|
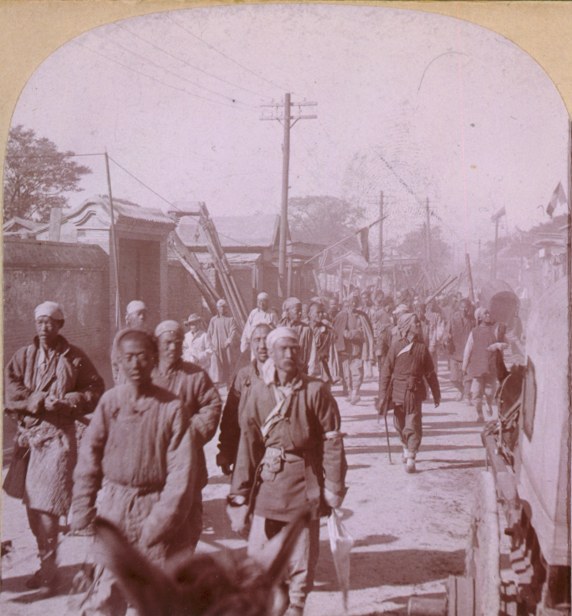
Boxer Movement
The Boxers, officially known as the Society of Righteous and Harmonious Fists () among Boxer movement#Names, other names, were a Chinese secret society based in Northern and southern China, Northern China that carried out the Boxer Rebellion from 1899 to 1901. The movement was made up of independent local village groups, many of which kept their membership secret, making the total number of participants difficult to estimate, but it may have included as many as 100,000. They originally attacked the Qing dynasty, Qing government, but soon called upon it to resist foreign influence. In the summer of 1900, groups of Boxer fighters destroyed foreign owned property, such as railroads and telegraphs, and murdered Christians, Christian missionaries and Chinese Christians. They then supported the Empress Dowager Cixi, Empress Dowager in resisting the Eight-Nation Alliance, resulting foreign invasion, which all but destroyed the group and ended the Rebellion, though some members cont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
War Flag
A war ensign, also known as a military flag, battle flag, or standard, is a variant of a national flag for use by a country's military forces when on land. The nautical equivalent is a naval ensign. Under the strictest sense of the term, few countries today currently have distinct war flags, most using a flag design that is also the state flag or general national flag for this purpose. __TOC__ History Field signs were used in early warfare at least since the Bronze Age. The word ''standard'' itself is from an Old Frankish term for a field sign (not necessarily a flag). The use of flags as field signs apparently emerges in Asia, during the Iron Age, possibly in either China or India.flag. (2008). Encyclopædia Britannica. Chicago: Encyclopædia Britannica. in Achaemenid Persia, each army division had its own standard, and "all officers had banners over their tents".E. Pottier, ''Douris'', London, 1909, p. 105 fig. 20, Plate XXV.b Early field signs that include, but are not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Empress Dowager Cixi
Empress Dowager Cixi ( ; 29 November 1835 – 15 November 1908) was a Manchu noblewoman of the Yehe Nara clan who effectively but periodically controlled the Chinese government in the late Qing dynasty as empress dowager and regent for almost 50 years, from 1861 until her death in 1908. Selected as a Concubinage in China, concubine of the Xianfeng Emperor in her adolescence, she gave birth to a son, Zaichun, in 1856. After the Xianfeng Emperor's death in 1861, his five-year-old son became the Tongzhi Emperor, and Cixi assumed the role of co-empress dowager alongside Xianfeng's widow, Empress Dowager Ci'an. Cixi ousted a group of regents appointed by the late emperor and assumed the regency along with Ci'an. Cixi then consolidated control over the dynasty when she installed her nephew as the Guangxu Emperor at the death of the Tongzhi Emperor in 1875. Ci'an continued as co-regent until her death in 1881. Cixi supervised the Tongzhi Restoration, a series of moderate reforms that hel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Los Angeles
Los Angeles, often referred to by its initials L.A., is the List of municipalities in California, most populous city in the U.S. state of California, and the commercial, Financial District, Los Angeles, financial, and Culture of Los Angeles, cultural center of Southern California. With an estimated 3,878,704 residents within the city limits , it is the List of United States cities by population, second-most populous in the United States, behind only New York City. Los Angeles has an Ethnic groups in Los Angeles, ethnically and culturally diverse population, and is the principal city of a Metropolitan statistical areas, metropolitan area of 12.9 million people (2024). Greater Los Angeles, a combined statistical area that includes the Los Angeles and Riverside–San Bernardino metropolitan areas, is a sprawling metropolis of over 18.5 million residents. The majority of the city proper lies in Los Angeles Basin, a basin in Southern California adjacent to the Pacific Ocean in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Berkeley, California
Berkeley ( ) is a city on the eastern shore of San Francisco Bay in northern Alameda County, California, United States. It is named after the 18th-century Anglo-Irish bishop and philosopher George Berkeley. It borders the cities of Oakland, California, Oakland and Emeryville, California, Emeryville to the south and the city of Albany, California, Albany and the Unincorporated area, unincorporated community of Kensington, California, Kensington to the north. Its eastern border with Contra Costa County, California, Contra Costa County generally follows the ridge of the Berkeley Hills. The 2020 United States census, 2020 census recorded a population of 124,321. Berkeley is home to the oldest campus in the University of California, the University of California, Berkeley, and the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, which is managed and operated by the university. It also has the Graduate Theological Union, one of the largest religious studies institutions in the world. Berkeley is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of California Press
The University of California Press, otherwise known as UC Press, is a publishing house associated with the University of California that engages in academic publishing. It was founded in 1893 to publish scholarly and scientific works by faculty of the University of California, established 25 years earlier in 1868. As the publishing arm of the University of California system, the press publishes over 250 new books and almost four dozen multi-issue journals annually, in the humanities, social sciences, and natural sciences, and maintains approximately 4,000 book titles in print. It is also the digital publisher of Collabra and Luminos open access (OA) initiatives. The press has its administrative office in downtown Oakland, California, an editorial branch office in Los Angeles, and a sales office in New York City, New York, and distributes through marketing offices in Great Britain, Asia, Australia, and Latin America. A Board consisting of senior officers of the University of Cali ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guan County, Shandong
Guan County () is a county of western Shandong province, People's Republic of China, bordered by Hebei province to the west. It is administered by Liaocheng City. The population was in 1999. History As an isolated county, with relatively low education levels and a weak orthodox gentry, Guan long served as center for secret societies and heterodox sects. For example Guan was one of the earliest places where Yi-he boxing was practised, namely in 1779. This material arts style later served as base for the prominent Yìhéquán (Boxer) movement. In 1861–63, the county was also the center of a rebellion against the Qing dynasty, led by Song Jing-shi and supported by the White Lotus. In the last decades of the Qing Empire and the early Republic, Guan County was home to the Red as well as Green Gang The Green Gang ( zh, t=青幫, p=Qīng Bāng) was a Chinese secret society and criminal organization, which was prominent in criminal, social and political activity in Shanghai dur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
White Lotus Societies
Illustration of a meeting of the Pure Land Buddhist White Lotus Society of Li_Gonglin.html" ;"title="Lushan Huiyuan in the style of Li Gonglin">Lushan Huiyuan in the style of Li Gonglin, The term White Lotus Society () or White Lotus Teaching () refers to a variety of religious and political groups that emerged in China over many centuries. Initially, the name was associated with Pure Land Buddhism, Pure Land Buddhist organizations that sought to promote devotional practices centered on rebirth in a Buddhist Pure land, Pure Land. These early societies emphasized spiritual salvation through faith, chanting of Amitābha's name (''nianfo''), and adherence to moral precepts. Over time, however, the term "White Lotus" became associated with diverse salvationist and apocalyptic movements, often blending elements of Buddhism, Daoism, and Chinese folk religion. Many later White Lotus groups adopted millenarian ideologies, predicting the imminent arrival of a new age or a divine savio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Big Swords Society
The Big Swords Society () or Great Knife Society was a traditional peasant group most noted for the killing of two German Catholic missionaries at the Juye Incident in 1897 at Zhang Jia Village where the missionaries were ambushed in their sleep by about 30 armed men. The Big Swords Society was widespread in North China during the Qing Dynasty and noted for its reckless courage. Rather than one large overarching organization, the Big Swords were local groups of small-holders and tenant farmers organized to defend villages against roaming bandits, warlords, tax collectors or later the Communists and Japanese. Early history The Society was founded in the early 1890s by Liu Shiduan, who lived in Caozhou prefecture in southwestern Shandong. The Grand Masters of these societies claimed to make the members invulnerable to bullets by magic. Both the Big Swords and Red Spears societies took part in the Boxer Rebellion in North China in 1900. During the first three decades of the 20th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Romanization Of Chinese
Romanization of Chinese is the use of the Latin alphabet to transliterate Varieties of Chinese, Chinese. Chinese uses a logographic script and its Chinese characters, characters do not represent phonemes directly. There have been many systems using Romanization, Roman characters to represent Chinese throughout history. Linguist Daniel Kane (linguist), Daniel Kane wrote, "It used to be said that sinologists had to be like musicians, who might compose in one key and readily transcribe into other keys." The dominant international standard for Standard Chinese, Standard Mandarin since about 1982 has been Pinyin, Hanyu Pinyin, invented by a group of Chinese linguists, including Zhou Youguang, in the 1950s. Other well-known systems include Wade–Giles (Beijing Mandarin) and Yale romanization (Yale romanization of Mandarin, Beijing Mandarin and Yale romanization of Cantonese, Cantonese). There are many uses for Chinese romanization. Most broadly, it is used to provide a useful way for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wade–Giles
Wade–Giles ( ) is a romanization system for Mandarin Chinese. It developed from the system produced by Thomas Francis Wade during the mid-19th century, and was given completed form with Herbert Giles's '' A Chinese–English Dictionary'' (1892). The romanization systems in common use until the late 19th century were based on the Nanjing dialect, but Wade–Giles was based on the Beijing dialect and was the system of transcription familiar in the English-speaking world for most of the 20th century. Both of these kinds of transcription were used in postal romanizations (romanized place-names standardized for postal uses). In mainland China, Wade–Giles has been mostly replaced by Hanyu Pinyin, which was officially adopted in 1958, with exceptions for the romanized forms of some of the most commonly used names of locations and persons, and other proper nouns. The romanized name for most locations, persons and other proper nouns in Taiwan is based on the Wade–Giles der ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pinyin
Hanyu Pinyin, or simply pinyin, officially the Chinese Phonetic Alphabet, is the most common romanization system for Standard Chinese. ''Hanyu'' () literally means 'Han Chinese, Han language'—that is, the Chinese language—while ''pinyin'' literally means 'spelled sounds'. Pinyin is the official romanization system used in China, Singapore, Taiwan, and by the United Nations. Its use has become common when transliterating Standard Chinese mostly regardless of region, though it is less ubiquitous in Taiwan. It is used to teach Standard Chinese, normally written with Chinese characters, to students in mainland China and Singapore. Pinyin is also used by various Chinese input method, input methods on computers and to lexicographic ordering, categorize entries in some Chinese dictionaries. In pinyin, each Chinese syllable is spelled in terms of an optional initial (linguistics), initial and a final (linguistics), final, each of which is represented by one or more letters. Initi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zhili
Zhili, alternately romanized as Chihli, was a northern administrative region of China since the 14th century that lasted through the Ming dynasty and Qing dynasty until 1911, when the region was dissolved, converted to a province, and renamed Hebei in 1928. History The name ''Zhili'' means "directly ruled" and indicates regions directly ruled by the imperial government of China. - See Jeremiah Jenne's statements. Zhili province was first constituted during the Ming dynasty when the capital of China was located at Nanjing along the Yangtze River. In 1403, the Ming Yongle Emperor relocated the capital to Beiping, which was subsequently renamed Beijing.Susan Naquin, ''Peking: Temples and City Life, 1400-1900'', p xxxiii The region known as North Zhili was composed of parts of the modern provinces of Hebei, Henan, Shandong, including the provincial-level municipalities of Beijing and Tianjin. There was another region located around the "reserve capital" Nanjing known as South Zhil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |