|
Bosulif
Bosutinib, sold under the brand name Bosulif, is a small molecule BCR-ABL and src tyrosine kinase inhibitor used for the treatment of chronic myelogenous leukemia. Originally synthesized by Wyeth, it is being developed by Pfizer. Mechanism It is an ATP-competitive Bcr-Abl tyrosine-kinase inhibitor with an additional inhibitory effect on Src family kinases (including Src, Lyn and Hck). It has also shown activity against the receptors for platelet derived growth factor and vascular endothelial growth factor. Bosutinib inhibited 16 of 18 imatinib-resistant forms of Bcr-Abl expressed in murine myeloid cell lines, but did not inhibit T315I and V299L mutant cells. Bosutinib is metabolized through CYP3A4. Medical uses Bosutinib received US FDA and EU European Medicines Agency approval in September 2012, and March 2013, respectively for the treatment of adults with Philadelphia chromosome-positive (Ph+) chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) with resistance, or intolerance to prior ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pfizer
Pfizer Inc. ( ) is an American Multinational corporation, multinational Pharmaceutical industry, pharmaceutical and biotechnology corporation headquartered at The Spiral (New York City), The Spiral in Manhattan, New York City. Founded in 1849 in New York by German entrepreneurs Charles Pfizer (1824–1906) and Charles F. Erhart (1821–1891), Pfizer is one of the oldest pharmaceutical companies in North America. Pfizer develops and produces medicines and vaccines for immunology, oncology, cardiology, endocrinology, and neurology. The company's largest products by sales are the Pfizer–BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine ($11 billion in 2023 revenues), apixaban ($6 billion in 2023 revenues), a pneumococcal conjugate vaccine ($6 billion in 2023 revenues), palbociclib ($4 billion in 2023 revenues), and tafamidis ($3 billion in 2023 revenues). In 2023, 46% of the company's revenues came from the United States, 6% came from Japan, and 48% came from other countries. Pfizer has been a publi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oral Administration
Oral administration is a route of administration whereby a substance is taken through the Human mouth, mouth, swallowed, and then processed via the digestive system. This is a common route of administration for many medications. Oral administration can be easier and less painful than other routes of administration, such as Injection (medicine), injection. However, the onset of action is relatively low, and the effectiveness is reduced if it is not absorbed properly in the digestive system, or if it is broken down by digestive enzymes before it can reach the bloodstream. Some medications may cause gastrointestinal side effects, such as nausea or vomiting, when taken orally. Oral administration can also only be applied to conscious patients, and patients able to swallow. Terminology ''Per os'' (; ''P.O.'') is an adverbial phrase meaning literally from Latin "through the mouth" or "by mouth". The expression is used in medicine to describe a treatment that is taken orally (but not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philadelphia Chromosome
The Philadelphia chromosome or Philadelphia translocation (Ph) is an abnormal version of chromosome 22 where a part of the ''ABL (gene), Abelson murine leukemia'' 1 (''ABL1'') gene on chromosome 9 breaks off and attaches to the ''BCR (gene), breakpoint cluster region'' (''BCR'') gene in chromosome 22. The balanced reciprocal Translocation (genetics), translocation between the long arms of 9 and 22 chromosomes [t (9; 22) (q34; q11)] results in the fusion gene ''BCR::ABL1''. The Oncogene, oncogenic protein with persistently enhanced tyrosine kinase (TK) activity transcribed by the ''BCR''::''ABL1'' fusion gene can lead to rapid, uncontrolled growth of immature white blood cells that accumulates in the blood and bone marrow. The Philadelphia chromosome is present in the bone marrow cells of a vast majority ''chronic myelogenous leukemia'' (CML) patients. The expression patterns off different BCR-ABL1 transcripts vary during the progression of CML. Each variant is present in a distinct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
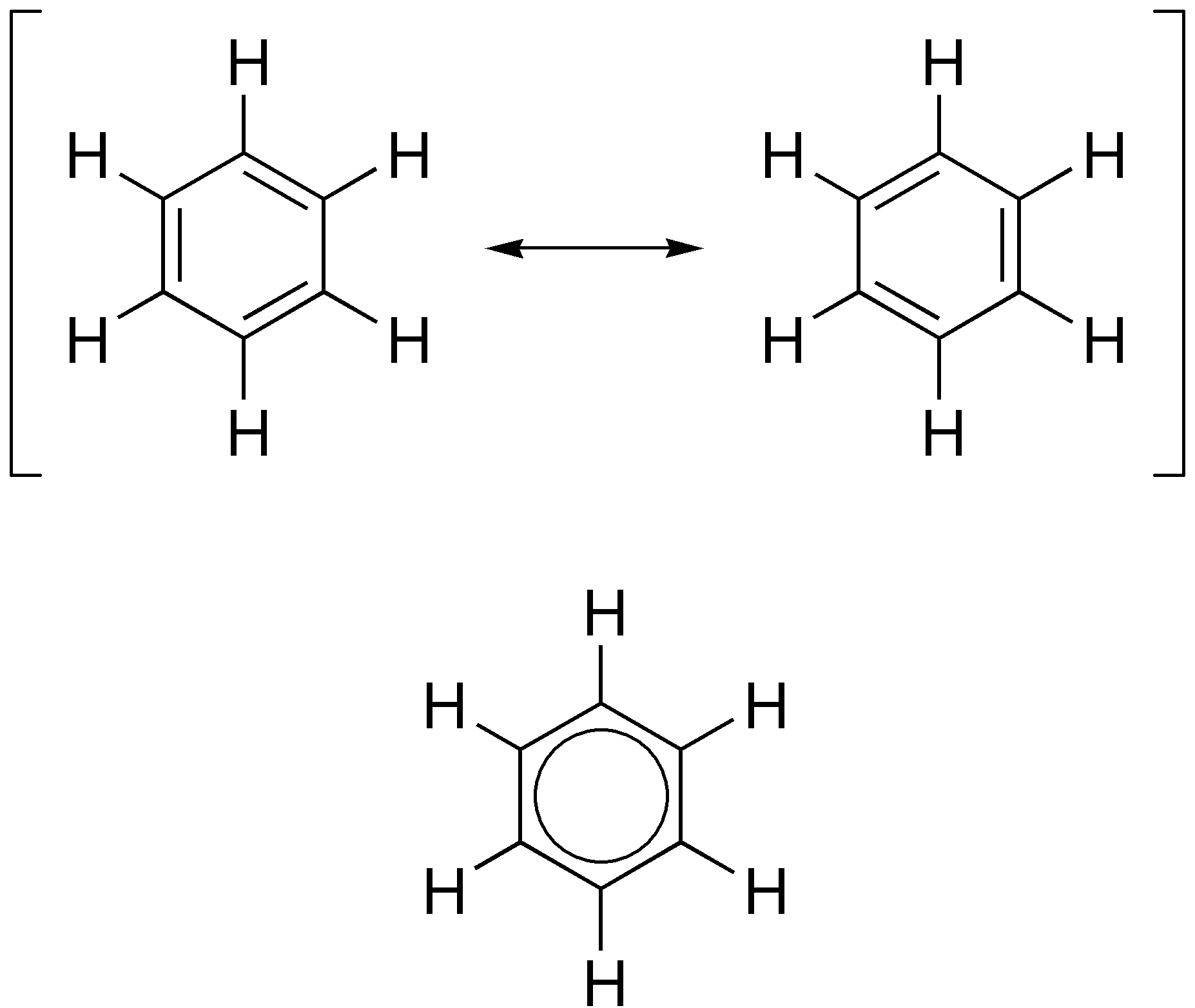
Aromatic Nitriles
In organic chemistry, aromaticity is a chemical property describing the way in which a conjugated ring of unsaturated bonds, lone pairs, or empty orbitals exhibits a stabilization stronger than would be expected from conjugation alone. The earliest use of the term was in an article by August Wilhelm Hofmann in 1855. There is no general relationship between aromaticity as a chemical property and the olfactory properties of such compounds. Aromaticity can also be considered a manifestation of cyclic delocalization and of resonance. This is usually considered to be because electrons are free to cycle around circular arrangements of atoms that are alternately single- and double- bonded to one another. This commonly seen model of aromatic rings, namely the idea that benzene was formed from a six-membered carbon ring with alternating single and double bonds (cyclohexatriene), was developed by Kekulé (see History section below). Each bond may be seen as a hybrid of a single bond ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quinolines
Quinoline is a heterocyclic aromatic organic compound with the chemical formula C9H7N. It is a colorless hygroscopic liquid with a strong odor. Aged samples, especially if exposed to light, become yellow and later brown. Quinoline is only slightly soluble in cold water but dissolves readily in hot water and most organic solvents. Quinoline itself has few applications, but many of its derivatives are useful in diverse applications. A prominent example is quinine, an alkaloid found in plants. Over 200 biologically active quinoline and quinazoline alkaloids are identified. 4-Hydroxy-2-alkylquinolines (HAQs) are involved in antibiotic resistance. Occurrence and isolation Quinoline was first extracted from coal tar in 1834 by German chemist Friedlieb Ferdinand Runge; he called quinoline ''leukol'' ("white oil" in Greek). Coal tar remains the principal source of commercial quinoline. In 1842, French chemist Charles Gerhardt obtained a compound by dry distilling quinine, str ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catechol Ethers
Catechol ( or ), also known as pyrocatechol or 1,2-dihydroxybenzene, is an organic compound with the molecular formula . It is the ''ortho'' isomer of the three isomeric benzenediols. This colorless compound occurs naturally in trace amounts. It was first discovered by destructive distillation of the plant extract catechin. About 20,000 tonnes of catechol are now synthetically produced annually as a commodity organic chemical, mainly as a precursor to pesticides, flavors, and fragrances. Small amounts of catechol occur in fruits and vegetables. Isolation and synthesis Catechol was first isolated in 1839 by Edgar Hugo Emil Reinsch (1809–1884) by distilling it from the solid tannic preparation catechin, which is the residuum of catechu, the boiled or concentrated juice of ''Mimosa catechu'' ('' Acacia catechu''). Upon heating catechin above its decomposition point, a substance that Reinsch first named ''Brenz-Katechusäure'' (burned catechu acid) sublimated as a white efflore ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Discovery And Development Of Bcr-Abl Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors
Bcr-Abl tyrosine-kinase inhibitors (TKI) are the first-line therapy for most patients with chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML). More than 90% of CML cases are caused by a chromosomal abnormality that results in the formation of a so-called Philadelphia chromosome. This abnormality was discovered by Peter Nowell in 1960 and is a consequence of fusion between the Abelson ( Abl) tyrosine kinase gene at chromosome 9 and the break point cluster ( Bcr) gene at chromosome 22, resulting in a chimeric oncogene (Bcr-Abl) and a constitutively active Bcr-Abl tyrosine kinase that has been implicated in the pathogenesis of CML. Compounds have been developed to selectively inhibit the tyrosine kinase. Before the 2001 U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval of imatinib, no drugs were available to alter the natural progression of CML. Only cytotoxic drugs such as busulfan, hydroxyurea or interferon-alpha (rIFN-α) were utilized. Even though the first Bcr-Abl TK inhibitor was named "the mag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
P-glycoprotein
P-glycoprotein 1 (permeability glycoprotein, abbreviated as P-gp or Pgp) also known as multidrug resistance protein 1 (MDR1) or ATP-binding cassette sub-family B member 1 (ABCB1) or cluster of differentiation 243 (CD243) is an important protein of the cell membrane that pumps many foreign substances out of cells. More formally, it is an ATP-dependent efflux pump with broad substrate specificity. It exists in animals, fungi, and bacteria, and it likely evolved as a defense mechanism against harmful substances. P-gp is extensively distributed and expressed in the intestinal epithelium where it pumps xenobiotics (such as toxins or drugs) back into the intestinal lumen, in liver cells where it pumps them into bile ducts, in the cells of the proximal tubule of the kidney where it pumps them into urinary filtrate (in the proximal tubule), and in the capillary endothelial cells composing the blood–brain barrier and blood–testis barrier, where it pumps them back into the ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |