|
Bosquet
In the French formal garden, a ''bosquet'' (French, from Italian ''boschetto'', "grove, wood") is a formal plantation of trees in a wide variety of forms, some open at the bottom and others not. At a minimum a bosquet can be five trees of identical species planted as a quincunx (like a 5 dice), or set in strict regularity as to rank and file, so that the trunks line up as one passes along either face. In large gardens they were dense artificial woodland, often covering large areas, with tall hedges on the outside and other trees inside the hedges. Symbolic of order in a humanized and tamed gardens of the French Renaissance and Baroque French formal gardens, the bosquet is an analogue of the orderly orchard, an amenity that has been intimately associated with pleasure gardening from the earliest Persian gardens of the Achaemenid Empire. Bosket is an English rendition of the word, now obsolete; the usual English term for a large hedged bosquet was a "wilderness", while smaller un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
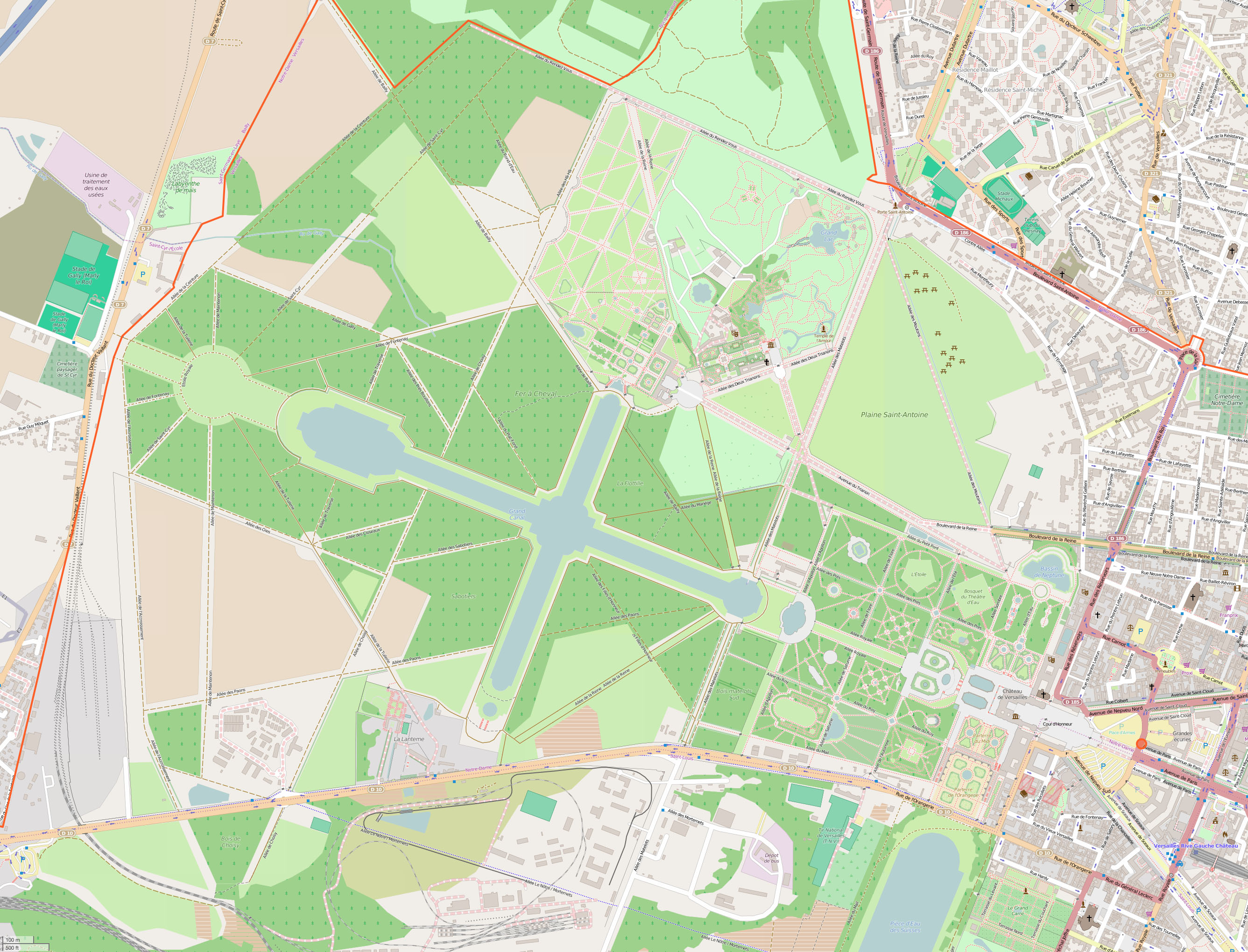
Gardens Of Versailles
The Gardens of Versailles ( ) occupy part of what was once the ''Domaine royal de Versailles'', the royal demesne of the Palace of Versailles, château of Versailles. Situated to the west of the Palace of Versailles, palace, the gardens cover some of land, much of which is landscaped in the classic French formal garden style perfected here by André Le Nôtre. Beyond the surrounding belt of woodland, the gardens are bordered by the urban areas of Versailles (city), Versailles to the east and Le Chesnay to the north-east, by the National Arboretum de Chèvreloup to the north, the Versailles plain (a protected wildlife preserve) to the west, and by the Satory Forest to the south. Administered by the Public Establishment of the Palace, Museum and National Estate of Versailles, an autonomous public entity operating under the aegis of the Ministry of Culture (France), French Ministry of Culture, the gardens are now one of the most visited public sites in France, receiving more than s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wilderness (garden History)
In the Western history of gardening, from the 16th to early 19th centuries, a wilderness was a highly artificial and formalized type of woodland, forming a section of a large garden. Though examples varied greatly, a typical English style was a number of geometrically-arranged compartments (often called "quarters") closed round by hedges, each compartment planted inside with relatively small trees. Between the compartments there were wide walkways or "alleys", usually of grass, sometimes of gravel. The wilderness provided shade in hot weather, and relative privacy. Though often said by garden writers at the time to be intended for meditation and reading, the wilderness was much used for walking, and often flirtation. There were few if any flowers, but there might be statues, and some seating, especially in garden rooms or ''salle vertes'' ("green rooms"), clearings left empty. Some had other features, such as a garden maze.HEALD"Wilderness" Woudstra, 3–11; Eburne and Taylor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Garden Room
In gardening, a garden room is a secluded and partly enclosed space within a garden that creates a room-like effect. Such spaces have been part of garden design for centuries. Generally they are regarded as different from terraces and patios just outside a building, although in practice these are often the parts of a garden that are most used as a room, with tables and chairs. Walls and hedges may form part of the boundaries of a garden room, but plants, usually at least a few feet tall, will do as well. Apart from the entrances to the room, these should normally enclose the space. There may be furniture, especially for sitting down, but this is not essential. In architecture, the term "garden room" may be used for a sunroom, conservatory, or any room with a good view of a garden, or even one decorated with a garden theme. A small single-roomed building for leisure in a garden is usually called a summer house, gazebo, or garden house. Below a certain size a very small gard ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
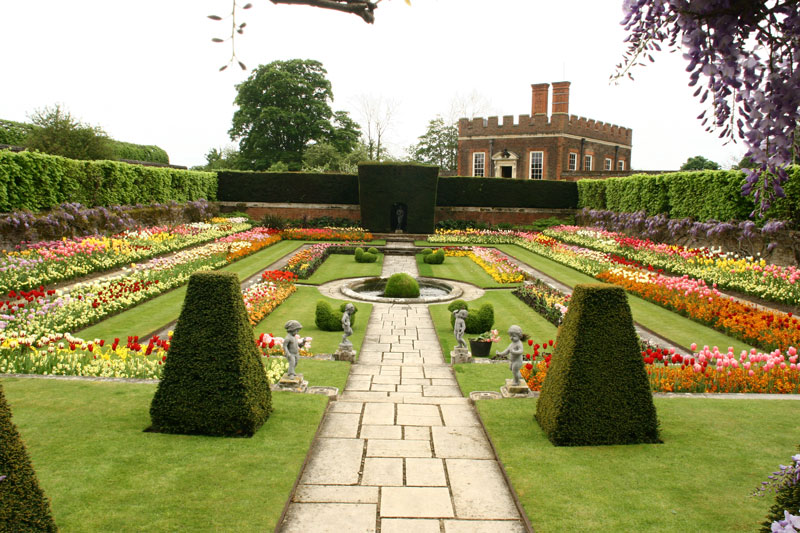
French Formal Garden
The French formal garden, also called the , is a style of "Landscape architecture, landscape" garden based on symmetry and the principle of imposing order on nature. Its epitome is generally considered to be the Gardens of Versailles designed during the 17th century by the landscape architect André Le Nôtre for Louis XIV and widely copied by other Template:Royal houses of Europe, European courts.Éric Mension-Rigau, "Les jardins témoins de leur temps" in ''Historia (revue), Historia'', n° 7/8 (2000). Classicism was also expressed in horticulture. Jean-Baptiste de La Quintinie introduced an art of fruit pruning and bedding techniques that were to have a lasting impact on production gardens. But the term ‘classical garden’ was only used for pleasure gardens. History Renaissance influence The ''jardin à la française'' evolved from the French Renaissance garden, a style which was inspired by the Italian Renaissance garden at the beginning of the 16th century. The Ita ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jacques Boyceau
Jacques Boyceau, sieur de la Barauderie (ca. 1560 – 1633) was a French garden designer, the superintendent of royal gardens under Louis XIII of France, Louis XIII, whose posthumously produced ''Traité du iardinage selon les raisons de la nature et de l'art. Ensemble divers desseins de parterres, pelouzes, bosquets et autres ornements'' was published in 1638. Its sixty engravings after Boyceau's designs make it one of the milestones in tracing the history of the Garden à la française (French formal garden). His nephew Jacques de Menours, who produced the volume, included an engraved frontispiece with the portrait of Boyceau. A few of the plates show formally planted ''bosquets'', but the majority are of designs for parterres. The accompanying text asserts that some of these designs have been used at royal residences: the Palais du Luxembourg, where the two axes at right angles survive from Boyceau's original plan, the Jardin des Tuileries, the newly built château of Sain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
André Mollet
André Mollet (died before 16 June 1665) was a French garden designer, the son of Claude Mollet—gardener to three French kings—and the grandson of Jacques Mollet, gardener at the château d'Anet, where Italian formal gardening was introduced to France. Royal appointment André Mollet became royal gardener to Queen Christina in Stockholm. His lasting record is his handsomely-printed folio, ''Le Jardin de plaisir'' ("The Pleasure Garden" Stockholm 1651, which he illustrated with meticulous intaglio printing, copperplate engravings after his own designs, and which, with an eye to a European aristocratic clientele, he published in Swedish, French and German. In his designs the rich patterning of parterres, which had formerly been a garden feature of interest in isolation, was for the first time arranged in significant relation to the plan of the house. Mollet's designs coordinated the elements of scythed turf—making its debut here as an essential element of garden design� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parterre
A ''parterre'' is a part of a formal garden constructed on a level substrate, consisting of symmetrical patterns, made up by plant beds, plats, low hedges or coloured gravels, which are separated and connected by paths. Typically it was the part of the garden nearest the house, perhaps after a terrace. The view of a parterre from inside the house, especially from the upper floors, was a major consideration in its design. The word "parterre" was and is used both for the whole part of the garden containing parterres and for each individual section between the "alleys". The pattern or the borders of the beds may be marked by low, tightly pruned, evergreen hedge (gardening) , hedging, and their interiors may be planted with flowers or other plants or filled with mulch or gravel. Parterres need not have any flowers at all, and the originals from the 17th and 18th centuries had far fewer than modern survivals or reconstructions. Statues or small evergreen trees, clipped as pyra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palace Of Versailles
The Palace of Versailles ( ; ) is a former royal residence commissioned by King Louis XIV located in Versailles, Yvelines, Versailles, about west of Paris, in the Yvelines, Yvelines Department of Île-de-France, Île-de-France region in France. The palace is owned by the government of France and since 1995 has been managed, under the direction of the Ministry of Culture (France), French Ministry of Culture, by the Public Establishment of the Palace, Museum and National Estate of Versailles. About 15,000,000 people visit the palace, park, or gardens of Versailles every year, making it one of the most popular tourist attractions in the world. Louis XIII built a hunting lodge at Versailles in 1623. His successor, Louis XIV, expanded the château into a palace that went through several expansions in phases from 1661 to 1715. It was a favourite residence for both kings, and in 1682, Louis XIV moved the seat of his court and government to Versailles, making the palace the ''de fact ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jardin De Naples Château D'Amboise
Jardin may refer to: Places *Jardin, Isère, a village in Isère, France *Le Jardin, a village in Corrèze, France *Jardin, Colombia, a town in Antioquia Family name *Alexandre Jardin (born 1965), French writer and film director *Frédéric Jardin (born 1968), French film director *Nicolas-Henri Jardin (1720–1799), French architect, introduced neoclassicism to Danish architecture *Pascal Jardin (1934–1980), French screenwriter *Véronique Jardin (born 1966), French Olympic swimmer See also *Dujardin *Jardine {{disambiguation, geo, surname ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jardin Des Tuileries
The Tuileries Garden (, ) is a public garden between the Louvre and the Place de la Concorde in the 1st arrondissement of Paris, France. Created by Catherine de' Medici as the garden of the Tuileries Palace in 1564, it was opened to the public in 1667 and became a public park after the French Revolution. Since the 19th century, it has been a place for Parisians to celebrate, meet, stroll and relax. During the 2024 Summer Olympics and Paralympics, it was the site of the Olympic and Paralympic cauldron. History The Italian Garden of Catherine de' Medici (16th century) File:Tuileries projet et jardins.jpg, Plan for the palace and gardens by Jacques I Androuet du Cerceau, 1576–1579 File:Map of Tuileries and Louvre, as in c. 1589.png, Plan of the Tuileries garden in about 1589. The Louvre is to the right In July 1559, after the accidental death of her husband, Henry II, Queen Catherine de' Medici decided to leave her residence of the Hôtel des Tournelles, at the easter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jardin Du Luxembourg
The Jardin du Luxembourg (), known in English as the Luxembourg Garden, colloquially referred to as the Jardin du Sénat (Senate Garden), is located in the 6th arrondissement of Paris, France. The creation of the garden began in 1612 when Marie de' Medici, the widow of King Henry IV, constructed the Luxembourg Palace as her new residence. The garden today is owned by the French Senate, which meets in the palace. It covers 23 hectares (56.8 acres) and is known for its lawns, tree-lined promenades, tennis courts, flowerbeds, model sailboats on its octagonal Grand Bassin, as well as picturesque Medici Fountain, built in 1620. The name Luxembourg comes from the Latin Mons Lucotitius, the name of the hill where the garden is located, and locally the garden is informally called "le Luco". History In 1611, Marie de' Medici, the widow of Henry IV and the regent for the King Louis XIII, decided to build a palace in imitation of the Pitti Palace in her native Florence. She pu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |