|
Borrell II
Borrell II (died 993) was the count of Barcelona, Girona and Ausona from 945 and count of Urgell from 948. Borrell was first seen acting as count during the reign of his father Sunyer II in 945 at the consecration of the nunnery church of Sant Pere de les Puelles in Barcelona. In 947, Sunyer retired to monastic life and ceded the government of his realms jointly to his sons Borrell and Miro I. In 948, Borrell inherited Urgell from his uncle Sunifred II. Sunyer died in 950, and Miro died in 966, leaving Borrell sole ruler of more than half of Old Catalonia, a status which led outsiders and flatterers to refer to him as ''dux Gothiae'', "Duke of Gothia". His own documents almost all refer to him merely as ''comes et marchio'', "Count and Marquis". History Borrell was the son of Sunyer. In 967 he married Letgarda, who is speculated to have been daughter of a Count of Toulouse or Rouergue based on the names given to her children. By her Borrell had two sons and two daughters: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
House Of Barcelona
The House of Barcelona was a medieval dynasty that ruled the County of Barcelona continuously from 878 and the Crown of Aragon from 1137 (as kings from 1162) until 1410. They descend from the Bellonids, the descendants of Wilfred the Hairy. They inherited most of the Catalan counties by the thirteenth century and established a territorial Principality of Catalonia, uniting it with the Kingdom of Aragon through marriage and conquering numerous other lands and kingdoms until the death of the last Legitimacy (family law), legitimate male of the main branch, Martin the Humanist, in 1410. Cadet branches of the house continued to rule County of Urgell, Urgell (since 992) and Duke of Gandia, Gandia. Cadet branches of the dynasty had also ruled Ausona intermittently from 878 until 1111, Provence from 1112 to 1245, and Kingdom of Sicily, Sicily from 1282 to 1409. By the Compromise of Caspe of 1412 the Crown of Aragon passed to a branch of the House of Trastámara, descended from the ''i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Almanzor
Abu ʿĀmir Muḥammad ibn ʿAbdullāh ibn Abi ʿĀmir al-Maʿafiri (), nicknamed al-Manṣūr (, "the Victorious"), which is often Latinized as Almanzor in Spanish, Almansor in Catalan language, Catalan and Almançor in Portuguese ( 938 – 8 August 1002), was a Muslim Arab al-Andalus, Andalusi military leader and politician, statesman. As the chancellor of the Caliphate of Córdoba, Umayyad Caliphate of Córdoba and ''hajib'' (chamberlain) for Caliph Hisham II, Almanzor was effectively ruler of Islamic Iberia. Born in Turrush to a family of Yemeni Arab origin with some juridical ancestors, ibn Abi ʿĀmir left for Córdoba, Spain, Córdoba when still young to be trained as a ''faqīh''. After a few humble beginnings, he joined the court administration and soon gained the confidence of Subh of Córdoba, Subh, Umm al-walad, mother of the children of Caliph Al-Hakam II. Thanks to her patronage and his own efficiency, he quickly expanded his role. During the caliphate of Al-Hakam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sack Of Barcelona (985)
In the year 985, the Córdoban general Almanzor launched a military campaign against the County of Barcelona The County of Barcelona (, ) was a polity in northeastern Iberian Peninsula, originally located in the southern frontier region of the Carolingian Empire. In the 10th century, the Counts of Barcelona progressively achieved independence from F ..., which culminated in the sacking and razing of Barcelona. Raid In May 985, the Córdoban general, Almanzor, left Córdoba with his army and marched towards the County of Barcelona. The army was accompanied by a fleet departing from Cartagena. Almanzor entered the lands of the county. The Count, Borrell II, learned of the upcoming raid and decided to confront the Muslims. Both armies met Moncada in late June, and the Córdoban army successfully routed the Catalans and killed 500 of their troops. Borrel escaped from the battlefield and headed towards Barcelona. Almanzor arrived in the city on July 1 and besieged the city fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Rovirans
The Battle of Rovirans or Matabous was fought in 985 near Terrassa, between the Christian troops of Borrell II and the Muslim troops of Almanzor. The troops of Borell were defeated and Almanzor was able to continue with his campaign, reaching as far as Barcelona, which he sacked. Battle Almanzor left Córdoba on May 5, 985, and headed to Murcia to stock up on provisions for the expedition, which followed the Mediterranean coast, collecting cavalry in Valencia and Tortosa, while Gaspar Feliu and Montfort returned to Toledo and passed through Zaragoza and Lleida. Borrell II tried to stop him and waited for him in Robirans, near Terrassa but he was defeated. Five hundred Barcelonian knights died and were beheaded. Aftermath Borrell II, his son Ramon Borrell and the cavalry that survived retreated towards Caldes de Montbui but were again defeated in Manresa and had to hide in the woods. Almanzor headed for Barcelona Barcelona ( ; ; ) is a city on the northeastern co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
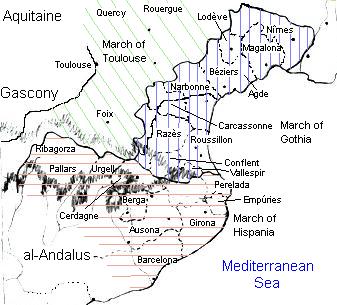
Hispanic March
The Spanish March or Hispanic March was a march or military buffer zone established c. 795 by Charlemagne in the eastern Pyrenees and nearby areas, to protect the new territories of the Christian Carolingian Empire—the Duchy of Gascony, the Duchy of Aquitaine, and Septimania—from the Muslim Umayyad Emirate of Córdoba in al-Andalus. In its broader meaning, the ''Spanish March'' sometimes refers to a group of early Iberian and trans-Pyrenean lordships or counts coming under Frankish rule. As time passed, these lordships merged or gained independence from Frankish imperial rule. Geographical context The area of the Spanish March broadly corresponds to the eastern regions between the Pyrenees and the Ebro. The local population of the march was diverse. It included Basques in its northwestern valleys, the Jews of Occitania, and a large Occitano-Romance-speaking population governed by the Visigothic Code, all of them under the influence of al-Andalus since their lords had vow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Otto II
Otto II (955 – 7 December 983), called the Red (), was Holy Roman Emperor from 973 until his death in 983. A member of the Ottonian dynasty, Otto II was the youngest and sole surviving son of Otto the Great and Adelaide of Italy. Otto II was made joint-ruler of Germany in 961, at an early age, and his father named him co-Emperor in 967 to secure his succession to the throne. His father also arranged for Otto II to marry the Byzantine Princess Theophanu, who would be his wife until his death. When his father died after a 37-year reign, the eighteen-year-old Otto II became absolute ruler of the Holy Roman Empire in a peaceful succession. Otto II spent his reign continuing his father's policy of strengthening Imperial rule in Germany and extending the borders of the Empire deeper into Southern Italy. Otto II also continued the work of Otto I in subordinating the Catholic Church to Imperial control. Early in his reign, Otto II defeated a major revolt against his rule from othe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematical Association Of America
The Mathematical Association of America (MAA) is a professional society that focuses on mathematics accessible at the undergraduate level. Members include university A university () is an educational institution, institution of tertiary education and research which awards academic degrees in several Discipline (academia), academic disciplines. ''University'' is derived from the Latin phrase , which roughly ..., college, and high school teachers; graduate and undergraduate students; pure and applied mathematicians; computer scientists; statisticians; and many others in academia, government, business, and industry. The MAA was founded in 1915 and is headquartered at 11 Dupont in the Dupont Circle, Washington, D.C., Dupont Circle neighborhood of Washington, D.C. The organization publishes mathematics journals and books, including the ''American Mathematical Monthly'' (established in 1894 by Benjamin Finkel), the most widely read mathematics journal in the world according to re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Santa Maria De Ripoll
The Monastery of Santa Maria de Ripoll is a Benedictine monastery, built in the Romanesque style, located in the town of Ripoll in Catalonia, Spain. Although much of the present church is 19th century rebuilding, the sculptured portico is a renowned work of Romanesque art. History The Monastery of Santa María de Ripoll was founded in 888 by Count Wilfred the Hairy (called Guifré el Pilós in Catalan) who used it as a centre to bring about the repopulation of the region after conquering it. Wilfred's son, Ridulph, was educated there and was later abbot of the monastery, as well as bishop of Urgell. The monastery grew rapidly, and was subsequently reconsecrated in 935, 977 and 1032, though the monks are known to have been established there permanently only from 1025 or 1032. The scriptorium and the monastic school quickly gained renown under Arnold Scholasticus. The monastery had several offshoots which included the abbeys of St. Martin-du-Canigou (now in France) and that of Sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atto Of Vic
Atto (; died 971) was the bishop of Vic from 957 until his death. He had the bishopric of Vic raised to an archbishopric, but was assassinated by his opponents in 971. Notes References * * * 971 deaths Bishops of Vic 10th-century Catalan bishops Year of birth missing {{Spain-RC-bishop-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pope Sylvester II
Pope Sylvester II (; – 12 May 1003), originally known as Gerbert of Aurillac, was a scholar and teacher who served as the bishop of Rome and ruled the Papal States from 999 to his death. He endorsed and promoted study of Science in the medieval Islamic world, Moorish and Greco-Roman Science in classical antiquity, arithmetic, mathematics and astronomy, reintroducing to Western Christianity, Western Christendom the abacus, armillary sphere, and water organ, which had been lost to Greek East and Latin West, Latin Europe since fall of the Western Roman Empire, the fall of the Western Roman Empire. He is said to be the first in Christian Europe (outside of Al-Andalus) to introduce the decimal numeral system using the Hindu-Arabic numeral system. Early life Gerbert was born about 946, or at any rate between 945 and 950. His exact birthplace is unknown, but it must have been in what was then the Duchy of Aquitaine, part of the France in the Middle Ages, Kingdom of France. More prec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gerald Of Aurillac
Gerald of Aurillac (or Saint Gerald) ( 855 – c. 909) is a French saint of the Roman Catholic Church, also recognized by other religious denominations of Christianity. Life Gerald was born into the Gallo-Roman nobility, counting Cesarius of Arles among his forebears, though the title "Count of Aurillac" was not held by his father, to whose estates he succeeded, and was assumed by him in later life. He was related to Robert de Turlande. The details of his life known today come primarily from ''The Life of St. Gerald of Aurillac'' (c. 930–931) written by Odo of Cluny. Writing twenty years after the event, Abbot Odo of Cluny described how William, duke of Aquitaine, had entreated Gerald to abandon the ''militia regia'', the feudal service performed directly to the king and pay homage to himself, "for the sake of love". Gerald resisted, having recently assumed the title of ''comes'' and doubtless preferring to owe his fealty to the more distant liege, the king at Paris. Accord ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emperor Otto I
Otto I (23 November 912 – 7 May 973), known as Otto the Great ( ) or Otto of Saxony ( ), was East Francia, East Frankish (Kingdom of Germany, German) king from 936 and Holy Roman Emperor from 962 until his death in 973. He was the eldest son of Henry the Fowler and Matilda of Ringelheim. Otto inherited the Duchy of Saxony and the kingship of the Germans upon his father's death in 936. He continued his father's work of unifying all German tribes into a single kingdom and greatly expanded the king's powers at the expense of the aristocracy. Through strategic marriages and personal appointments, Otto installed members of his family in the kingdom's most important duchies. This reduced the various dukes, who had previously been co-equals with the king, to royal subjects under his authority. Otto transformed the church in Germany to strengthen royal authority and subjected its clergy to his personal control. After putting down a brief civil war among the rebellious duchies, Otto de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |