|
Boli (fetish)
A ''boli'' (plural: ''boliw'') is a Fetishism, fetish of the Bambara people, Bambara or Malinké of Mali. Uses and customs The ''boli'' can be zoomorphic (mostly a buffalo or a zebu) or even sometimes anthropomorphic. The populations of Mali who practice the so-called ''bamanaya'' cult, that is to say who indulge in the sacrifices of animals on the ''boliw'' and who communicate with the afterlife through masked dancers say they are Bamana. In the Mandinka people, Mandingo religions a ''boli'' is an object said "charged", that is to say that by its magic it is able to accomplish extraordinary things, such as to give death, predict the future, or take possession of someone. The boli, which can also be made up of human or animal placenta, clay, tissue, skin, etc., is itself the symbol of the placenta. It is considered a living being and contains within it a core that can be either a stone, a metal or any other material. This nucleus or "grain" symbolizes the vital energy. The more ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fetishism
A fetish is an object believed to have supernatural powers, or in particular, a human-made object that has power over others. Essentially, fetishism is the attribution of inherent non-material value, or powers, to an object. Talismans and amulets are related. Fetishes are often used in spiritual or religious context. Historiography The word ''fetish'' derives from the French , which comes from the Portuguese ("spell"), which in turn derives from the Latin ("artificial") and ("to make"). The term ''fetish'' has evolved from an idiom used to describe a type of object created in the interaction between European travelers and Native West Africans in the early modern period to an analytical term that played a central role in the perception and study of non-Western art in general and African art in particular. William Pietz, who, in 1994, conducted an extensive ethno-historical study of the fetish, argues that the term originated in the coast of West Africa during the sixteenth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Musée D'Ethnographie Du Trocadéro
The Musée d'Ethnographie du Trocadéro (Ethnographic Museum of the Trocadéro, also called simply the Musée du Trocadéro) was the first Anthropology, anthropological museum in Paris, founded in 1878. It closed in 1935 when the building that housed it, the Trocadéro Palace, was demolished; its descendant is the Musée de l'Homme, housed in the Trocadéro, Paris#The new Palais de Chaillot, Palais de Chaillot on the same site, and its French collections formed the nucleus of the Musée national des Arts et Traditions Populaires (France), Musée National des Arts et Traditions Populaires, also in the Palais de Chaillot. Numerous modern artists visited it and were influenced by its "primitive" art, in particular Picasso during the period when he was working on ''Les Demoiselles d'Avignon'' (1907). History The museum was founded in 1878 by the Ministry of Public Education as the ''Muséum ethnographique des missions scientifiques'' (Ethnographic Museum of Scientific Expeditions) and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magic Items
Magic or magick most commonly refers to: * Magic (supernatural), beliefs and actions employed to influence supernatural beings and forces ** ''Magick'' (with ''-ck'') can specifically refer to ceremonial magic * Magic (illusion), also known as stage magic, the art of appearing to perform supernatural feats * Magical thinking, the belief that unrelated events are causally connected, particularly as a result of supernatural effects Magic or magick may also refer to: Art and entertainment Film and television * ''Magic'' (1917 film), a silent Hungarian drama * ''Magic'' (1978 film), an American horror film * ''Magic'', a 1983 Taiwanese film starring Wen Chao-yu * Magic (TV channel), a British music television station Literature * Magic in fiction, the genre of fiction that uses supernatural elements as a theme * '' Magic: A Fantastic Comedy'', a 1913 play by G. K. Chesterton * ''Magic'' (short story collection), a 1996 short story collection by Isaac Asimov * ''Magic' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
African Art
African art encompasses modern and historical paintings, sculptures, installations, and other visual cultures originating from indigenous African diaspora, African communities across the African continent. The definition may also include the art of the African diasporas, such as art in African-American, Caribbean, and South American societies inspired by African traditions. Although diverse there are unifying artistic themes across the visual cultures from the continent of Africa. Often, art was not created for its own sake, but for social, political, or religious purposes. African art is characterized by an emphasis on conceptual or symbolic representations, rather than imitating nature, aiming to capture the subject's spiritual essence. Pottery#Africa, Pottery, Metalworking, metalwork, sculpture, Architecture of Africa, architecture, textile art, and fiber art are important Visual arts, visual art forms across Africa and may be included in the study of African Art. The term � ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bamana
Bambara or Bambarra may refer to: * Bambara people, an ethnic group, primarily in Mali ** Bambara language, their language, a Manding language ** Bamana Empire, a state that flourished in present-day Mali (1640s–1861) * ''Bambara'' (beetle), a genus of feather-winged beetles * Bambara groundnut, a traditional food crop in Africa (''Vigna subterranea'') * Bambarra, a settlement on Middle Caicos, Turks and Caicos Islands * Bambara (band), a New York post-punk band Persons with the surname * Toni Cade Bambara (1939–1995), American author, social activist, and college professor See also * Mbabaram (other) Mbabaram (Babaram) may refer to: * Mbabaram people, an Australian ethnic group * Mbabaram language, an extinct language of Australia See also * Bambara (other) {{dab Language and nationality disambiguation pages ..., an Australian people and language {{Disambiguation, surname Language and nationality disambiguation pages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Musée D'ethnographie De Neuchâtel
The Musée d'ethnographie de Neuchâtel (MEN) is a museum of ethnography in Neuchâtel, Switzerland established in 1904. The collections consist of 50,000 objects from all regions of the world, with about half from Africa. The MEN is well known for its museology of the rupture (''muséololgie de la rupture''), initiated by in the 1980s. This exhibition policy aims at questioning the objects' meaning and the museum's social role. Starting in 2015, major renovations were undertaken on the museum's buildings. The historical part was renovated first, followed by the temporary exhibitions building, ending in 2020. Since 2017 the reference exhibition is ''L'impermanence des choses'', centered on the museum's collections. History The collections before the establishment of the museum The collections' first objects came from Charles-Daniel de Meuron, Charles Daniel de Meuron's cabinet of natural history donated to the city in 1795. The cabinet included two hundred ethnographic pieces, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Musée De L'Homme
The Musée de l'Homme (; literally "Museum of Mankind" or "Museum of Humanity") is an anthropology museum in Paris, France. It was established in 1937 by Paul Rivet for the 1937 ''Exposition Internationale des Arts et Techniques dans la Vie Moderne''. It is the descendant of the Musée d'Ethnographie du Trocadéro, founded in 1878. The Musée de l'Homme is a research center under the authority of various ministries, and it groups several entities from the French National Centre for Scientific Research, CNRS. The Musée de l'Homme is one of the seven departments of the Muséum national d'histoire naturelle. The Musée de l'Homme occupies most of the Passy wing of the Palais de Chaillot in the 16th arrondissement. The vast majority of its collection was transferred to the Musée du quai Branly, Quai Branly museum. History Earlier Collections The Musée de l'Homme has inherited items from historical collections created as early as the 16th century, from cabinets of curiosities, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marcel Griaule
Marcel Griaule (16 May 1898 – 23 February 1956) was a French author and anthropologist known for his studies of the Dogon people of West Africa, and for pioneering ethnographic field studies in France. He worked together with Germaine Dieterlen and Jean Rouch on African subjects. His publications number over 170 books and articles for scholarly journals. Biography Born in Aisy-sur-Armançon, Griaule received a good education and was preparing to become an engineer and enrolled at the prestigious Lycée Louis-le-Grand when in 1917 at the end of World War I he volunteered to become a pilot in the French Air Force. In 1920 he returned to university, where he attended the lectures of Marcel Mauss and Marcel Cohen. Intrigued by anthropology, he gave up plans for a technical career. In 1927 he received a degree from the École Nationale de Langues Orientales, where he concentrated on Amharic and Ge'ez. Between 1928 and 1933 Griaule participated in two large-scale et ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
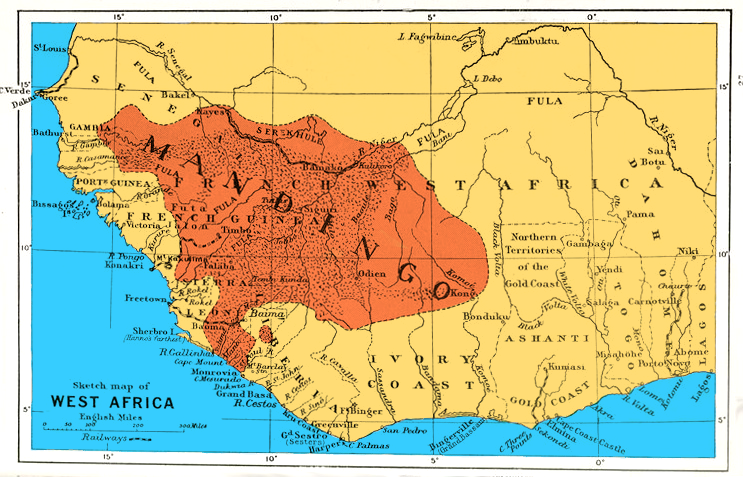
Bambara People
The Bambara ( or ''Banmana'') are a Mandé peoples, Mandé ethnic group native to much of West Africa, primarily southern Mali, Ivory Coast, Guinea, Burkina Faso and Senegal. They have been associated with the historic Bambara Empire. Today, they make up the largest Mande peoples, Mandé ethnic group in Mali, with 80% of the population speaking the Bambara language, regardless of ethnicity. Ethnonym According to the ''Encyclopedia of Africa'', "Bambara" means "believer" or "infidel"; the group acquired the name because it resisted Islam after the religion was introduced in 1854 by Toucouleur people, Toucouleur conqueror Omar Saidou Tall. History The Bamana originated as a royal section of the Mandinka people. Both Manding and Bambara are part of the Mandé ethno-linguistic group, whose divergence is dated to at least about 7,000 years ago, and branches of which are associated with sites near Tichitt (now subsumed by the Sahara in southern Mauritania), where urban centers be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michel Leiris
Julien Michel Leiris (; 20 April 1901, Paris – 30 September 1990, Saint-Hilaire, Essonne) was a French surrealist writer and ethnographer. Part of the Surrealist group in Paris, Leiris became a key member of the College of Sociology with Georges Bataille and head of research in ethnography at the CNRS. Biography Michel Leiris obtained his ''baccalauréat'' in philosophy at the Lycée Janson de Sailly in 1918 and after a brief attempt at studying chemistry, he developed a strong interest in jazz and poetry. Between 1921 and 1924, Leiris met a number of important figures such as Max Jacob, Georges Henri Rivière, Jean Dubuffet, Robert Desnos, Georges Bataille and the artist André Masson, who soon became his mentor. Through Masson, Leiris became a member of the Surrealist movement, contributed to ''La Révolution surréaliste'', published ''Simulacre'' (1925), and ''Le Point Cardinal'' (1927), and wrote a surrealist novel ''Aurora'' (1927–28; first published in 1946). In 192 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mandinka People
The Mandinka or Malinke are a West African ethnic group primarily found in southern Mali, The Gambia, southern Senegal and eastern Guinea. Numbering about 11 million, they are the largest subgroup of the Mandé peoples and one of the List of ethnic groups of Africa, largest ethnolinguistic groups in Africa. They speak the Manding languages in the Mande language family, which are a ''lingua franca'' in much of West Africa. They are predominantly Subsistence agriculture, subsistence farmers and live in rural villages. Their largest urban center is Bamako, the capital of Mali. The Mandinka are the descendants of the Mali Empire, which rose to power in the 13th century under the rule of king Sundiata Keita, who founded an empire that would go on to span a large part of West Africa. They migrated west from the Niger River in search of better agricultural lands and more opportunities for conquest. Nowadays, the Mandinka inhabit the West Sudanian savanna region extending from The Gambia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |