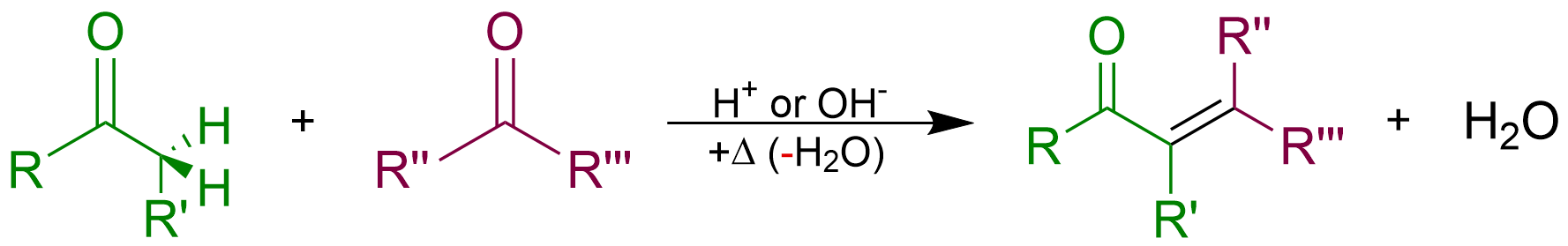|
Borsche–Drechsel Cyclization
The Borsche–Drechsel cyclization is a chemical reaction used to synthesize tetrahydrocarbazoles by the acid-catalyzed cyclization of cyclohexanone arylhydrazones. The reaction was first described by in 1888 and by in 1908. Borsche–Drechsel cyclization is the central step in Borsche–Drechsel carbazole synthesis, where in the first step phenylhydrazine is condensation reaction, condensed with cyclohexanone to form the cyclohexanone phenylhydrazone, and in the final step the resulting tetrahydrocarbazole is oxidized to carbazole itself. Mechanism The reaction has been described in the literature as proceeding in a manner similar to the Fischer indole synthesis. : Here, the acid-catalyzed proton transfer first converts the cyclohexanone phenylhydrazone 1 to the intermediate 2. Subsequently, a heat-induced sigmatropic reaction occurs to produce 3, which is protonated and cyclizes into 4. Elimination of ammonia then leads to the final product, the tetrahydrocarbazole 5. Se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Reaction
A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the chemistry, chemical transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. When chemical reactions occur, the atoms are rearranged and the reaction is accompanied by an Gibbs free energy, energy change as new products are generated. Classically, chemical reactions encompass changes that only involve the positions of electrons in the forming and breaking of chemical bonds between atoms, with no change to the Atomic nucleus, nuclei (no change to the elements present), and can often be described by a chemical equation. Nuclear chemistry is a sub-discipline of chemistry that involves the chemical reactions of unstable and radioactive Chemical element, elements where both electronic and nuclear changes can occur. The substance (or substances) initially involved in a chemical reaction are called reagent, reactants or reagents. Chemical reactions are usually characterized by a chemical change, and they yield one or more Product (c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phenylhydrazine
Phenylhydrazine is the chemical compound with the formula . It is often abbreviated as . It is also found in edible mushrooms. Properties Phenylhydrazine forms monoclinic prisms that melt to an oil around room temperature which may turn yellow to dark red upon exposure to air. Phenylhydrazine is miscible with ethanol, diethyl ether, chloroform and benzene. It is sparingly soluble in water. Preparation Phenylhydrazine is prepared by reacting aniline with sodium nitrite in the presence of hydrogen chloride to form the diazonium salt, which is subsequently reduced using sodium sulfite in the presence of sodium hydroxide to form the final product.''Merck Index of Chemicals and Drugs, 9th ed.'' monograph 7098 History Phenylhydrazine was the first hydrazine derivative characterized, reported by Hermann Emil Fischer in 1875. He prepared it by reduction of a phenyl diazonium salt using sulfite salts. Fischer used phenylhydrazine to characterize sugars via formation of hydrazones ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Condensation Reaction
In organic chemistry, a condensation reaction is a type of chemical reaction in which two molecules are combined to form a single molecule, usually with the loss of a small molecule such as water. If water is lost, the reaction is also known as a dehydration synthesis. However other molecules can also be lost, such as ammonia, ethanol, acetic acid and hydrogen sulfide. The addition of the two molecules typically proceeds in a step-wise fashion to the addition product, usually in equilibrium, and with loss of a water molecule (hence the name condensation). The reaction may otherwise involve the functional groups of the molecule, and is a versatile class of reactions that can occur in acidic or basic conditions or in the presence of a catalyst. This class of reactions is a vital part of life as it is essential to the formation of peptide bonds between amino acids and to the biosynthesis of fatty acids. Many variations of condensation reactions exist. Common examples include ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclohexanone
Cyclohexanone is the organic compound with the formula (CH2)5CO. The molecule consists of six-carbon cyclic molecule with a ketone functional group. This colorless oily liquid has a sweet odor reminiscent of benzaldehyde. Over time, samples of cyclohexanone assume a pale yellow color. Cyclohexanone is slightly soluble in water and miscible with common organic solvents. Millions of tonnes are produced annually, mainly as a precursor to nylon. History and synthesis The compound was discovered by in 1888 among the products of AC electrolysis of slightly acidified water solutions of phenol. He named it hydrophenoketone and correctly suggested that phenol was first hydrogenated by electrolytic hydrogen to cyclohexanol, which he wasn't able to isolate, and then oxidized by electrolytic oxygen. Laboratory synthesis Cyclohexanone can be prepared from cyclohexanol by oxidation with chromium trioxide ( Jones oxidation). An alternative method utilizes the safer and more readily avai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbazole
Carbazole is an aromatic Heterocyclic compound, heterocyclic organic compound. It has a tricyclic structure, consisting of two six-membered benzene rings fused on either side of a five-membered nitrogen-containing ring. The compound's structure is based on the indole structure, but in which a second benzene ring is fused onto the five-membered ring at the 2–3 position of indole (equivalent to the 9a–4a double bond in carbazole, respectively). Carbazole is a constituent of tobacco smoke. History Carl Graebe and Carl Andreas Glaser, Carl Glaser first isolated the compound from coal tar in 1872. Production Few carbazole production methods are economically viable, due to limited demand. During coal tar distillation, carbazole concentrates in the anthracene distillate and must be removed before anthraquinone production; that waste product is the major industrial carbazole source. Polar compounds (e.g., ketones) selectively precipitate it from the anthracene; a more modern techn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fischer Indole Synthesis
The Fischer indole synthesis is a chemical reaction that produces the aromatic Heterocyclic compound, heterocycle indole from a (substituted) phenylhydrazine and an aldehyde or ketone under acidic conditions. The reaction was discovered in 1883 by Emil Fischer. Today migraine, antimigraine drugs of the triptan class are often synthesized by this method. This reaction can be catalyzed by Brønsted acids such as HCl, sulfuric acid, H2SO4, polyphosphoric acid and p-toluenesulfonic acid or Lewis acids such as boron trifluoride, zinc chloride, and aluminium chloride. Several reviews have been published. Reaction mechanism The reaction of a (substituted) phenylhydrazine with a carbonyl (aldehyde or ketone) initially forms a phenylhydrazone which isomerization, isomerizes to the respective enamine (or 'ene-hydrazine'). After protonation, a cyclic sigmatropic rearrangement, [3,3]-sigmatropic rearrangement occurs producing a diimine. The resulting diimine forms a cyclic aminoacetal (or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sigmatropic Reaction
In organic chemistry, a sigmatropic reaction () is a pericyclic reaction wherein the net result is one sigma bond (σ-bond) is changed to another σ-bond in an intramolecular reaction. In this type of rearrangement reaction, a substituent moves from one part of a π-system to another part with simultaneous rearrangement of the π-system. True sigmatropic reactions are usually uncatalyzed, although Lewis acid catalysis is possible. Sigmatropic reactions often have transition-metal catalysts that form intermediates in analogous reactions. The most well-known of the sigmatropic rearrangements are the ,3 Cope rearrangement, Claisen rearrangement, Carroll rearrangement, and the Fischer indole synthesis. Overview of sigmatropic shifts Woodward–Hoffman sigmatropic shift nomenclature Sigmatropic rearrangements are concisely described by an order term ,j'', which is defined as the migration of a σ-bond adjacent to one or more π systems to a new position (i−1) and (j−1) atom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ammonia
Ammonia is an inorganic chemical compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the chemical formula, formula . A Binary compounds of hydrogen, stable binary hydride and the simplest pnictogen hydride, ammonia is a colourless gas with a distinctive pungent smell. It is widely used in fertilizers, refrigerants, explosives, cleaning agents, and is a precursor for numeous chemicals. Biologically, it is a common nitrogenous waste, and it contributes significantly to the nutritional needs of terrestrial organisms by serving as a precursor to fertilisers. Around 70% of ammonia produced industrially is used to make fertilisers in various forms and composition, such as urea and diammonium phosphate. Ammonia in pure form is also applied directly into the soil. Ammonia, either directly or indirectly, is also a building block for the synthesis of many chemicals. In many countries, it is classified as an List of extremely hazardous substances, extremely hazardous substance. Ammonia is toxic, cau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bucherer Carbazole Synthesis
The Bucherer carbazole synthesis is a chemical reaction used to synthesize carbazoles from 2-naphthols and aryl hydrazines using sodium bisulfite. The reaction is named after Hans Theodor Bucherer. See also * Borsche-Drechsel cyclization *Bucherer reaction The Bucherer reaction in organic chemistry is the reversible conversion of a naphthol to a naphthylamine in the presence of ammonia and sodium bisulfite. The reaction is widely used in the synthesis of dye precursors aminonaphthalenesulfonic ac ... References * * {{Organic reactions Nitrogen heterocycle forming reactions Heterocycle forming reactions Name reactions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitrogen Heterocycle Forming Reactions
Nitrogen is a chemical element; it has symbol N and atomic number 7. Nitrogen is a nonmetal and the lightest member of group 15 of the periodic table, often called the pnictogens. It is a common element in the universe, estimated at seventh in total abundance in the Milky Way and the Solar System. At standard temperature and pressure, two atoms of the element bond to form N2, a colourless and odourless diatomic gas. N2 forms about 78% of Earth's atmosphere, making it the most abundant chemical species in air. Because of the volatility of nitrogen compounds, nitrogen is relatively rare in the solid parts of the Earth. It was first discovered and isolated by Scottish physician Daniel Rutherford in 1772 and independently by Carl Wilhelm Scheele and Henry Cavendish at about the same time. The name was suggested by French chemist Jean-Antoine-Claude Chaptal in 1790 when it was found that nitrogen was present in nitric acid and nitrates. Antoine Lavoisier suggested instead the nam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |