|
Borispol
Boryspil (, ) is a city and the administrative center of Boryspil Raion in Kyiv Oblast (region) in northern and central Ukraine. It hosts the administration of Boryspil urban hromada, one of the hromadas of Ukraine. The population was estimated as Name Official sources state that the city is named after Prince Boris, of Boris and Gleb, two sons of Vladimir the Great, who were both murdered during the internecine wars of 1015–1019. According to Petro Tronko in his History of cities and villages in Ukrainian SSR, the locality where Boryspil is located was named as "Borysove pole" (Borys's field) when in 1015 a son of Vladimir the Great Borys returning from another raid against Pechenegs died from hands of hired assassins. Others state that the name of the city is of the Greek origin; it consists of two parts ''Borys'' from Borysthenes (the Greek name for Dnieper) and ''Pil'' from Polis (the Ukrainized version of the Greek word). The city also has a sister city, Hopkins, Min ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boryspil Raion
Boryspil Raion () is an raion, administrative raion (district) in east-central Kyiv Oblast of Ukraine. Its capital (political), administrative center is the city of Boryspil. Population: On 18 July 2020, as part of the administrative reform of Ukraine, the number of raions of Kyiv Oblast was reduced to seven, and the area of Boryspil Raion was significantly expanded. Two abolished raions, Pereiaslav-Khmelnytskyi Raion, Pereiaslav-Khmelnytskyi and Yahotyn Raions, as well as the cities of Boryspil and Pereiaslav, which were previously incorporated as City of regional significance (Ukraine), cities of oblast significance and did not belong to the raion, were merged into Boryspil Raion. The area of the raion before the reform was . The January 2020 estimate of the raion population was Geography The Boryspil raion is located in the east-central area of the Kyiv Oblast, and has a total area of 146 km2. On the raion's southern border flows the Dnieper River (''Dnipro''). Near the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
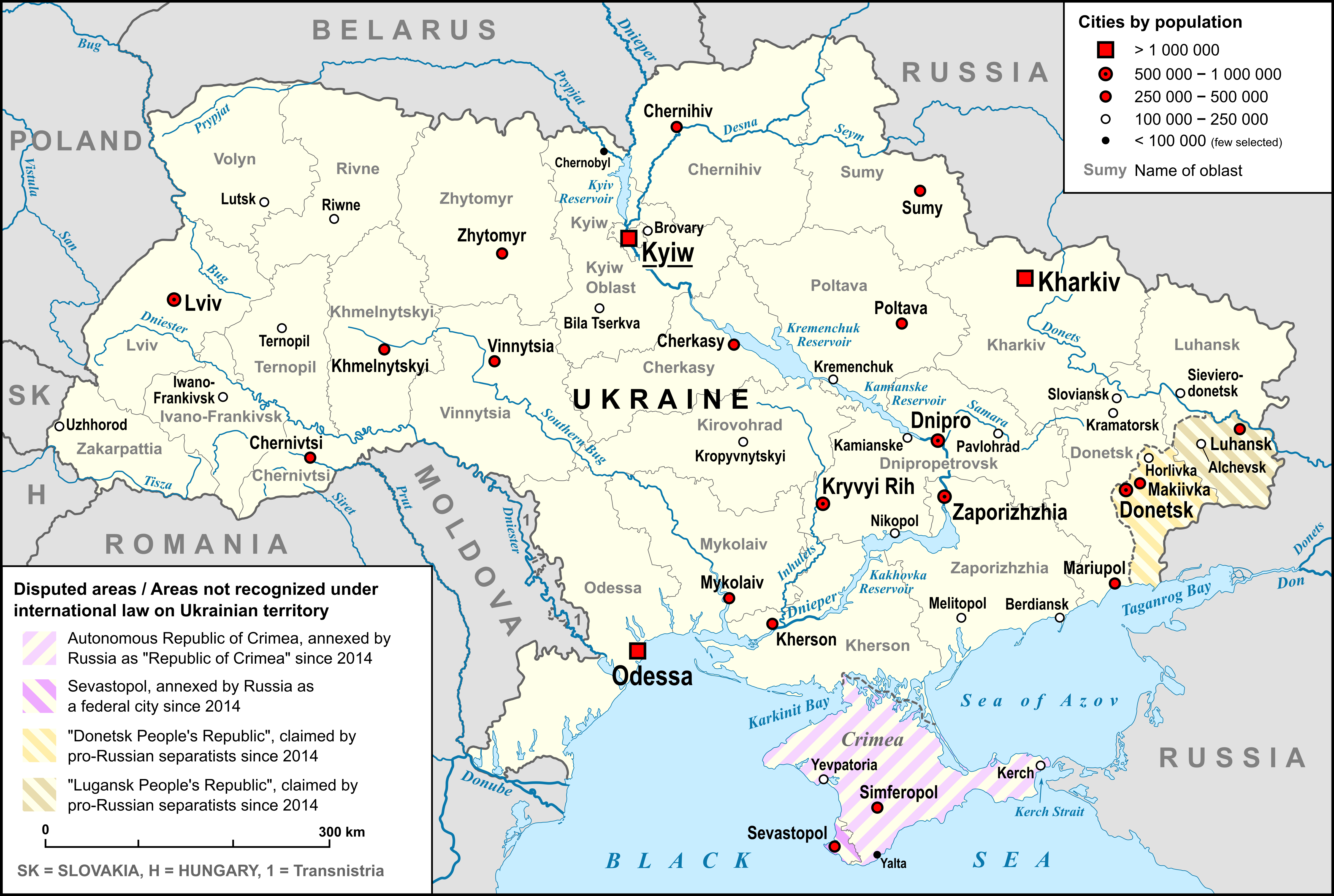
List Of Cities In Ukraine
There are 463 populated places in Ukraine, populated places in Ukraine that have been officially granted city status () by the Verkhovna Rada, the country's parliament, as of 23 April 2025. Settlements with more than 10,000 people are eligible for city status although the status is typically also granted to settlements of historical or regional importance. Smaller settlements are Populated places in Ukraine#Rural settlements, rural settlements () and villages (). Historically, there were systems of city rights, granted by the territorial lords, which defined the status of a place as a ''misto'' or ''selo''. In the past, cities were self-governing and had several privileges. The list of cities is roughly ordered by population and the 2022 estimates are compared to the 2001 Ukrainian census, except for Chernobyl for which the population is an unofficial estimate. The City with special status, cities with special status are shown in ''italic''. The average population size is 62,000. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dnieper
The Dnieper or Dnepr ( ), also called Dnipro ( ), is one of the major transboundary rivers of Europe, rising in the Valdai Hills near Smolensk, Russia, before flowing through Belarus and Ukraine to the Black Sea. Approximately long, with a drainage basin of , it is the longest river of Ukraine and Belarus and the fourth- longest river in Europe, after the Volga, Danube, and Ural rivers. In antiquity, the river was part of the Amber Road trade routes. During the Ruin in the later 17th century, the area was contested between the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth and Russia, dividing what is now Ukraine into areas described by its right and left banks. During the Soviet period, the river became noted for its major hydroelectric dams and large reservoirs. The 1986 Chernobyl disaster occurred on the Pripyat River, a tributary of the Dnieper, just upstream from its confluence with the Dnieper. The Dnieper is an important navigable waterway for the economy of Ukraine and i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ratusz
A ''Ratusz'' (; ; ) is a historic administrative building in countries that adopted the Magdeburg rights such as the Holy Roman Empire, Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth and others. It was distinguished with a bell tower ( lookout or a clock tower). Unlike a regular city hall which may or may not have any specific architectural compositions, ) always consisted of a building with a tower. was primarily designated as a city hall, traditionally built in the centre of a town or in the middle of a town square or more common market square (freedom of trade as the main goal of Magdeburg rights). Although the old ratusz can still maintain the function of a seat of local government, frequently it is separated from the contemporary city government, the administrative building housing the town council, and often serves as a museum of local history (for example in Ivano-Frankivsk and Tarnów among many others). History Prominent examples of a historic can be found in at least 82 Polish c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lübeck Law
The Lübeck law () was the family of codified municipal law developed at Lübeck, which became a free imperial city in 1226 and is located in present-day Schleswig-Holstein. It was the second most prevalent form of municipal law in medieval and early modern Germany next to the Magdeburg Law. Lübeck Law provided for municipal self-government and self-administration yet did not negate dependence upon a lord, be it a bishop, duke, king or, in Lübeck's case, an emperor. Instead, it allowed the cities a certain degree of autonomy and self-reliance in legislative, judicial and executive matters. While these authorities were vested in the city council (Rat), the members of which could be elected by co-option, the Lübeck Law represents a significant modernization of governance in that a class of burghers, as opposed to nobles, were responsible for the day-to-day affairs of governing. The Lübeck Law is not analogous to Hanseatic law. Hanseatic cities adopted either Lübeck or Magde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magdeburg Rights
Magdeburg rights (, , ; also called Magdeburg Law) were a set of town privileges first developed by Otto I, Holy Roman Emperor (936–973) and based on the Flemish Law, which regulated the degree of internal autonomy within cities and villages granted by the local ruler. Named after the city of Magdeburg, these town charters were perhaps the most important set of Middle Ages, medieval laws in Central Europe. They became the basis for the German town laws developed during many centuries in the Holy Roman Empire. The Magdeburg rights were adopted and adapted by numerous monarchs, including the rulers of Crown of Bohemia, Bohemia, Kingdom of Hungary, Hungary, Crown of Poland, Poland, and Grand Duchy of Lithuania, Lithuania, a milestone in the urbanization of the region which prompted the development of thousands of villages and cities. Provisions Being a member of the Hanseatic League, Magdeburg was one of the most important trade cities, maintaining commerce with the Low Countries ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sigismund III Vasa
Sigismund III Vasa (, ; 20 June 1566 – 30 April 1632 N.S.) was King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania from 1587 to 1632 and, as Sigismund, King of Sweden from 1592 to 1599. He was the first Polish sovereign from the House of Vasa. Religiously zealous, he imposed Catholicism across the vast realm, and his crusades against neighbouring states marked Poland's largest territorial expansion. As an enlightened despot, he presided over an era of prosperity and achievement, further distinguished by the transfer of the country's capital from Kraków to Warsaw. Sigismund was the son of King John III of Sweden and his first wife, Catherine Jagiellon, daughter of King Sigismund I of Poland. Elected monarch of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth in 1587, he sought to unify Poland and Sweden under one Catholic kingdom, and when he succeeded his deceased father in 1592 the Polish–Swedish union was created. Opposition in Protestant Sweden caused a war against Sigismund headed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Registered Cossacks
Registered Cossacks (, ) comprised special Cossack units of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth army in the 16th and 17th centuries. Registered Cossacks became a military formation of the Commonwealth army beginning in 1572 soon after the Union of Lublin (1569), when most of the territory of modern Ukraine passed to the Crown of Poland. Registered Cossack formations were based on the Zaporozhian Cossacks who already lived on the lower reaches of the Dnieper River amidst the Pontic steppes as well as on self-defense formations within settlements in the region of modern Central and Southern Ukraine. History Origins In 1524, King Sigismund I commissioned Semen Połozowicz and Krzysztof Kmitycz to organize permanent Cossack units to defend the lower Dnieper; however, the plan was not implemented due to a lack of funds. The starosta of Cherkasy, Ostap Dashkevych, revived the idea at the 1533 Polish Sejm in Piotrków Trybunalski. Dashkevych tried to show that in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sejm Of The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth
The General Sejm (, ) was the bicameral legislature of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. It was established by the Union of Lublin in 1569 following the merger of the legislatures of the two states, the Sejm of the Kingdom of Poland and the Seimas of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania. It was one of the primary elements of the democratic governance in the Commonwealth (see Golden Liberty). The sejm was a powerful political institution. The king could not pass laws without its approval. The two chambers of a sejm were the Senate (''senat'') consisting of high ecclesiastical and secular officials, and the lower house, (''izba poselska''), the sejm proper, of lower ranking officials and the representatives of all szlachta. Together with the king, the three were known as the sejming estates, or estates of the sejm (''stany sejmujące'', literally, "deliberating estates"). Duration and frequencies of the sejms changed over time, with the six-week sejm session convened every two years ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Union Of Lublin
The Union of Lublin (; ) was signed on 1 July 1569 in Lublin, Poland, and created a single state, the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, one of the largest countries in Europe at the time. It replaced the personal union of the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania with a real union and an elective monarchy, as Sigismund II Augustus, the last of the Jagiellons, remained childless after three marriages. In addition, the autonomy of Royal Prussia was largely abandoned. The Duchy of Livonia, tied to Lithuania in real union since the Union of Grodno (1566), became a Polish–Lithuanian Condominium (international law), condominium. The Commonwealth was ruled by a single elected monarch who carried out the duties of King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania, and governed with a common Senate and diet (assembly), parliament (the ''Sejm''). The Union is seen by some as an evolutionary stage in the Polish–Lithuanian Union, Polish–Lithuanian alliance and perso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grand Duchy Of Lithuania
The Grand Duchy of Lithuania was a sovereign state in northeastern Europe that existed from the 13th century, succeeding the Kingdom of Lithuania, to the late 18th century, when the territory was suppressed during the 1795 Partitions of Poland, partitions of Poland–Lithuania. The state was founded by Lithuanians (tribe), Lithuanians, who were at the time a Lithuanian mythology, polytheistic nation of several united Baltic tribes from Aukštaitija. By 1440 the grand duchy had become the largest European state, controlling an area from the Baltic Sea in the north to the Black Sea in the south. The grand duchy expanded to include large portions of the former Kievan Rus' and other neighbouring states, including what is now Belarus, Lithuania, most of Ukraine as well as parts of Latvia, Moldova, Poland and Russia. At its greatest extent, in the 15th century, it was the largest state in Europe. It was a multinational state, multi-ethnic and multiconfessionalism, multiconfessional sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |