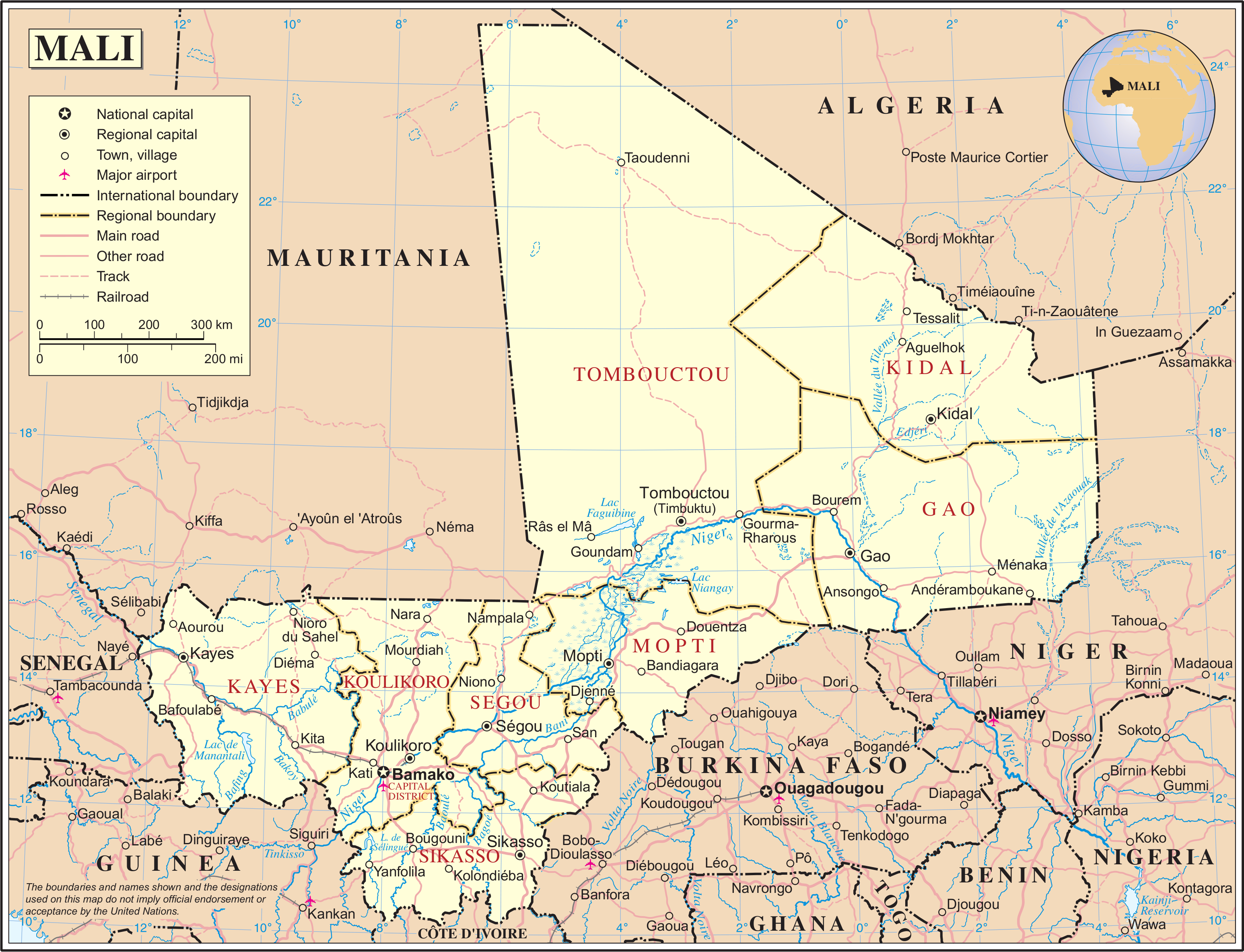
|
Bougouni Region
Bougouni is a commune and city in Mali, the administrative center of Bougouni Cercle, which is in turn found in the administrative region of Sikasso. Bougouni is located 170 km south of Bamako and 210 km west of the city of Sikasso. It covers an area of 7 square kilometres and as at the 2009 Census the commune had a population of 59,679, mostly Fulas (; ) and Bambaras (). History Bougouni was established as a quarantine area for surrounding villages, but gradually developed independently. The name means 'small house' in Bambara. Bougouni was the fourteenth commune created by the French colonial authorities of French Sudan. On July 10, 1894, Bougouni became the administrative center of the commune under its first administrator, Lieutenant Gouraud. Bougouni held an important set of colonial archives which were lost in a fire during the March 1991 uprising against President Moussa Traoré. Geography Bougouni, like many cities of Mali, enjoys sufficient rainfall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Communes Of Mali
A Commune (administrative division), commune is the third-level administrative unit in Mali. Mali is divided into ten Regions of Mali, regions and one capital district (Bamako). These subdivisions bear the name of their principal city. The regions are divided into 56 Cercles of Mali, cercles. The cercles and the district are divided into 703 communes, with 36 urban communes and 667 rural communes, while some larger cercles still contain Arrondissements of Mali, arrondissements above the commune level, these are organisational areas with no independent power or office. Rural communes are subdivided into villages, while urban communes are subdivided into ''quartier'' (wards or quarters). Communes usually bear the name of their principal town. The capital, Bamako, consists of six urban communes. There were initially 701 communes until Law ''No. 01-043'' of 7 June 2001 created two new rural communes in the desert region in the north east of the country: Alata, Mali, Alata, Ménaka Cerc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Sudan
French Sudan (; ') was a French colonial territory in the Federation of French West Africa from around 1880 until 1959, when it joined the Mali Federation, and then in 1960, when it became the independent state of Mali. The colony was formally called French Sudan from 1890 until 1899 and then again from 1921 until 1958, and had a variety of different names over the course of its existence. The colony was initially established largely as a military project led by French troops, but in the mid-1890s it came under civilian administration. A number of administrative reorganizations in the early 1900s brought increasing French administration over issues like agriculture, religion, and slavery. Following World War II, the African Democratic Rally (RDA) under Modibo Keïta became the most significant political force pushing for independence. French Sudan initially retained close connections with France and joined in a short-lived federation with Senegal in 1959, but ties to both ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mali Empire
The Mali Empire (Manding languages, Manding: ''Mandé''Ki-Zerbo, Joseph: ''UNESCO General History of Africa, Vol. IV, Abridged Edition: Africa from the Twelfth to the Sixteenth Century'', p. 57. University of California Press, 1997. or ''Manden Duguba''; ) was an empire in West Africa from 1226 to 1610. The empire was founded by Sundiata Keita () and became renowned for the wealth of its rulers, especially Mansa Musa (Musa Keita). At its peak, Mali was the largest empire in West Africa, widely influencing the culture of the region through the spread of Manding languages, its language, laws, and customs. The empire began as a small Mandinka people, Mandinka kingdom at the upper reaches of the Niger River, centered around the Manding region. It began to develop during the 11th and 12th centuries as the Ghana Empire, or Wagadu, declined and trade epicentres shifted southward. The Pre-imperial Mali, history of the Mali Empire before the 13th century is unclear, as there are conflict ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Cities In Mali
This list of cities in Mali tabulates all the largest communes in the country of Mali (including those in the north-eastern portion where the Mali Government no longer exercises de facto control). Besides the largest cities and towns (all urban communes are shown), this table also includes other large rural communes with a population in excess of 50,000. By far the largest agglomeration in Mali is the capital, Bamako, with a population of 1,809,106 (at the 2009 Census). Thus about 12½ percent of Mali's population lives in Bamako. Cities The following table lists all communes with over 50,000 population from the 1 April 2009 census, together with the higher-level administrative unit (Regions of Mali, ''région'') and second-level unit (Cercles of Mali, ''cercle'') in which each is situated. The population figures refer to the real city (i.e. commune) without any suburbs in neighbouring communes. Bamako is a separate capital district and is not within any ''région'' or ''cer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deutscher Wetterdienst
The () or DWD for short, is the German Meteorological Service, based in Offenbach am Main, Germany, which monitors weather and meteorological conditions over Germany and provides weather services for the general public and for nautical, aviation, hydrometeorological or agricultural purposes. It is attached to the Federal Ministry for Transport. The DWDs principal tasks include warning against weather-related dangers and monitoring and rating climate changes affecting Germany. The organisation runs atmospheric models on their supercomputer for precise weather forecasting. The DWD also manages the national climate archive and one of the largest specialised libraries on weather and climate worldwide. History The DWD was formed on 11 November 1952 when the weather services of the western occupation zones were merged. In 1954, the Federal Republic of Germany joined the World Meteorological Organization (WMO). In 1990, following the reunification, the weather services of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Köppen Climate Classification
The Köppen climate classification divides Earth climates into five main climate groups, with each group being divided based on patterns of seasonal precipitation and temperature. The five main groups are ''A'' (tropical), ''B'' (arid), ''C'' (temperate), ''D'' (continental), and ''E'' (polar). Each group and subgroup is represented by a letter. All climates are assigned a main group (the first letter). All climates except for those in the ''E'' group are assigned a seasonal precipitation subgroup (the second letter). For example, ''Af'' indicates a tropical rainforest climate. The system assigns a temperature subgroup for all groups other than those in the ''A'' group, indicated by the third letter for climates in ''B'', ''C'', ''D'', and the second letter for climates in ''E''. Other examples include: ''Cfb'' indicating an oceanic climate with warm summers as indicated by the ending ''b.'', while ''Dwb'' indicates a semi-Monsoon continental climate, monsoonal continental climate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tropical Savanna Climate
Tropical savanna climate or tropical wet and dry climate is a tropical climate sub-type that corresponds to the Köppen climate classification categories ''Aw'' (for a dry "winter") and ''As'' (for a dry "summer"). The driest month has less than of precipitation and also less than 100-\left (\frac \right)mm of precipitation. This latter fact is in a direct contrast to a tropical monsoon climate, whose driest month sees less than of precipitation but has ''more'' than 100-\left (\frac \right) of precipitation. In essence, a tropical savanna climate tends to either see less overall rainfall than a tropical monsoon climate or have more pronounced dry season(s). It is impossible for a tropical savanna climate to have more than as such would result in a negative value in that equation. In tropical savanna climates, the dry season can become severe, and often drought conditions prevail during the course of the year. Tropical savanna climates often feature tree-studded grasslands due ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Koumantou
Koumantou is a commune and town in Mali, in the Cercle of Bougouni in the Sikasso Region. It is located near the Ivorian border. The commune includes 38 villages spread over 1268 km2. As of 2009 the commune had a population of 51,348. The commune's economy is heavily agricultural, relying particularly on millet, corn, sorghum, peanuts, and cotton. The Compagnie malienne pour le développement du textile (CMDT) has a cotton-processing factory located in the town. A festival of music and traditional danse, organized by the Association for the Development of the Commune of Koumantou (ADAKOM), was held from 19 to 22 May 2005, in the villages of Koumantou, Niamala, and Kôla. The festival celebrated such traditional instruments as the buru, mpolon, and balafon. See also * List of cities in Mali This list of cities in Mali tabulates all the largest communes in the country of Mali (including those in the north-eastern portion where the Mali Government no longer exerci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cercle (Mali)
A cercle ( French for "circle") is the second-level administrative unit in Mali. Mali is divided into eight ''régions'' and one capital district (Bamako); the ''régions'' are subdivided into 49 ''cercles''. These subdivisions bear the name of their principal city. During French colonial rule in Mali, a cercle was the smallest unit of French political administration that was headed by a European officer. A cercle consisted of several cantons, each of which in turn consisted of several villages. In 1887, the Cercle of Bafoulabé was the first cercle to be created in Mali. In most of former French West Africa, the term ''cercle'' was changed to prefecture or department after independence, but this was not done in Mali. Some cercles (and the district) were, prior to the 1999 local government reorganisation, further divided into arrondissements, especially in urban areas or the vast northern regions (such as Kidal), which consisted of a collection of communes. Since these re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aurillac
Aurillac (; ) is the prefecture of the Cantal department, in the Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes region of France. Geography Aurillac is at above sea level and located at the foot of the Cantal mountains in a small sedimentary basin. The city is built on the banks of the Jordanne, a tributary of the Cère. It is south of Paris and north of Toulouse. Aurillac was part of a former Auvergne province called Haute-Auvergne and is only away from the heart of the Auvergne Volcano Park. Access to the commune is by numerous roads including the D922 from Naucelles in the north, the D17 from Saint-Simon in the north-east, Route nationale N122 from Polminhac in the east which continues to Sansac-de-Marmiesse in the south-west, the D920 to Arpajon-sur-Cère in the south-east, and the D18 to Ytrac in the west. Aurillac station, in the centre of town, lies on the Figeac-Arvant railway. It has rail connections to Clermont-Ferrand, Brive-la-Gaillarde and Toulouse. About 50% of the com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moussa Traoré
Moussa Traoré (25 September 1936 – 15 September 2020) was a Malian military officer, politician, and dictator who served as the second President of Mali from 1968 to 1991. As a lieutenant, he led the military ousting of President Modibo Keïta in 1968. Thereafter he served as head of state until March 1991, when he was overthrown by popular protests and a military coup. During his tenure, political activity was banned, marking a shift to authoritarian control. His right-hand man Tiécoro Bagayoko oversaw a regime of surveillance with the help of informants. He dismantled the socialist economic policies of his predecessor, Modibo Keïta. He was twice condemned to death in the 1990s, but eventually pardoned on both occasions and freed in 2002. He retired from public life and died in 2020. Early life Born in Kayes Region, Traoré studied at Kita and at the military academy in Fréjus, France. He returned to Mali in 1960, after its 1959 independence. He became second lieute ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |