|
Brain Atlas
A brain atlas is composed of serial sections along different anatomical planes of the healthy or diseased developing or adult animal or human brain where each relevant brain structure is assigned a number of coordinates to define its outline or volume. Brain atlases are contiguous, comprehensive results of visual brain mapping and may include anatomical, genetic or functional features. A functional brain atlas is made up of N regions of interest, where these regions are typically defined as spatially contiguous and functionally coherent patches of gray matter. In most atlases, the three dimensions are: latero-lateral (x), dorso-ventral (y) and rostro-caudal (z). The possible sections are * coronal * sagittal * transverse Surface maps are sometimes used in addition to the 3D serial section maps Besides the human brain, brain atlases exist for the brains of the mouse, rhesus macaques, ''Drosophila'', pig and others. Notable examples include the Allen Brain Atlas, BrainMaps, B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anatomical Plane
An anatomical plane is a hypothetical plane used to transect the body, in order to describe the location of structures or the direction of movements. In human anatomy and non-human anatomy, four principal planes are used: the median plane, sagittal plane, coronal plane, and transverse plane. * The median plane or midsagittal plane passes through the middle of the body, dividing it into left and right halves. * A para sagittal plane is any plane that runs parallel to the median plane, also dividing the body into left and right sections. * The dorsal plane divides the body into dorsal (towards the backbone) and ventral (towards the belly) parts. In human anatomy coronal plane is preferred, or sometimes the frontal plane, and the description may reference splitting the body into front and back parts, but this phrasing is not as clear for animals with a horizontal spine like quadrupeds or fish. * The transverse plane, also called the axial plane or horizontal plane, is perpendi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drosophila
''Drosophila'' (), from Ancient Greek δρόσος (''drósos''), meaning "dew", and φίλος (''phílos''), meaning "loving", is a genus of fly, belonging to the family Drosophilidae, whose members are often called "small fruit flies" or pomace flies, vinegar flies, or wine flies, a reference to the characteristic of many species to linger around overripe or rotting fruit. They should not be confused with the Tephritidae, a related family, which are also called fruit flies (sometimes referred to as "true fruit flies"); tephritids feed primarily on unripe or ripe fruit, with many species being regarded as destructive agricultural pests, especially the Mediterranean fruit fly. One species of ''Drosophila'' in particular, ''Drosophila melanogaster'', has been heavily used in research in genetics and is a common model organism in developmental biology. The terms "fruit fly" and "''Drosophila''" are often used synonymously with ''D. melanogaster'' in modern biological literatur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stereotaxic Atlas
A stereotaxic atlas is a number of records of brain structure of a particular animal accompanied with coordinates used in stereotactic surgery Stereotactic surgery is a minimally invasive form of surgery, surgical intervention that makes use of a three-dimensional coordinates, coordinate system to locate small targets inside the body and to perform on them some action such as ablation, .... Stereotaxic atlases are developed using MRI data from a large number of subjects to visualize the topology of the brain. This allows for highly accurate, minimally invasive surgery based on 3D imaging. The development of stereotaxic atlases has been particularly important in making it possible to operate on areas deep in the brain that are not accessible through traditional surgical methods. References External linksA Stereotaxic Atlas Of The Brain Of The Zebra Finch Neurosurgery {{surgery-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neuroanatomy
Neuroanatomy is the study of the structure and organization of the nervous system. In contrast to animals with radial symmetry, whose nervous system consists of a distributed network of cells, animals with bilateral symmetry have segregated, defined nervous systems. Their neuroanatomy is therefore better understood. In vertebrates, the nervous system is segregated into the internal structure of the brain and spinal cord (together called the central nervous system, or CNS) and the series of nerves that connect the CNS to the rest of the body (known as the peripheral nervous system, or PNS). Breaking down and identifying specific parts of the nervous system has been crucial for figuring out how it operates. For example, much of what neuroscientists have learned comes from observing how damage or "lesions" to specific brain areas affects behavior or other neural functions. For information about the composition of non-human animal nervous systems, see nervous system. For information a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Connectome
A connectome () is a comprehensive map of neural connections in the brain, and may be thought of as its " wiring diagram". These maps are available in varying levels of detail. A functional connectome shows connections between various brain regions, but not individual neurons. These are available for large animals, including mice and humans, are normally obtained by techniques such as MRI, and have a scale of millimeters. At the other extreme are neural connectomes, which show individual neurons and their interconnections. These are usually obtained by electron microscopy (EM) and have a scale of nanometers. They are only available for small creatures such as the worm ''C. Elegans'' and the fruit fly ''Drosophila melanogaster'', and small regions of mammal brains. Finally there are chemical connectomes, showing which neurons emit, and are sensitive to, a wide variety of neuromodulators. The significance of the connectome stems from the realization that the structure an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brain Mapping
Brain mapping is a set of neuroscience techniques predicated on the mapping of (biological) quantities or properties onto spatial representations of the (human or non-human) brain resulting in maps. According to the definition established in 2013 by Society for Brain Mapping and Therapeutics (SBMT), brain mapping is specifically defined, in summary, as the study of the anatomy and function of the brain and spinal cord through the use of neuroimaging, imaging, immunohistochemistry, molecular genetics, molecular & optogenetics, stem cell and cellular biology, engineering, neurophysiology and nanotechnology. In 2024, a team of 287 researchers completed a full brain mapping of an adult animal (a ''Drosophila melanogaster'', or fruit fly) and published their results in Nature (journal), ''Nature''. Overview All neuroimaging is considered part of brain mapping. Brain mapping can be conceived as a higher form of neuroimaging, producing brain images supplemented by the result of add ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BigBrain
BigBrain is a freely accessible high-resolution 3D digital atlas of the human brain, released in June 2013 by a team of researchers at the Montreal Neurological Institute and the German Forschungszentrum Jülich and is part of the European Human Brain Project.The isotropic 3D spatial resolution of the BigBrain atlas is 20 μm, much finer than the typical 1 mm resolution of other existing 3D models of the human brain such as the Allen Brain Atlas. In 2014, BigBrain was cited in the top 10 MIT Technology Review. Acquisition The atlas was created from the brain of an unidentified 65-year-old man (it was "65-year-old female", according to "BigBrain: An Ultrahigh-Resolution3D Human Brain Model", page 1472, Amunts K et al., SCIENCE, 21 JUNE 2013 VOL 340) who died with no known brain pathology. His brain, after being removed from the skull, was first scanned using an MRI machine, then embedded in paraffin and sliced into 7,404 20 μm thick sections using a large-scale micr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
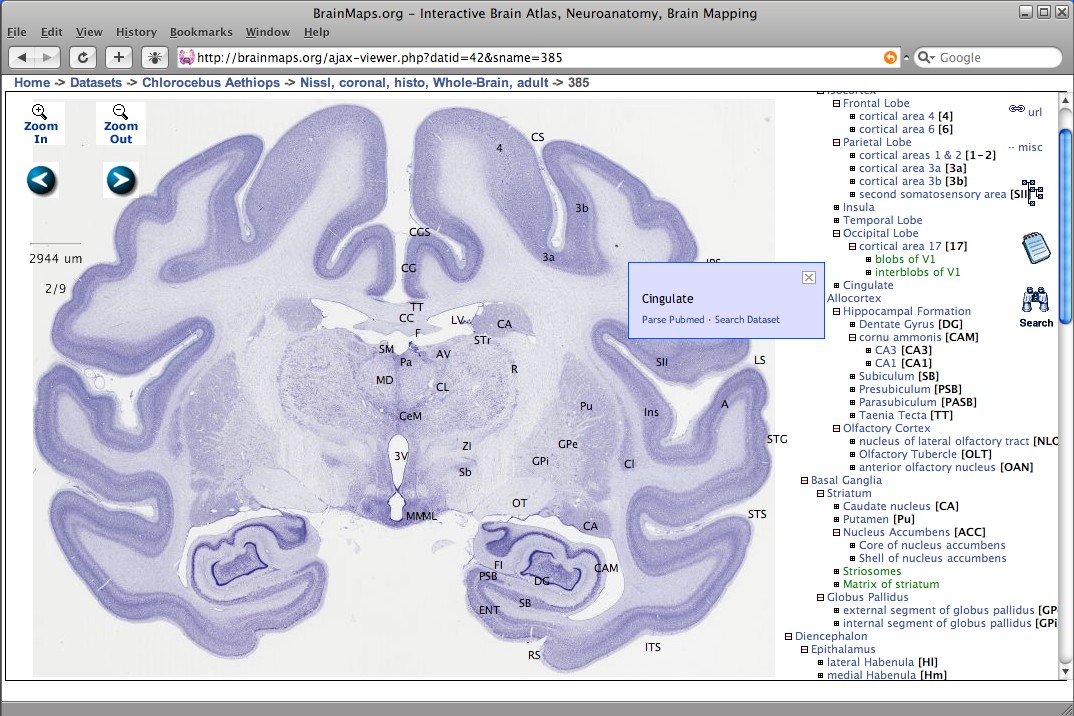
BrainMaps
BrainMaps is an NIH-funded interactive zoomable high-resolution digital brain atlas and virtual microscope that is based on more than 140 million megapixels (140 terabytes) of scanned images of serial sections of both primate and non-primate brains and that is integrated with a high-speed database for querying and retrieving data about brain structure and function over the internet. Currently featured are complete brain atlas datasets for 16 species; a few of which are: ''Macaca mulatta'', '' Chlorocebus aethiops'', '' Felis silvestris catus'', ''Mus musculus'', ''Rattus norvegicus'', and ''Tyto alba''. The project's principal investigator was UC Davis neuroscientist Ted Jones from 2005 through 2011, after which the role was taken by W. Martin Usrey. Description BrainMaps uses multiresolution image formats for representing massive brain images, and a dHTML/Javascript front-end user interface for image navigation, both similar to the way that Google Maps works for geospatial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allen Brain Atlas
The Allen Mouse and Human Brain Atlases are projects within the Allen Institute for Brain Science which seek to combine genomics with neuroanatomy by creating gene expression maps for the mouse and human brain. They were initiated in September 2003 with a $100 million donation from Paul G. Allen and the first atlas went public in September 2006. , seven brain atlases have been published: Mouse Brain Atlas, Human Brain Atlas, Developing Mouse Brain Atlas, Developing Human Brain Atlas, Mouse Connectivity Atlas, Non-Human Primate Atlas, and Mouse Spinal Cord Atlas. There are also three related projects with data banks: Glioblastoma, Mouse Diversity, and Sleep. It is the hope of the Allen Institute that their findings will help advance various fields of science, especially those surrounding the understanding of neurobiological diseases. The atlases are free and available for public use online. History In 2001, Paul Allen gathered a group of scientists, including James Watson and St ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhesus Macaque
The rhesus macaque (''Macaca mulatta''), colloquially rhesus monkey, is a species of Old World monkey. There are between six and nine recognised subspecies split between two groups, the Chinese-derived and the Indian-derived. Generally brown or grey in colour, it is in length with a tail and weighs . It is native to South Asia, South, Central Asia, Central, and Southeast Asia and has the widest geographic range of all non-human primates, occupying a great diversity of altitudes and habitats. The rhesus macaque is diurnality, diurnal, arboreal, and terrestrial. It is mostly herbivorous, feeding mainly on fruit, but also eating seeds, roots, buds, Bark (botany), bark, and cereals. Rhesus macaques living in cities also eat human food and trash. They are gregarious, with troops comprising 20–200 individuals. The social groups are matrilineal. Individuals communicate with a variety of facial expressions, vocalisations, body postures, and gestures. As a result of the rhesus macaq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Brain
The human brain is the central organ (anatomy), organ of the nervous system, and with the spinal cord, comprises the central nervous system. It consists of the cerebrum, the brainstem and the cerebellum. The brain controls most of the activities of the human body, body, processing, integrating, and coordinating the information it receives from the sensory nervous system. The brain integrates sensory information and coordinates instructions sent to the rest of the body. The cerebrum, the largest part of the human brain, consists of two cerebral hemispheres. Each hemisphere has an inner core composed of white matter, and an outer surface – the cerebral cortex – composed of grey matter. The cortex has an outer layer, the neocortex, and an inner allocortex. The neocortex is made up of six Cerebral cortex#Layers of neocortex, neuronal layers, while the allocortex has three or four. Each hemisphere is divided into four lobes of the brain, lobes – the frontal lobe, frontal, pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mouse Brain
A mouse (: mice) is a small rodent. Characteristically, mice are known to have a pointed snout, small rounded ears, a body-length scaly tail, and a high breeding rate. The best known mouse species is the common house mouse (''Mus musculus''). Mice are also popular as pets. In some places, certain kinds of Apodemus, field mice are locally common. They are known to invade homes for food and shelter. Mice are typically distinguished from rats by their size. Generally, when a muroid rodent is discovered, its common name includes the term ''mouse'' if it is smaller, or ''rat'' if it is larger. The common terms ''rat'' and ''mouse'' are not Taxonomy (biology), taxonomically specific. Typical mice are classified in the genus ''Mus (genus), Mus'', but the term ''mouse'' is not confined to members of ''Mus'' and can also apply to species from other genera such as the deer mouse, deer mouse (''Peromyscus''). Fancy mouse, Domestic mice sold as pets often differ substantially in size f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |