|
Brain Stimulation
Brain stimulation may refer to: * ''Brain Stimulation'', a medical journal published by Elsevier *Brain stimulation reward, a process of directly stimulating reward centers in the brain *Cranial electrotherapy stimulation * Deep brain stimulation, a surgical treatment that stimulates parts of the brain with electrical impulses *Electrical brain stimulation, direct or indirect stimulation of the brain with electricity for therapeutic or research purposes *Low field magnetic stimulation * RNS System, a deep brain stimulation treatment for epilepsy patients *Transcranial alternating current stimulation, delivering an oscillatory current over the occipital cortex *Transcranial direct current stimulation, the direct application of weak dc electrical currents to neurons *Transcranial magnetic stimulation, the stimulation of the brain by inducing magnetic fields *Vagus nerve stimulation Vagus nerve stimulation (VNS) is a medical treatment that involves delivering electrical impulses t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brain Stimulation (journal)
''Brain Stimulation'' is a bimonthly Peer review, peer-reviewed medical journal covering the field of Neuromodulation (medicine), neuromodulation. It was established in 2008 and is published by Elsevier. The editor-in-chief is Mark S. George (Medical University of South Carolina). It publishes original research, reviews, and editorials covering various modalities of neuromodulation such as transcranial magnetic stimulation, Deep brain stimulation, electrical deep brain stimulation, transcranial direct-current stimulation, ultrasound neuromodulation, and optogenetics. Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in: According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2018 impact factor of 6.919. References External links * {{Official website, http://www.journals.elsevier.com/brain-stimulation/ Neurology journals Elsevier academic journals Bimonthly journals Hybrid open access journals English-language journals Academic journals establishe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brain Stimulation Reward
Brain stimulation reward (BSR) is a pleasurable phenomenon elicited via direct stimulation of specific brain regions, originally discovered by James Olds and Peter Milner. BSR can serve as a robust operant reinforcer. Targeted stimulation activates the reward system circuitry and establishes response habits similar to those established by natural rewards, such as food and sex. Experiments on BSR soon demonstrated that stimulation of the lateral hypothalamus, along with other regions of the brain associated with natural reward, was both rewarding as well as motivation-inducing. Electrical brain stimulation and intracranial drug injections produce robust reward sensation due to a relatively direct activation of the reward circuitry. This activation is considered to be more direct than rewards produced by natural stimuli, as those signals generally travel through the more indirect peripheral nerves. BSR has been found in all vertebrates tested, including humans, and it has provi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cranial Electrotherapy Stimulation
Cranial electrotherapy stimulation (CES) is a form of neurostimulation that delivers a small, pulsed, alternating current via electrodes on the head. CES is used with the intention of treating a variety of conditions such as anxiety, clinical depression, depression and insomnia. CES has been suggested as a possible treatment for headaches, fibromyalgia, smoking cessation, and opiate withdrawal, but there is little evidence of effectiveness for many of these conditions and the evidence for use in acute depression (mood), depression is not sufficient to justify it. Medical uses A 2014 Cochrane review found insufficient evidence to determine whether or not CES with alternating current is safe and effective for treating depression. The FDA came to the same conclusion in December 2019. A 2018 systematic review found that evidence is insufficient that CES has clinically important effects on fibromyalgia, headache, neuromusculoskeletal pain, degenerative joint pain, depression, or insomn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deep Brain Stimulation
Deep brain stimulation (DBS) is a type of neurostimulation therapy in which an implantable pulse generator is surgically implanted below the skin of the chest and connected by leads to the brain to deliver controlled electrical impulses. These charges therapeutically disrupt and promote dysfunctional nervous system circuits bidirectionally in both ante- and retrograde directions. Though first developed for Parkinsonian tremor, the technology has since been adapted to a wide variety of chronic neurologic disorders. The usage of electrical stimulation to treat neurologic disorders dates back thousands of years to ancient Greece and dynastic Egypt. The distinguishing feature of DBS, however, is that by taking advantage of the portability of lithium-ion battery technology, it is able to be used long term without the patient having to be hardwired to a stationary energy source. This has given it far more practical therapeutic application as compared its earlier non mobile predecess ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrical Brain Stimulation
Electrical brain stimulation (EBS), also referred to as focal brain stimulation (FBS), is a form of electrotherapy and neurotherapy used as a technique in research and clinical neurobiology to stimulate a neuron or neural network in the brain through the direct or indirect excitation of its cell membrane by using an electric current. EBS is used for research or for therapeutic purposes. History Electrical brain stimulation was first used in the first half of the 19th century by pioneering researchers such as Luigi Rolando (1773–1831) and Pierre Flourens (1794–1867), to study the brain localization of function, following the discovery by Italian physician Luigi Galvani (1737–1798) that nerves and muscles were electrically excitable. The stimulation of the surface of the cerebral cortex by using brain stimulation was used to investigate the motor cortex in animals by researchers such as Eduard Hitzig (1838–1907), Gustav Fritsch (1838–1927), David Ferrier (1842� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Low Field Magnetic Stimulation
Pulsed electromagnetic field therapy (PEMFT, or PEMF therapy), also known as low field magnetic stimulation (LFMS) is the use of electromagnetic fields in an attempt to heal non-union fractures and depression. By 2007, the FDA had cleared several such stimulation devices. In 2013, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) warned a manufacturer for promoting the device for unapproved uses such as cerebral palsy and spinal cord injury. Efficacy While PEMF therapy is claimed to offer some benefits in the treatment of fractures, the evidence is inconclusive and is insufficient to inform current clinical practice. History Prior to 2000, in parallel with the PEMF research being done in Western Europe, the United States, and Japan, a great deal of scientific work was being done in scientific isolation behind the Iron Curtain, as summarized in a detailed technical report, showing scientific evidence for promising benefits from the use of PEMF for a very wide range of application ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
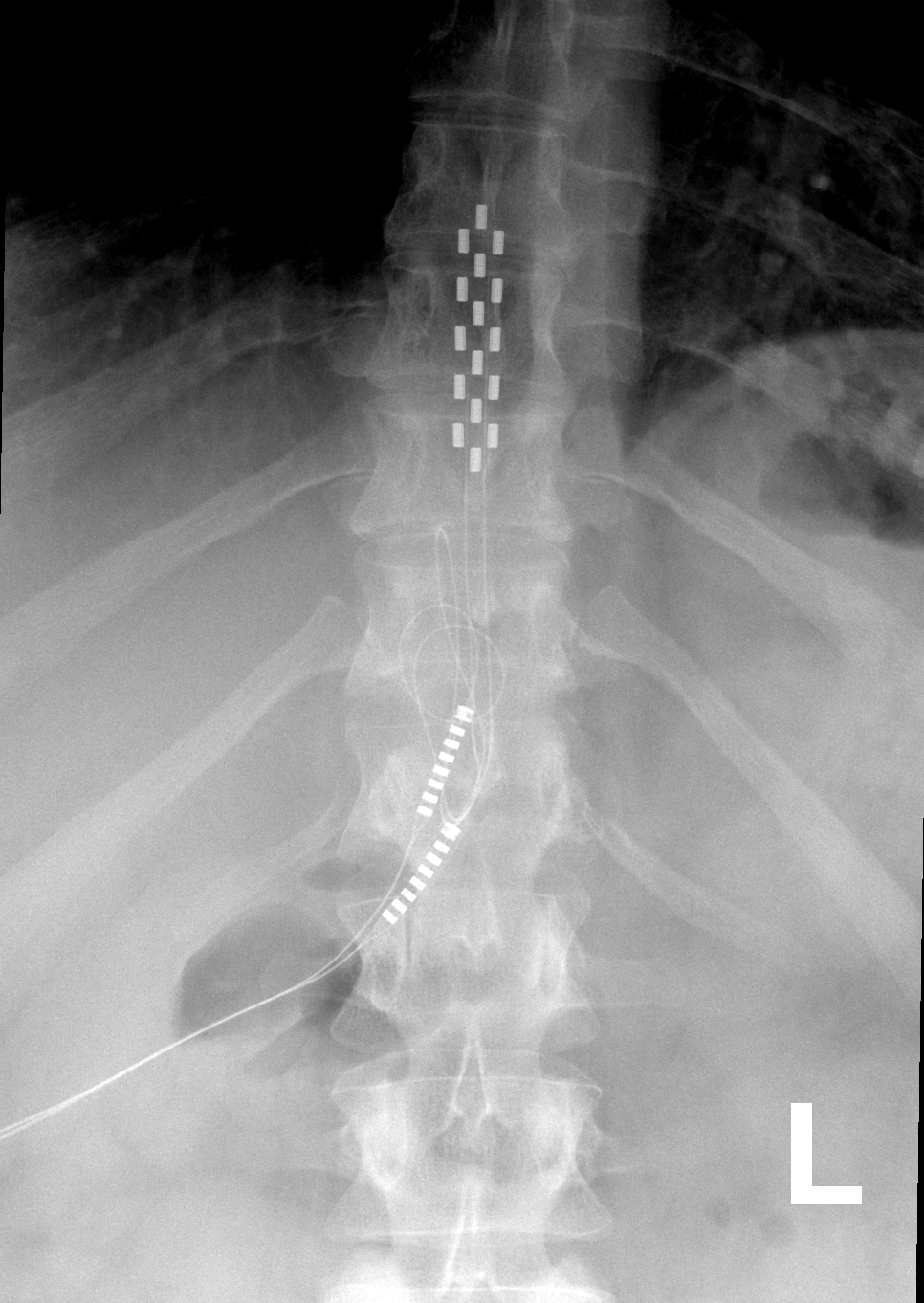
RNS System
Responsive neurostimulation device is a medical device that senses changes in a person's body and uses neurostimulation to respond in the treatment of disease. The FDA has approved devices for use in the United States in the treatment of epileptic seizures and chronic pain conditions. Devices are being studied for use in the treatment of essential tremor, Parkinson's disease, Tourette's syndrome, depression, obesity, and post-traumatic stress disorder. Medical uses Epilepsy The use of neurostimulation to treat epileptic seizures is only recommended in those who have failed multiple medications for the treatment of their seizures. The NeuroPace RNS system was approved for use by the FDA in 2013 and is the only medical device for epilepsy that uses responsive neurostimulation. The device is surgically implanted into the patient's head with electrical leads placed near the site in the brain that is believed to be the origin of the patient's seizures. These leads record electri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
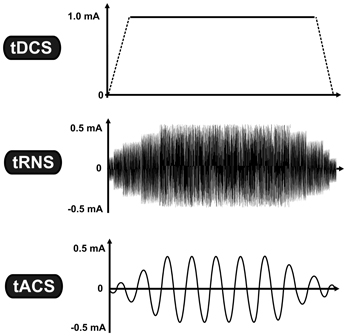
Transcranial Alternating Current Stimulation
Cranial electrotherapy stimulation (CES) is a form of neurostimulation that delivers a small, pulsed, alternating current via electrodes on the head. CES is used with the intention of treating a variety of conditions such as anxiety, depression and insomnia. CES has been suggested as a possible treatment for headaches, fibromyalgia, smoking cessation, and opiate withdrawal, but there is little evidence of effectiveness for many of these conditions and the evidence for use in acute depression is not sufficient to justify it. Medical uses A 2014 Cochrane review found insufficient evidence to determine whether or not CES with alternating current is safe and effective for treating depression. The FDA came to the same conclusion in December 2019. A 2018 systematic review found that evidence is insufficient that CES has clinically important effects on fibromyalgia, headache, neuromusculoskeletal pain, degenerative joint pain, depression, or insomnia; low-strength evidence suggests mod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation
Transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) is a form of neuromodulation that uses constant, low direct current delivered via electrodes on the head. This type of neurotherapy was originally developed to help patients with brain injuries or neuropsychiatric conditions such as major depressive disorder. It can be contrasted with cranial electrotherapy stimulation, which generally uses alternating current the same way, as well as transcranial magnetic stimulation. Research shows increasing evidence for tDCS as a treatment for depression. There is mixed evidence about whether tDCS is useful for cognitive enhancement in healthy people. There is no strong evidence that tDCS is useful for memory deficits in Parkinson's disease and Alzheimer's disease, non-neuropathic pain, nor for improving arm or leg functioning and muscle strength in people recovering from a stroke. There is emerging supportive evidence for tDCS in the management of schizophreniaespecially for negative symptoms. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation
Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) is a noninvasive neurostimulation technique in which a changing magnetic field is used to induce an electric current in a targeted area of the brain through electromagnetic induction. A device called a stimulator generates electric pulses that are delivered to a magnetic coil placed against the scalp. The resulting magnetic field penetrates the skull and induces a secondary electric current in the underlying brain tissue, modulating neural activity. Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS) is a safe, effective, and FDA-approved treatment for major depressive disorder (approved in 2008), chronic pain (2013), and obsessive-compulsive disorder (2018). It has strong evidence for certain neurological and psychiatric conditions—especially depression (with a large effect size), neuropathic pain, and stroke recovery—and emerging advancements like iTBS and image-guided targeting may improve its efficacy and efficiency. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vagus Nerve Stimulation
Vagus nerve stimulation (VNS) is a medical treatment that involves delivering electrical impulses to the vagus nerve. Initially developed by James Leonard Corning to compress or stimulate the carotid sheath, VNS typically refers to an implantable electrode. However, non-invasive VNS delivered transcutaneously via the auricular branch of the vagus nerve, or through the skin to the cervical nerve, is being investigated in clinical research. Invasive VNS is used as an adjunct treatment for certain types of intractable epilepsy, cluster headaches, migraine, treatment-resistant depression and stroke rehabilitation. Medical use Epilepsy VNS is used to treat drug-resistant epilepsy. For refractive epilepsy, cervical VNS on the left side is FDA-approved. In the United States, VNS is approved as adjunctive therapy for those 4 years of age or older with refractory focal onset seizures. In the European Union, VNS is approved as an adjunctive therapy for patients with either generalized or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |