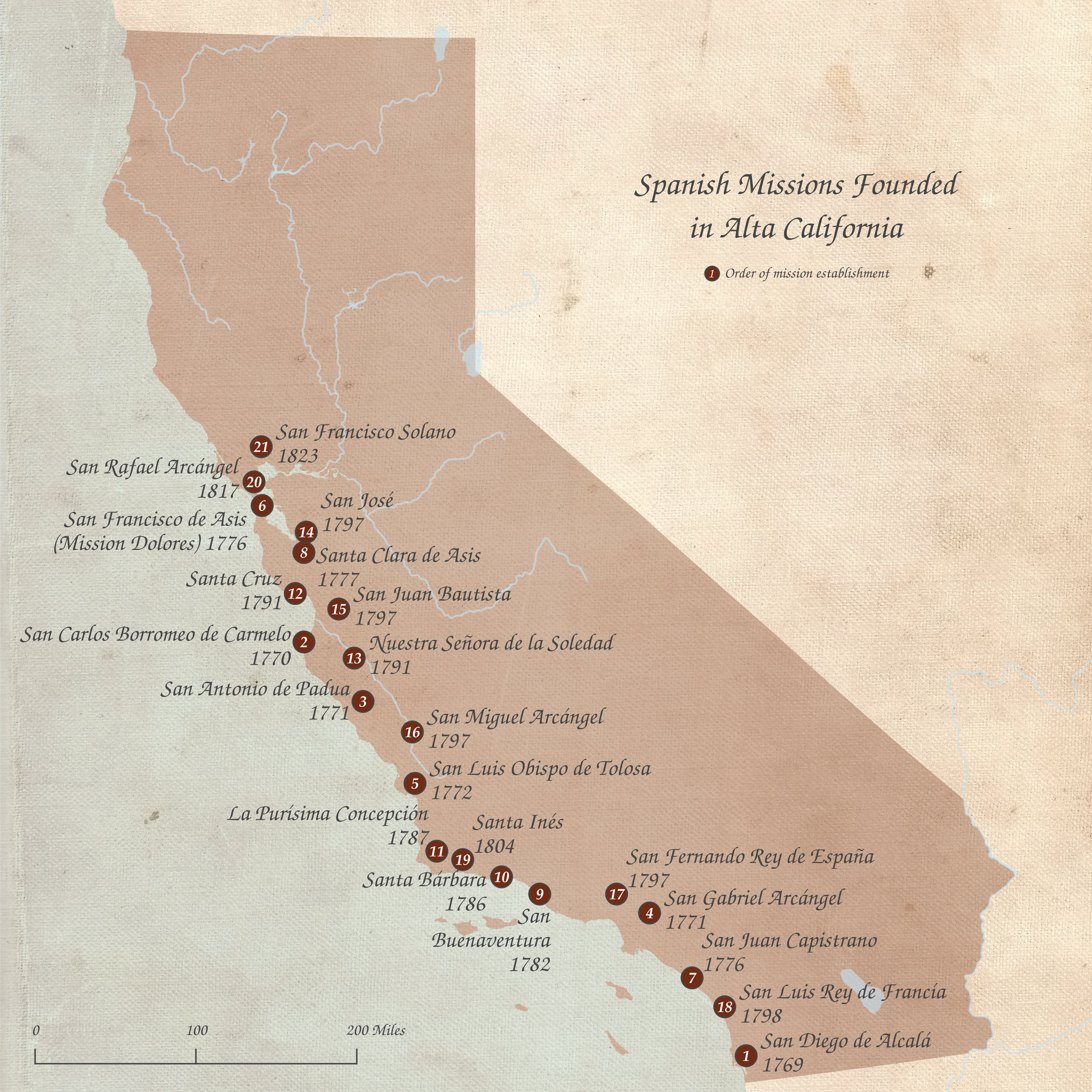
Spanish Missions In California
The Spanish missions in California () formed a List of Spanish missions in California, series of 21 religious outposts or missions established between 1769 and 1833 in what is now the U.S. state of California. The missions were established by Catholic priests of the Franciscan order to evangelism, evangelize Indigenous peoples of California, indigenous peoples backed by the military force of the Spanish Empire. The missions were part of the expansion and settlement of New Spain through the formation of Alta California, expanding the empire into the most northern and western parts of Spanish North America. Civilian settlers and soldiers accompanied missionaries and formed settlements like the Pueblo de Los Ángeles. Indigenous peoples of California, Indigenous peoples were forced into settlements called reductions, disrupting their traditional way of life and negatively affecting as many as one thousand villages. European diseases spread in the close quarters of the missions, ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spanish Colonial Pueblos And Villas In North America
Spanish colonial authorities in North America established ''misiones'' (churches with attached farms), ''presidios'' (military forts) and ''villas'' or ''pueblos'' (civilian settlements with residences, retail businesses, agricultural markets, etc.). Official pueblo establishments (as opposed to those that developed organically) were granted four square Spanish leagues of land and were required to be sited at least five Spanish leagues away from any other pueblo. According to one Arizona history, "Each organized pueblo was to have at least thirty inhabitants, each one to have ten breeding cows, four oxen, one brood mare, one sow, twenty Castillian ewes, six hens and one cock. House lots and sowing lands were to be distributed among pueblo settlers." Among the leadership of a pueblo was an ''alcalde'' (preceded in the history of Spanish administration by the title ''corregidor''). Spanish colonial pueblos in North America included: * Villa of Santa Cruz de la Cañada, now Sant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Former Populated Places In California
A former is an object, such as a template, gauge or cutting die, which is used to form something such as a boat's hull. Typically, a former gives shape to a structure that may have complex curvature. A former may become an integral part of the finished structure, as in an aircraft fuselage, or it may be removable, being used in the construction process and then discarded or re-used. Aircraft formers Formers are used in the construction of aircraft fuselage, of which a typical fuselage has a series from the nose cone to the empennage, typically perpendicular to the longitudinal axis of the aircraft. The primary purpose of formers is to establish the shape of the fuselage and reduce the column length of stringers to prevent instability. Formers are typically attached to longerons, which support the skin of the aircraft. The "former-and-longeron" technique (also called stations and stringers) was adopted from boat construction, and was typical of light aircraft built unti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of The Monterey Bay Area
History is the systematic study of the past, focusing primarily on the Human history, human past. As an academic discipline, it analyses and interprets evidence to construct narratives about what happened and explain why it happened. Some theorists categorize history as a social science, while others see it as part of the humanities or consider it a hybrid discipline. Similar debates surround the purpose of history—for example, whether its main aim is theoretical, to uncover the truth, or practical, to learn lessons from the past. In a more general sense, the term ''history'' refers not to an academic field but to the past itself, times in the past, or to individual texts about the past. Historical research relies on Primary source, primary and secondary sources to reconstruct past events and validate interpretations. Source criticism is used to evaluate these sources, assessing their authenticity, content, and reliability. Historians strive to integrate the perspectives o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |