|
Bowden Glacier
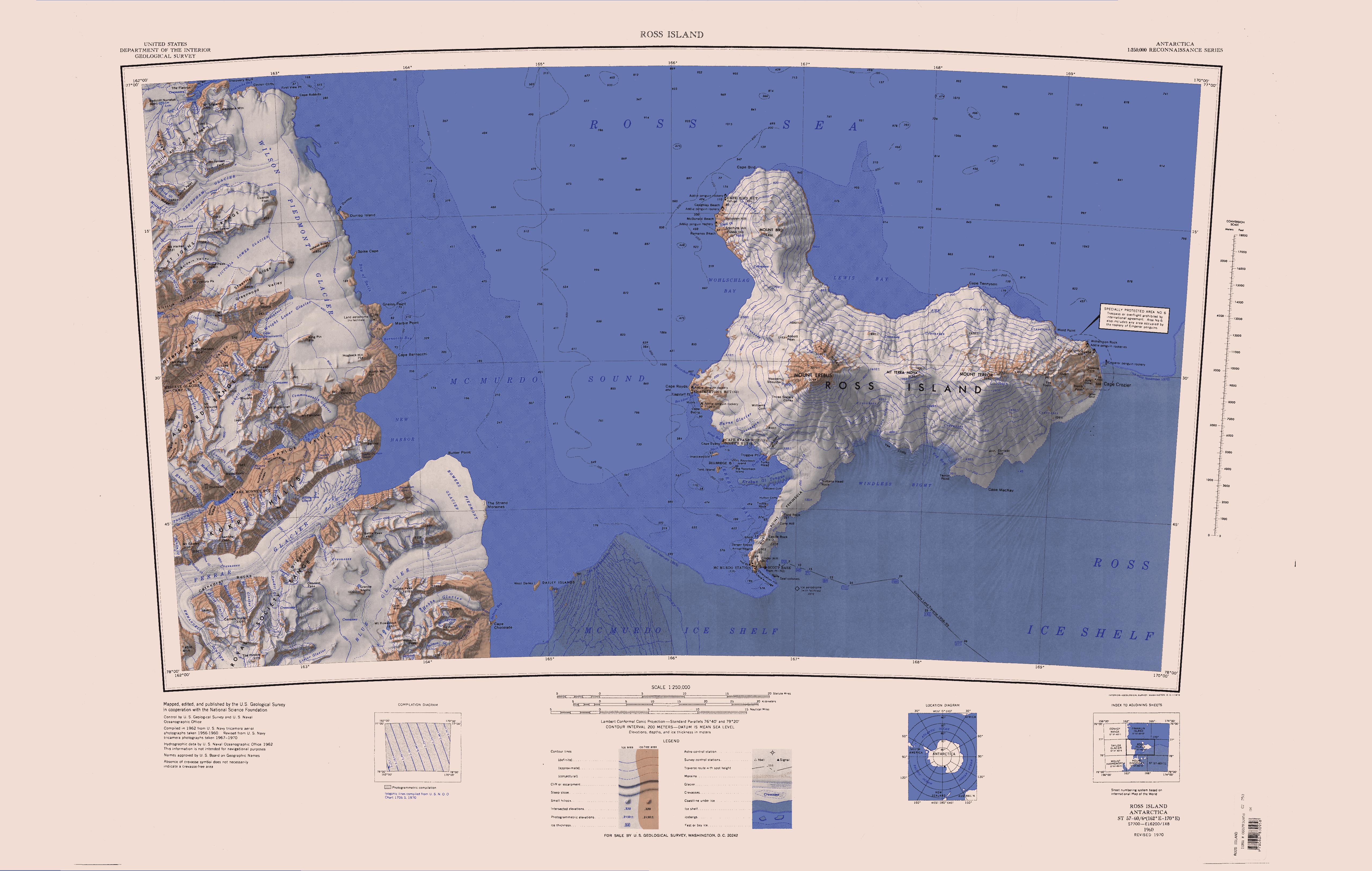
Blue Glacier () is a large glacier which flows into Bowers Piedmont Glacier about south of New Harbour, in Victoria Land, Antarctica. It was discovered by the British National Antarctic Expedition (BrNAE) under Robert Falcon Scott, 1901–04, who gave it this name because of its clear blue ice at the time of discovery. Location Blue Glacier rises to the north of Armitage Saddle, and flows north. The coastal range that borders the lower Koettlitz Glacier and the McMurdo Ice Shelf lies to the east, and the Royal Society Range is to the west. In its lower section the Blue Glacier turns to the east and joins the Bowers Piedmont Glacier on the west coast of the McMurdo Sound. Left tributary glaciers Glaciers entering from the left (west) flowing from the Royal Society Range, include (from south to north) Salient, Hooker, Mitchell, Spring, Covert, Amos Glacier and Geoid Glacier. Salient Glacier . A glacier draining northeast into the head of the Blue Glacier from the slopes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean (also known as the Antarctic Ocean), it contains the geographic South Pole. Antarctica is the fifth-largest continent, being about 40% larger than Europe, and has an area of . Most of Antarctica is covered by the Antarctic ice sheet, with an average thickness of . Antarctica is, on average, the coldest, driest, and windiest of the continents, and it has the highest average elevation. It is mainly a polar desert, with annual Climate of Antarctica#Precipitation, precipitation of over along the coast and far less inland. About 70% of the world's freshwater reserves are frozen in Antarctica, which, if melted, would raise global sea levels by almost . Antarctica holds the record for the Lowest temperature recorded on Earth, lowest measured temperature on Earth, . The coastal regions can reach temperatures over in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salient Ridge
Mount Lister () is a massive mountain, high, forming the highest point in the Royal Society Range of Victoria Land, Antarctica. It was discovered by the British National Antarctic Expedition (1901–1904) which named it for Lord Joseph Lister, President of the Royal Society, 1895–1900. Location Mount Lister is in central Royal Society Range, the highest point on the main north-south ridge that includes The Pimple and Chaplains Tableland to the north and Mount Hooker, Salient Peak and Mount Rücker to the south. McConchie Ridge and Salient Ridge extend east from Salient Peak. Armitage Saddle connects the massif to the Denton Hills to the east. Emmanuel Glacier and its tributary Carleton Glacier run north along the east side of the ridge to Ferrar Glacier. Howchin Glacier flows southeast from the ridge system towards Koettlitz Glacier, while Salient Glacier, Hooker Glacier and Lister Glacier flow northeast into Blue Glacier. Features Features and nearby features ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pearsall Ridge
Briggs Hill () is a conspicuous ice-free hill, high, standing on the south side of Ferrar Glacier between Descent Glacier and Overflow Glacier in Victoria Land, Antarctica. It was charted by the British Antarctic Expedition, 1910–13, under Scott, and named by the United States Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names (US-ACAN) for Raymond S. Briggs, United States Antarctic Research Program meteorologist at McMurdo Station in 1962, and station scientific leader there in 1963. Location Briggs Hill is in the northeast of the Royal Society Range. It faces Ferrar Glacier to the northwest. and is bound by the Descent Glacier to the southwest and the Overflow Glacier to the northeast. Descent Pass is to the southeast, leading towards Granite Knolls and the Blue Glacier. Features Features and nearby features include: Mount Huxley . A mountain, high, between lower Condit Glacier and Descent Glacier, marginal to Ferrar Glacier. Named in 1992 by US-ACAN after Leonard Huxley, edit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ibarra Peak
Mount Lister () is a massive mountain, high, forming the highest point in the Royal Society Range of Victoria Land, Antarctica. It was discovered by the British National Antarctic Expedition (1901–1904) which named it for Lord Joseph Lister, President of the Royal Society, 1895–1900. Location Mount Lister is in central Royal Society Range, the highest point on the main north-south ridge that includes The Pimple and Chaplains Tableland to the north and Mount Hooker, Salient Peak and Mount Rücker to the south. McConchie Ridge and Salient Ridge extend east from Salient Peak. Armitage Saddle connects the massif to the Denton Hills to the east. Emmanuel Glacier and its tributary Carleton Glacier run north along the east side of the ridge to Ferrar Glacier. Howchin Glacier flows southeast from the ridge system towards Koettlitz Glacier, while Salient Glacier, Hooker Glacier and Lister Glacier flow northeast into Blue Glacier. Features Features and nearby featur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ball Peak
The Newall Glacier () is a glacier in the east part of the Asgard Range of Victoria Land, It flows east between Mount Newall and Mount Weyant into the Wilson Piedmont Glacier. The Newall Glacier was mapped by the N.Z. Northern Survey Party of the CTAE, 1956-58, who named it after nearby Mount Newall. Location The Newall Glacier forms to the east of the Lacroix Glacier, which flows south into Taylor Valley. It flows northeast, past the head of Suess Glacier, past Mount Valkyrie to the west and Mount Weyant to the east. It turns east and is joined by the Loftus Glacier below Mount Newall. It continues east past the head of Commonwealth Glacier and joins with Wright Lower Glacier as it flows into Wilson Piedmont Glacier. Features Features, from southwest to northeast, include Lyons Cone, Twickler Cone, Unwin Ledge, Hothern Cliffs, Mount Hall, Loftus Glacier, Mount Weyant, Mount Saga, Hetha Peak, Commanda Glacier and Repeater Glacier. Lyons Cone . A cone shaped peak north- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tasman Ridge
Mount Lister () is a massive mountain, high, forming the highest point in the Royal Society Range of Victoria Land, Antarctica. It was discovered by the British National Antarctic Expedition (1901–1904) which named it for Lord Joseph Lister, President of the Royal Society, 1895–1900. Location Mount Lister is in central Royal Society Range, the highest point on the main north-south ridge that includes The Pimple and Chaplains Tableland to the north and Mount Hooker, Salient Peak and Mount Rücker to the south. McConchie Ridge and Salient Ridge extend east from Salient Peak. Armitage Saddle connects the massif to the Denton Hills to the east. Emmanuel Glacier and its tributary Carleton Glacier run north along the east side of the ridge to Ferrar Glacier. Howchin Glacier flows southeast from the ridge system towards Koettlitz Glacier, while Salient Glacier, Hooker Glacier and Lister Glacier flow northeast into Blue Glacier. Features Features and nearby features ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |