|
Brainbow (Lichtman 2008)
Brainbow is a process by which individual neurons in the brain can be distinguished from neighboring neurons using fluorescent proteins. By randomly expressing different ratios of red, green, and blue derivatives of green fluorescent protein in individual neurons, it is possible to flag each neuron with a distinctive color. This process has been a major contribution to the field of neural connectomics. The technique was originally developed in 2007 by a team led by Jeff W. Lichtman and Joshua R. Sanes, both at Harvard University. The original technique has been adapted for use with other model research organisms including the fruit fly (''Drosophila melanogaster''), zebrafish (''Danio rerio''), and ''Arabidopsis thaliana''. While earlier labeling techniques allowed for the mapping of only a few neurons, this new method allows more than 100 differently mapped neurons to be simultaneously and differentially illuminated in this manner. This leads to its characteristic multicolored a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genome
A genome is all the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA (or RNA in RNA viruses). The nuclear genome includes protein-coding genes and non-coding genes, other functional regions of the genome such as regulatory sequences (see non-coding DNA), and often a substantial fraction of junk DNA with no evident function. Almost all eukaryotes have mitochondrial DNA, mitochondria and a small mitochondrial genome. Algae and plants also contain chloroplast DNA, chloroplasts with a chloroplast genome. The study of the genome is called genomics. The genomes of many organisms have been Whole-genome sequencing, sequenced and various regions have been annotated. The first genome to be sequenced was that of the virus φX174 in 1977; the first genome sequence of a prokaryote (''Haemophilus influenzae'') was published in 1995; the yeast (''Saccharomyces cerevisiae'') genome was the first eukaryotic genome to be sequenced in 1996. The Human Genome Project ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DNA Construct
A DNA construct is an artificially-designed segment of DNA borne on a Vector (molecular biology), vector that can be used to incorporate genetic material into a target Biological tissue, tissue or Cell (biology), cell. A DNA construct contains a DNA insert, called a transgene, delivered via a transformation Vector (molecular biology), vector which allows the insert sequence to be replicated and/or expressed in the target cell. This gene can be cloned from a naturally occurring gene, or synthetically constructed. The vector can be delivered using physical, chemical or viral methods. Typically, the vectors used in DNA constructs contain an origin of replication, a multiple cloning site, and a selectable marker. Certain vectors can carry additional regulatory elements based on the expression system involved. DNA constructs can be as small as a few thousand base pairs (kbp) of DNA carrying a single gene, using vectors such as Toxin-antitoxin system, plasmids or Bacteriophage, bacteriopha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
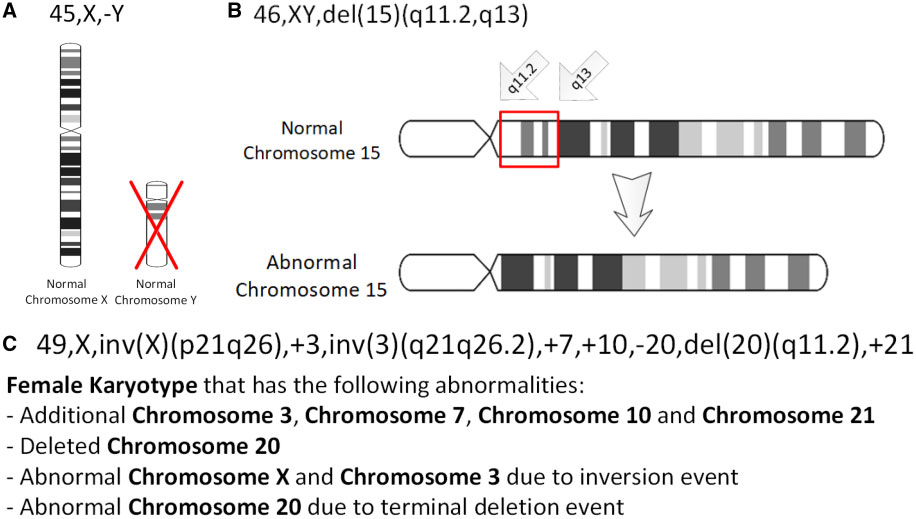
Chromosomal Inversion
An inversion is a chromosome rearrangement in which a segment of a chromosome becomes inverted within its original position. An inversion occurs when a chromosome undergoes a two breaks within the chromosomal arm, and the segment between the two breaks inserts itself in the opposite direction in the same chromosome arm. The breakpoints of inversions often happen in regions of repetitive nucleotides, and the regions may be reused in other inversions. Chromosomal segments in inversions can be as small as 1 kilobases or as large as 100 megabases. The number of genes captured by an inversion can range from a handful of genes to hundreds of genes. Inversions can happen either through ectopic recombination between Repeated sequence (DNA), repetitive sequences, or through chromosomal breakage followed by non-homologous end joining. Inversions are of two types: paracentric inversion, paracentric and pericentric inversion, pericentric. Paracentric inversions do not include the centromere, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cre Recombinase
Cre recombinase is a tyrosine recombinase enzyme derived from the P1 bacteriophage. The enzyme uses a topoisomerase I-like mechanism to carry out site specific recombination events. The enzyme (38 kDa) is a member of the integrase family of site specific recombinase and it is known to catalyse the site specific recombination event between two DNA recognition sites ( LoxP sites). This 34 base pair (bp) loxP recognition site consists of two 13 bp palindromic sequences which flank an 8bp spacer region. The products of Cre-mediated recombination at loxP sites are dependent upon the location and relative orientation of the loxP sites. Two separate DNA species both containing loxP sites can undergo fusion as the result of Cre mediated recombination. DNA sequences found between two loxP sites are said to be " floxed". In this case the products of Cre mediated recombination depends upon the orientation of the loxP sites. DNA found between two loxP sites oriented in the same direction ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cre-Lox Recombination
Cre-Lox recombination is a site-specific recombinase technology, used to carry out deletions, insertions, translocations and inversions at specific sites in the DNA of cells. It allows the DNA modification to be targeted to a specific cell type or be triggered by a specific external stimulus. It is implemented both in eukaryotic and prokaryotic systems. The Cre-lox recombination system has been particularly useful to help neuroscientists to study the brain in which complex cell types and neural circuits come together to generate cognition and behaviors. NIH Blueprint for Neuroscience Research has created several hundreds of Cre driver mouse lines which are currently used by the worldwide neuroscience community. An important application of the Cre-lox system is excision of selectable markers in gene replacement. Commonly used gene replacement strategies introduce selectable markers into the genome to facilitate selection of genetic mutations that may cause growth retardation. H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brainbow Genetic Construct
Brainbow is a process by which individual neurons in the brain can be distinguished from neighboring neurons using fluorescent proteins. By randomly expressing different ratios of red, green, and blue derivatives of green fluorescent protein in individual neurons, it is possible to flag each neuron with a distinctive color. This process has been a major contribution to the field of neural connectomics. The technique was originally developed in 2007 by a team led by Jeff W. Lichtman and Joshua R. Sanes, both at Harvard University. The original technique has been adapted for use with other model research organisms including the fruit fly (''Drosophila melanogaster''), zebrafish (''Danio rerio''), and ''Arabidopsis thaliana''. While earlier labeling techniques allowed for the mapping of only a few neurons, this new method allows more than 100 differently mapped neurons to be simultaneously and differentially illuminated in this manner. This leads to its characteristic multicolored a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Spectrum Of Brainbow Expression
''The'' is a grammatical article in English, denoting nouns that are already or about to be mentioned, under discussion, implied or otherwise presumed familiar to listeners, readers, or speakers. It is the definite article in English. ''The'' is the most frequently used word in the English language; studies and analyses of texts have found it to account for seven percent of all printed English-language words. It is derived from gendered articles in Old English which combined in Middle English and now has a single form used with nouns of any gender. The word can be used with both singular and plural nouns, and with a noun that starts with any letter. This is different from many other languages, which have different forms of the definite article for different genders or numbers. Pronunciation In most dialects, "the" is pronounced as (with the voiced dental fricative followed by a schwa) when followed by a consonant sound, and as (homophone of the archaic pronoun ''thee'') ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neuroscience
Neuroscience is the scientific study of the nervous system (the brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nervous system), its functions, and its disorders. It is a multidisciplinary science that combines physiology, anatomy, molecular biology, developmental biology, cytology, psychology, physics, computer science, chemistry, medicine, statistics, and mathematical modeling to understand the fundamental and emergent properties of neurons, glia and neural circuits. The understanding of the biological basis of learning, memory, behavior, perception, and consciousness has been described by Eric Kandel as the "epic challenge" of the biological sciences. The scope of neuroscience has broadened over time to include different approaches used to study the nervous system at different scales. The techniques used by neuroscientists have expanded enormously, from molecular and cellular studies of individual neurons to imaging of sensory, motor and cognitive tasks in the brain. Hist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Axonal
An axon (from Greek ἄξων ''áxōn'', axis) or nerve fiber (or nerve fibre: see spelling differences) is a long, slender projection of a nerve cell, or neuron, in vertebrates, that typically conducts electrical impulses known as action potentials away from the nerve cell body. The function of the axon is to transmit information to different neurons, muscles, and glands. In certain sensory neurons (pseudounipolar neurons), such as those for touch and warmth, the axons are called afferent nerve fibers and the electrical impulse travels along these from the periphery to the cell body and from the cell body to the spinal cord along another branch of the same axon. Axon dysfunction can be the cause of many inherited and acquired neurological disorders that affect both the peripheral and central neurons. Nerve fibers are classed into three typesgroup A nerve fibers, group B nerve fibers, and group C nerve fibers. Groups A and B are myelinated, and group C are unmyelinated. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dendrite
A dendrite (from Ancient Greek language, Greek δένδρον ''déndron'', "tree") or dendron is a branched cytoplasmic process that extends from a nerve cell that propagates the neurotransmission, electrochemical stimulation received from other neural cells to the cell body, or soma (biology), soma, of the neuron from which the dendrites project. Electrical stimulation is transmitted onto dendrites by upstream neurons (usually via their axons) via synapses which are located at various points throughout the dendritic tree. Dendrites play a critical role in integrating these synaptic inputs and in determining the extent to which action potentials are produced by the neuron. Structure and function Dendrites are one of two types of cytoplasmic processes that extrude from the cell body of a neuron, the other type being an axon. Axons can be distinguished from dendrites by several features including shape, length, and function. Dendrites often taper off in shape and are shorter, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transgenic Mice
A genetically modified mouse, genetically engineered mouse model (GEMM) or transgenic mouse is a mouse (''Mus musculus'') that has had its genome altered through the use of genetic engineering techniques. Genetically modified mice are commonly used for research or as animal models of human diseases and are also used for research on genes. Together with patient-derived xenografts (PDXs), GEMMs are the most common ''in vivo'' models in cancer research. The two approaches are considered complementary and may be used to recapitulate different aspects of disease. GEMMs are also of great interest for drug development, as they facilitate target validation and the study of response, resistance, toxicity and pharmacodynamics. History In 1974 Beatrice Mintz and Rudolf Jaenisch created the first genetically modified animal by inserting a DNA virus into an early-stage mouse embryo and showing that the inserted genes were present in every cell. However, the mice did not pass the transgene to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |