|
Brabant Island
Brabant Island is the second largest island of the Palmer Archipelago within the British Antarctic Territory, lying between Anvers Island and Liège Island. Brabant Island is long north-south, wide, and rises to in Mount Parry. The interior of the island is occupied by two mountain ranges, Solvay Mountains ( Cook Summit, 1590 m) in its southern part and Stribog Mountains (summit Mount Parry) in its central and northern parts. It was named by the Belgian Antarctic Expedition (1897–1899) under Adrien de Gerlache, who named it after the Belgian Province of Brabant, in recognition of the support given to the expedition by its citizens. A paper summarizing the Joint Services expedition of 1984–1985 describes the island as "notoriously inhospitable" and states that there is evidence for only six visits between the discovery in 1898 and 1984. Members of the expedition overwintered there in 1984–1985, and made the first ascent of Mount Parry. History On 6 February 202 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean (also known as the Antarctic Ocean), it contains the geographic South Pole. Antarctica is the fifth-largest continent, being about 40% larger than Europe, and has an area of . Most of Antarctica is covered by the Antarctic ice sheet, with an average thickness of . Antarctica is, on average, the coldest, driest, and windiest of the continents, and it has the highest average elevation. It is mainly a polar desert, with annual Climate of Antarctica#Precipitation, precipitation of over along the coast and far less inland. About 70% of the world's freshwater reserves are frozen in Antarctica, which, if melted, would raise global sea levels by almost . Antarctica holds the record for the Lowest temperature recorded on Earth, lowest measured temperature on Earth, . The coastal regions can reach temperatures over in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMS Protector (A173)
HMS ''Protector'' is a Royal Navy ice patrol ship built in Norway in mid 2000. As MV ''Polarbjørn'' (Norwegian: ''polar bear'') she operated under charter as a polar research icebreaker and a subsea support vessel. In 2011, she was chartered as a temporary replacement for the ice patrol ship and was purchased by the British Ministry of Defence in early September 2013. As DNV Ice Class 05 the vessel can handle first year ice up to 0.5 metres (20 in) thick. Service history (Norway) ''Polarbjørn'' was designed and built for long Antarctic expeditions and for supporting subsea work. ''Polarbjørn'' was equipped to DP2 class and had accommodation for 100 people. Large cargo holds and open deck areas provide storage capacity for ROVs and related equipment. A 50-ton knuckle-boom crane and the 25-ton stern A-frame allow equipment to be deployed over the side and over the stern. ''Polarbjørn'' worked in the "spot" market, on short-term charter. During 2009, the vessel was ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
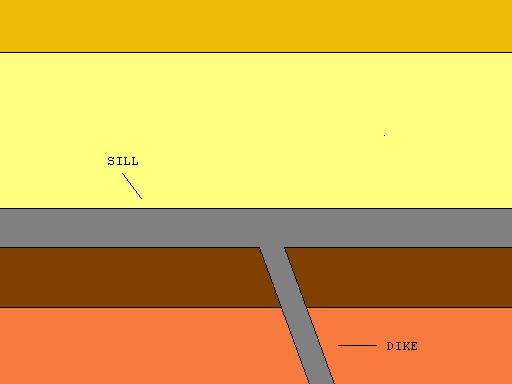
Hypabyssal
A subvolcanic rock, also known as a hypabyssal rock, is an intrusive igneous rock that is emplaced at depths less than within the crust, and has intermediate grain size and often porphyritic texture between that of volcanic rocks, which are extrusive igneous rocks, and plutonic rocks, which form much deeper in the ground. Subvolcanic rocks include diabase (also known as dolerite) and porphyry. Common examples of subvolcanic rocks are diabase, quartz dolerite, microgranite, and diorite. See also * Cone sheet * Dike (geology) * Igneous intrusion * Sill (geology) In geology, a sill is a tabular sheet intrusion that has intruded between older layers of sedimentary rock, beds of volcanic lava or tuff, or along the direction of foliation in metamorphic rock. A sill is a ''concordant intrusive sheet' ... References Igneous petrology Volcanology {{igneous-petrology-stub he:סלע געשי#סלעים תת-געשיים ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Early Eocene
In the geologic timescale the Ypresian is the oldest age (geology), age or lowest stage (stratigraphy), stratigraphic stage of the Eocene. It spans the time between , is preceded by the Thanetian Age (part of the Paleocene) and is followed by the Eocene Lutetian Age. The Ypresian is consistent with the Lower Eocene (Early Eocene). Events The Ypresian Age begins during the throes of the Paleocene–Eocene Thermal Maximum (PETM). The Fur Formation in Denmark, the Messel shales in Germany, the Oise amber of France and Cambay amber of India are of this age. The Eocene Okanagan Highlands are an uplands subtropical to temperate series of lakes from the Ypresian. The Ypresian is additionally marked by another warming event called the Early Eocene Climatic Optimum (EECO). The EECO is the longest sustained warming event in the Cenozoic record, lasting about 2–3 million years between 53 and 50 Ma. The interval is characterized by low oxygen-18 isotopes, high levels of atmospheric pCO2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sill (geology)
In geology, a sill is a tabular sheet intrusion that has intruded between older layers of sedimentary rock, beds of volcanic lava or tuff, or along the direction of foliation in metamorphic rock. A sill is a ''concordant intrusive sheet'', meaning that it does not cut across preexisting rock beds. Stacking of sills builds a sill complex. and a large magma chamber at high magma flux. In contrast, a dike is a discordant intrusive sheet, which does cut across older rocks. Formation Sills are fed by dikes, except in unusual locations where they form in nearly vertical beds attached directly to a magma source. The rocks must be brittle and fracture to create the planes along which the magma intrudes the parent rock bodies, whether this occurs along preexisting planes between sedimentary or volcanic beds or weakened planes related to foliation in metamorphic rock. These planes or weakened areas allow the intrusion of a thin sheet-like body of magma paralleling the existi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Granodiorite
Granodiorite ( ) is a coarse-grained (phaneritic) intrusive igneous rock similar to granite, but containing more plagioclase feldspar than orthoclase feldspar. The term banatite is sometimes used informally for various rocks ranging from granite to diorite, including granodiorite. The term ''granodiorite'' was first used by George F. Becker, G. F. Becker (1893) to describe granitic rocks in the Sierra Nevada, United States. Composition According to the QAPF diagram, granodiorite has a greater than 20% quartz by volume, and between 65% and 90% of the feldspar is plagioclase. A greater amount of plagioclase would designate the rock as tonalite. Granodiorite is felsic to intermediate composition, intermediate in composition. It is the Intrusive rock, intrusive igneous equivalent of the extrusive igneous dacite. It contains a large amount of sodium (Na) and calcium (Ca) rich plagioclase, potassium feldspar, quartz, and minor amounts of muscovite mica as the lighter colored miner ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intruded
Intrusive rock is formed when magma penetrates existing rock, crystallizes, and solidifies underground to form ''intrusions'', such as batholiths, dikes, sills, laccoliths, and volcanic necks.Intrusive RocksIntrusive rocks accessdate: March 27, 2017.Igneous intrusive rocks, accessdate: March 27, 2017.Britannica.comintrusive rock , geology , Britannica.com accessdate: March 27, 2017. Intrusion is one of the two ways igneous rock can form. The other is extrusion, such as a volcanic eruption or similar event. An intrusion is any body of intrusive igneous rock, formed from magma that cools and solidifies within the crust of the planet. In contrast, an ''extrusion'' consists of extrusive rock, formed above the surface of the crust. Some geologists use the term plutonic rock synonymously with intrusive rock, but other geologists subdivide intrusive rock, by crystal size, into coarse-grained plutonic rock (typically formed deeper in the Earth's crust in batholiths or stocks) and me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Danco Coast
The Danco Coast () is the portion of the west coast of the Antarctic Peninsula between Cape Sterneck and Cape Renard. This coast was explored in January and February 1898 by the Belgian Antarctic Expedition under Adrien de Gerlache, who named it for Lieutenant Emile Danco who died on the expedition. The coast is bordered by the Aguirre Passage which separates it from Lemaire Island. Places on the Danco Coast * Brabazon Point * Salvesen Cove Geology The Danco Coast Tectonic Block includes the Upper Permian-Triassic Trinity Peninsula Group, consisting of over 1000 m of metaturbidites folded during the Gondwanide orogeny. This group is overlain by the Lower Cretaceous Antarctic Peninsula Volcanic Group, with up to 2000 m of basaltic and andesitic lavas, tuffs and agglomerates, which were folded and faulted during the Tertiary. These two groups were intruded by the Berriasian-Cenomanian granite and gabbro sills of the Andean Instrusive Suite. A system of hypabbysal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Group (geology)
In geology, a group is a lithostratigraphic unit consisting of a series of related formations that have been classified together to form a group. Formations are the fundamental unit of stratigraphy. Groups may sometimes be combined into supergroups. Groups are useful for showing relationships between formations, and they are also useful for small-scale mapping or for studying the stratigraphy of large regions. Geologists exploring a new area have sometimes defined groups when they believe the strata within the groups can be divided into formations during subsequent investigations of the area. It is possible for only some of the strata making up a group to be divided into formations. An example of a group is the Glen Canyon Group, which includes (in ascending order) the Wingate Sandstone, the Moenave Formation, the Kayenta Formation, and the Navajo Sandstone. Each of the formations can be distinguished from its neighbor by its lithology, but all were deposited in the same ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lower Cretaceous
Lower may refer to: * ''Lower'' (album), 2025 album by Benjamin Booker * Lower (surname) * Lower Township, New Jersey *Lower Receiver (firearms) * Lower Wick Gloucestershire, England See also * Nizhny {{Disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volcaniclastic
Volcaniclastics are geologic materials composed of broken fragments (clasts) of volcanic rock. These encompass all clastic volcanic materials, regardless of what process fragmented the rock, how it was subsequently transported, what environment it was deposited in, or whether nonvolcanic material is mingled with the volcanic clasts. The United States Geological Survey defines volcaniclastics somewhat more narrowly, to include only rock composed of volcanic rock fragments that have been transported some distance from their place of origin. In the broad sense of the term, volcaniclastics includes pyroclastic rocks such as the Bandelier Tuff; cinder cones and other tephra deposits; the basal and capping breccia that characterize ʻaʻā lava flows; and lahars and debris flows of volcanic origin.Vincent 2000, pp.27-28 Volcaniclastics make up more of the volume of many volcanoes than do lava flows. Volcaniclastics may have contributed as much as a third of all sedimentation in the geolo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lava
Lava is molten or partially molten rock (magma) that has been expelled from the interior of a terrestrial planet (such as Earth) or a Natural satellite, moon onto its surface. Lava may be erupted at a volcano or through a Fissure vent, fracture in the Crust (geology), crust, on land or underwater, usually at temperatures from . The volcanic rock resulting from subsequent cooling is often also called ''lava''. A lava flow is an outpouring of lava during an effusive eruption. (An explosive eruption, by contrast, produces a mixture of volcanic ash and other fragments called tephra, not lava flows.) The viscosity of most lava is about that of ketchup, roughly 10,000 to 100,000 times that of water. Even so, lava can flow great distances before cooling causes it to solidify, because lava exposed to air quickly develops a solid crust that insulates the remaining liquid lava, helping to keep it hot and inviscid enough to continue flowing. Etymology The word ''lava'' comes from Ital ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |