|
Boris Mouravieff
Boris Petrovich Mouravieff (Russian language: Борис Муравьёв; 8 March 1890 – 2 September 1966) was a Russian historian, philosopher, writer and university professor. He is known for his three-volume work ''Gnosis: Study and Commentaries on the Esoteric Tradition of Eastern Orthodoxy''.Smoley, Richard, ''Inner Christianity: A Guide to the Esoteric Tradition''. Boston: Shambhala, 2002, p.41. Biography Early years: Russia Boris Mouravieff was born in Kronstadt, Imperial Russia, on 8 March 1890. He was the second of Count Piotr Petrovitch Mouravieff's three sons. His father was an Admiral and Secretary of State to the Russian Imperial Navy. His ancestors included General Prince Nicolas Mouravieff-Karski, Andreï Mouraviov (the author A. N. Mouravieff), General Count Michel Mouravieff-Vilenski and General Count Nicolas Mouravieff-Amourski. A commissioned officer of the Imperial Russian Naval Academy, Mouravieff rose through the ranks, in particular from 1909 to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
:Template:Infobox Writer/doc
Infobox writer may be used to summarize information about a person who is a writer/author (includes screenwriters). If the writer-specific fields here are not needed, consider using the more general ; other infoboxes there can be found in :People and person infobox templates. This template may also be used as a module (or sub-template) of ; see WikiProject Infoboxes/embed for guidance on such usage. Syntax The infobox may be added by pasting the template as shown below into an article. All fields are optional. Any unused parameter names can be left blank or omitted. Parameters Please remove any parameters from an article's infobox that are unlikely to be used. All parameters are optional. Unless otherwise specified, if a parameter has multiple values, they should be comma-separated using the template: : which produces: : , language= If any of the individual values contain commas already, add to use semi-colons as separators: : which produces: : , pseu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mikhail Muravyov-Vilensky
Count Mikhail Nikolayevich Muravyov (; 12 October 1796 in Moscow – 12 September 1866 in Saint Petersburg) was a Russian imperial statesman of the 19th century, most known for brutally putting down of Polish and Lithuanian uprisings and leading subsequent cultural and social depolonization of Northwestern Krai (today's Belarus and Lithuania). He should not be confused with his grandson, Mikhail Nikolayevich Muravyov, who served as Russian Foreign Minister between 1897 and 1900. Early years During his years at the University of Moscow, Muravyov set up the Mathematical Society, of which he would later become president. He volunteered during the Patriotic War of 1812 and was wounded at Borodino. In 1816 he became a co-founder of the first Decembrist societies, and, although he didn't actively participate in the movement after 1820, he was briefly apprehended by the police after their failed uprising in December 1825. By some sources he was cooperating with the investigation buyi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Orthodox Church
The Eastern Orthodox Church, officially the Orthodox Catholic Church, and also called the Greek Orthodox Church or simply the Orthodox Church, is List of Christian denominations by number of members, one of the three major doctrinal and jurisdictional groups of Christianity, with approximately 230 million baptised members. It operates as a Communion (Christian), communion of autocephalous churches, each governed by its Bishop (Orthodox Church), bishops via local Holy Synod, synods. The church has no central doctrinal or governmental authority analogous to the pope of the Catholic Church. Nevertheless, the Ecumenical Patriarch of Constantinople is recognised by them as ''primus inter pares'' (), a title held by the patriarch of Rome prior to 1054. As one of the oldest surviving religious institutions in the world, the Eastern Orthodox Church has played an especially prominent role in the history and culture of Eastern Europe, Eastern and Southeastern Europe. Since 2018, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bulgaria
Bulgaria, officially the Republic of Bulgaria, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern portion of the Balkans directly south of the Danube river and west of the Black Sea. Bulgaria is bordered by Greece and Turkey to the south, Serbia and North Macedonia to the west, and Romania to the north. It covers a territory of and is the tenth largest within the European Union and the List of European countries by area, sixteenth-largest country in Europe by area. Sofia is the nation's capital and List of cities and towns in Bulgaria, largest city; other major cities include Burgas, Plovdiv, and Varna, Bulgaria, Varna. One of the earliest societies in the lands of modern-day Bulgaria was the Karanovo culture (6,500 BC). In the 6th to 3rd century BC, the region was a battleground for ancient Thracians, Persians, Celts and Ancient Macedonians, Macedonians; stability came when the Roman Empire conquered the region in AD 45. After the Roman state splintered, trib ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constantinople
Constantinople (#Names of Constantinople, see other names) was a historical city located on the Bosporus that served as the capital of the Roman Empire, Roman, Byzantine Empire, Byzantine, Latin Empire, Latin, and Ottoman Empire, Ottoman empires between its consecration in 330 until 1930, when it was renamed to Istanbul. Initially as New Rome, Constantinople was founded in 324 during the reign of Constantine the Great on the site of the existing settlement of Byzantium, and shortly thereafter in 330 became the capital of the Roman Empire. Following the collapse of the Western Roman Empire in the late 5th century, Constantinople remained the capital of the Eastern Roman Empire (also known as the Byzantine Empire; 330–1204 and 1261–1453), the Latin Empire (1204–1261), and the Ottoman Empire (1453–1922). Following the Turkish War of Independence, the Turkish capital then moved to Ankara. Although the city had been known as Istanbul since 1453, it was officially renamed as Is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
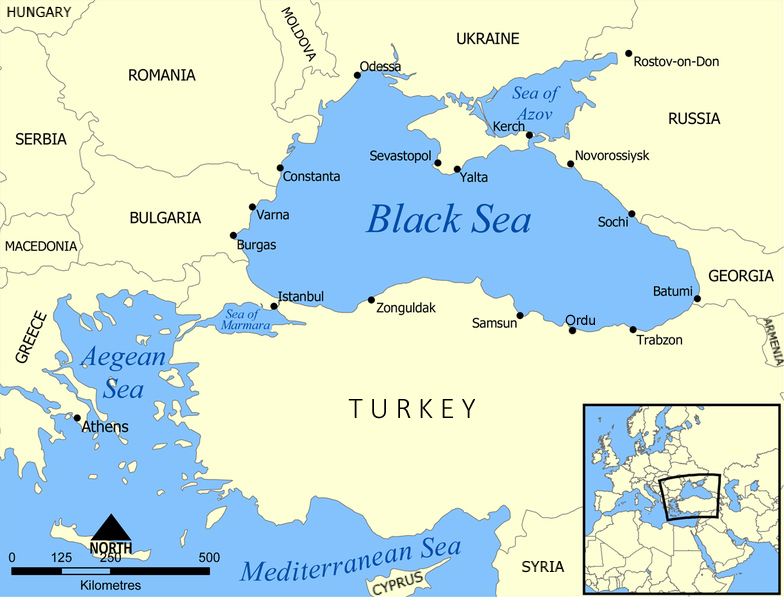
Crimea
Crimea ( ) is a peninsula in Eastern Europe, on the northern coast of the Black Sea, almost entirely surrounded by the Black Sea and the smaller Sea of Azov. The Isthmus of Perekop connects the peninsula to Kherson Oblast in mainland Ukraine. To the east, the Crimean Bridge, constructed in 2018, spans the Strait of Kerch, linking the peninsula with Krasnodar Krai in Russia. The Arabat Spit, located to the northeast, is a narrow strip of land that separates the Syvash lagoons from the Sea of Azov. Across the Black Sea to the west lies Romania and to the south is Turkey. The population is 2.4 million, and the largest city is Sevastopol. The region, internationally recognized as part of Ukraine, has been under Russian occupation of Crimea, Russian occupation since 2014. Called the Tauric Peninsula until the early modern period, Crimea has historically been at the boundary between the Classical antiquity, classical world and the Pontic–Caspian steppe, steppe. Greeks in pre-Rom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treaty Of Brest-Litovsk
The Treaty of Brest-Litovsk was a separate peace treaty signed on 3 March 1918 between Soviet Russia and the Central Powers (Germany, Austria-Hungary, the Ottoman Empire, and Bulgaria), by which Russia withdrew from World War I. The treaty, which followed months of negotiations after the armistice on the Eastern Front in December 1917, was signed at Brest-Litovsk (now Brest, Belarus). The Soviet delegation was initially headed by Adolph Joffe, and key figures from the Central Powers included Max Hoffmann and Richard von Kühlmann of Germany, Ottokar Czernin of Austria-Hungary, and Talaat Pasha of the Ottoman Empire. In January 1918, the Central Powers demanded secession of all occupied territories of the former Russian Empire. The Soviets sent a new peace delegation led by Leon Trotsky, which aimed to stall the negotiations while awaiting revolutions in Central Europe. A renewed Central Powers offensive launched on February 18 captured large territories in the Baltic reg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
October Revolution
The October Revolution, also known as the Great October Socialist Revolution (in Historiography in the Soviet Union, Soviet historiography), October coup, Bolshevik coup, or Bolshevik revolution, was the second of Russian Revolution, two revolutions in Russia in 1917. It was led by Vladimir Lenin's Bolsheviks as part of the broader Russian Revolution of 1917–1923. It began through an insurrection in Petrograd (now Saint Petersburg) on . It was the precipitating event of the Russian Civil War. The initial stage of the October Revolution, which involved the assault on Petrograd, occurred largely without any casualties. The October Revolution followed and capitalized on the February Revolution earlier that year, which had led to the abdication of Nicholas II and the creation of the Russian Provisional Government. The provisional government, led by Alexander Kerensky, had taken power after Grand Duke Michael Alexandrovich of Russia, Grand Duke Michael, the younger brother of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Georgy Lvov
Prince Georgy Yevgenyevich Lvov ( – 7/8 March 1925) was a Russian aristocrat, statesman and the first prime minister of the Russian Republic from 15 March to 20 July 1917. As Russia's ''de facto'' head of state, he led the Provisional Government after the February Revolution led to the suspension of the Russian monarchy. A member of the Lvov princely family, Lvov was born in Dresden, Germany, and gained national fame for his relief work in the Russian Far East during the Russo-Japanese War. In 1906, he was elected to the First Duma as a member of the Constitutional Democratic Party. After the February Revolution, Lvov was made head of the Provisional Government and oversaw a number of liberal reforms. A series of political crises ultimately brought down his government, and in July 1917 he resigned as prime minister and was succeeded by his war minister, Alexander Kerensky. After the October Revolution, Lvov was arrested by the Bolsheviks, but later escaped to France by wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander Kerensky
Alexander Fyodorovich Kerensky ( – 11 June 1970) was a Russian lawyer and revolutionary who led the Russian Provisional Government and the short-lived Russian Republic for three months from late July to early November 1917 ( N.S.). After the February Revolution of 1917, he joined the newly formed provisional government, first as Minister of Justice, then as Minister of War, and after July as the government's second Minister-Chairman. He was the leader of the social-democratic Trudovik faction of the Socialist Revolutionary Party. Kerensky was also a vice-chairman of the Petrograd Soviet, a position that held a sizable amount of power. Kerensky became the prime minister of the Provisional Government, and his tenure was consumed with World War I. Despite mass opposition to the war, Kerensky chose to continue Russia's participation. His government cracked down on anti-war sentiment and dissent in 1917, which made his administration even more unpopular. Kerensky remained in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black Sea Fleet
The Black Sea Fleet () is the Naval fleet, fleet of the Russian Navy in the Black Sea, the Sea of Azov and the Mediterranean Sea. The Black Sea Fleet, along with other Russian ground and air forces on the Crimea, Crimean Peninsula, are subordinate to the Southern Military District of the Russian Armed Forces. The fleet traces its history to its founding by Grigory Potemkin, Prince Potemkin on 13 May 1783 as part of the Imperial Russian Navy. The Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic, Russian SFSR inherited the fleet in 1918; with the founding of the Soviet Union in 1922, it became part of the Soviet Navy. Following the Dissolution of the Soviet Union, collapse of the Soviet Union in 1991, the Black Sea Fleet was partitioned between the Russia, Russian Federation and Ukraine in 1997, with Russia receiving title to 82% of the vessels. The Black Sea Fleet has its official primary headquarters and facilities at the Sevastopol Naval Base, Crimea, which Annexation of Crimea by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First World War
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting took place mainly in European theatre of World War I, Europe and the Middle Eastern theatre of World War I, Middle East, as well as in parts of African theatre of World War I, Africa and the Asian and Pacific theatre of World War I, Asia-Pacific, and in Europe was characterised by trench warfare; the widespread use of Artillery of World War I, artillery, machine guns, and Chemical weapons in World War I, chemical weapons (gas); and the introductions of Tanks in World War I, tanks and Aviation in World War I, aircraft. World War I was one of the List of wars by death toll, deadliest conflicts in history, resulting in an estimated World War I casualties, 10 million military dead and more than 20 million wounded, plus some 10 million civilian de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |